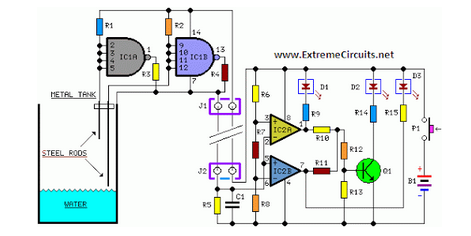
Astable Multivibrator I Circuit
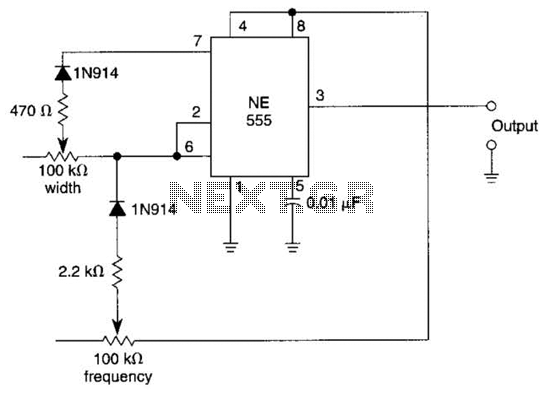
In this multivibrator circuit, frequency and pulse width can be separately controlled by using steering diodes (1N914) and two potentiometers.
This multivibrator circuit utilizes steering diodes, specifically the 1N914 type, to enable independent control over both the frequency and pulse width of the output waveform. The configuration typically involves two potentiometers, which are employed to adjust the timing components of the circuit.
The first potentiometer is connected in such a way that it influences the charging and discharging time of a capacitor, thereby affecting the frequency of oscillation. The second potentiometer adjusts the discharge path of the capacitor, which in turn modifies the pulse width of the output signal.
The use of steering diodes in this circuit is crucial, as they allow for the selective routing of current, ensuring that the timing characteristics can be altered without affecting the overall stability of the oscillation. The 1N914 diodes are chosen for their fast switching capabilities, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Overall, this multivibrator circuit design is versatile and can be used in various applications, such as signal generation, timer circuits, or pulse-width modulation systems. The ability to control frequency and pulse width independently makes it a valuable tool in electronic design and experimentation. In This multivibrator circuit frequency and pulse width can be separately controlled by using steering diodes (1N914) and two potentiometers. 🔗 External reference
This multivibrator circuit utilizes steering diodes, specifically the 1N914 type, to enable independent control over both the frequency and pulse width of the output waveform. The configuration typically involves two potentiometers, which are employed to adjust the timing components of the circuit.
The first potentiometer is connected in such a way that it influences the charging and discharging time of a capacitor, thereby affecting the frequency of oscillation. The second potentiometer adjusts the discharge path of the capacitor, which in turn modifies the pulse width of the output signal.
The use of steering diodes in this circuit is crucial, as they allow for the selective routing of current, ensuring that the timing characteristics can be altered without affecting the overall stability of the oscillation. The 1N914 diodes are chosen for their fast switching capabilities, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Overall, this multivibrator circuit design is versatile and can be used in various applications, such as signal generation, timer circuits, or pulse-width modulation systems. The ability to control frequency and pulse width independently makes it a valuable tool in electronic design and experimentation. In This multivibrator circuit frequency and pulse width can be separately controlled by using steering diodes (1N914) and two potentiometers. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713