AT89C2051/4051 Stepper Motor Interface
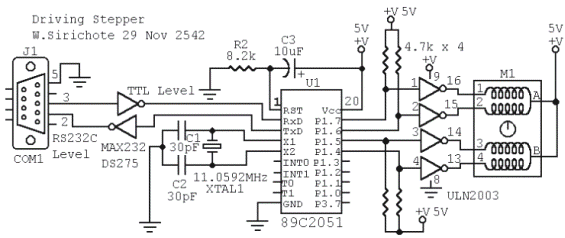
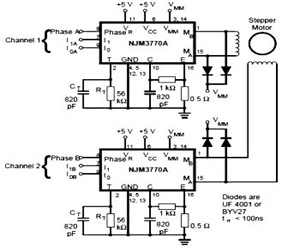
M1 is a stepper motor salvaged from an old disk drive. It features five pins: common, coil 1, coil 2, coil 3, and coil 4. The resistance measured between the common pin and each coil is approximately 75 Ohms. Each coil requires a driving current of about 60mA with a +5V supply. A Darlington transistor array, ULN2003, is utilized to enhance the driving capacity of the 2051 chip. Each output from the ULN2003 can provide a maximum of 500mA at 50V. Four output pins, P1.4 to P1.7, are connected to the inputs of the ULN2003 as illustrated in the circuit. Four 4.7k resistors assist the 2051 in delivering additional sourcing current from the +5V supply. The serial port is optional for various applications. Numerous resources are available that provide technical insights and applications for using stepper motors.
The M1 stepper motor is a crucial component in various applications, particularly in robotics and automation, where precise control of movement is essential. The motor's design, comprising five pins, allows for straightforward connectivity and control. The common pin serves as the reference point for the coils, which are energized in a specific sequence to achieve rotation. The measured resistance of approximately 75 Ohms indicates that the coils are designed to operate efficiently at low voltages, making them suitable for microcontroller applications.
The driving current requirement of 60mA per coil at a +5V supply ensures that the stepper motor operates within its specified limits, preventing overheating and potential damage. The use of the ULN2003 Darlington transistor array is a strategic choice, as it facilitates higher current handling capabilities while interfacing with the lower current outputs of the 2051 chip. This configuration allows for reliable control of the stepper motor without overloading the microcontroller.
The connection of output pins P1.4 to P1.7 to the ULN2003 enables the microcontroller to control the stepper motor's rotation direction and speed through pulse-width modulation (PWM). The inclusion of four 4.7k resistors serves to limit the current flowing from the 2051 chip to the ULN2003, ensuring that the microcontroller operates safely within its current specifications while still providing sufficient drive to the motor.
The optional serial port interface expands the versatility of the stepper motor application, allowing for integration into systems requiring remote control or communication with other devices. This feature is particularly beneficial in complex projects where feedback and control from a host computer or microcontroller are necessary.
In summary, the M1 stepper motor circuit exemplifies a well-designed system for controlling stepper motors using a microcontroller, with careful consideration given to current requirements, component selection, and circuit configuration. The availability of educational resources further enhances understanding and application of stepper motors in various fields.M1 is a stepper taken from an old disk drive. There are five pins, i. e. , common, coil 1, 2, 3 and 4. Resistance measured between common pin and each coil is about 75 Ohms. Driving current for each coil is then needed about 60mA at +5V supply. A Darlington transistor array, ULN2003 is used to increase driving capacity of the 2051 chip. Each outputprovides 500mA max at 50V. P1. 4 to P1. 7, four output pins are connected to the input of the ULN2003 as shown in the circuit. Four 4. 7k resistors help the 2051 to provide more sourcing current from the +5V supply. The serial port is optional for your exercises. Many have provided useful technical, and application of using stepper, see the links below. Jones on Stepping Motors Jones provides a tutorial covering the basic of stepping motors and control systems, including physics of the motor, circuits and software for motor control. 🔗 External reference
The M1 stepper motor is a crucial component in various applications, particularly in robotics and automation, where precise control of movement is essential. The motor's design, comprising five pins, allows for straightforward connectivity and control. The common pin serves as the reference point for the coils, which are energized in a specific sequence to achieve rotation. The measured resistance of approximately 75 Ohms indicates that the coils are designed to operate efficiently at low voltages, making them suitable for microcontroller applications.
The driving current requirement of 60mA per coil at a +5V supply ensures that the stepper motor operates within its specified limits, preventing overheating and potential damage. The use of the ULN2003 Darlington transistor array is a strategic choice, as it facilitates higher current handling capabilities while interfacing with the lower current outputs of the 2051 chip. This configuration allows for reliable control of the stepper motor without overloading the microcontroller.
The connection of output pins P1.4 to P1.7 to the ULN2003 enables the microcontroller to control the stepper motor's rotation direction and speed through pulse-width modulation (PWM). The inclusion of four 4.7k resistors serves to limit the current flowing from the 2051 chip to the ULN2003, ensuring that the microcontroller operates safely within its current specifications while still providing sufficient drive to the motor.
The optional serial port interface expands the versatility of the stepper motor application, allowing for integration into systems requiring remote control or communication with other devices. This feature is particularly beneficial in complex projects where feedback and control from a host computer or microcontroller are necessary.
In summary, the M1 stepper motor circuit exemplifies a well-designed system for controlling stepper motors using a microcontroller, with careful consideration given to current requirements, component selection, and circuit configuration. The availability of educational resources further enhances understanding and application of stepper motors in various fields.M1 is a stepper taken from an old disk drive. There are five pins, i. e. , common, coil 1, 2, 3 and 4. Resistance measured between common pin and each coil is about 75 Ohms. Driving current for each coil is then needed about 60mA at +5V supply. A Darlington transistor array, ULN2003 is used to increase driving capacity of the 2051 chip. Each outputprovides 500mA max at 50V. P1. 4 to P1. 7, four output pins are connected to the input of the ULN2003 as shown in the circuit. Four 4. 7k resistors help the 2051 to provide more sourcing current from the +5V supply. The serial port is optional for your exercises. Many have provided useful technical, and application of using stepper, see the links below. Jones on Stepping Motors Jones provides a tutorial covering the basic of stepping motors and control systems, including physics of the motor, circuits and software for motor control. 🔗 External reference