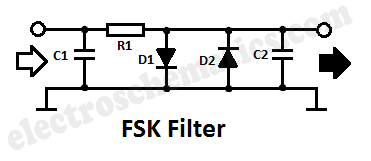
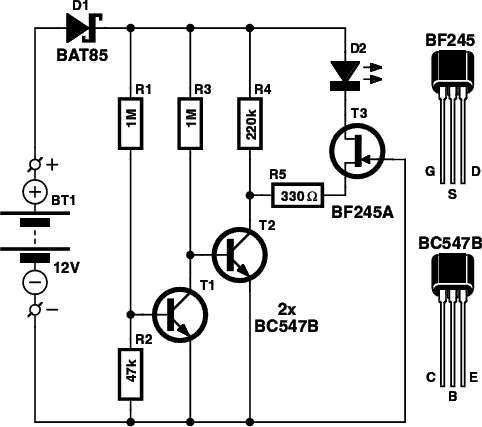
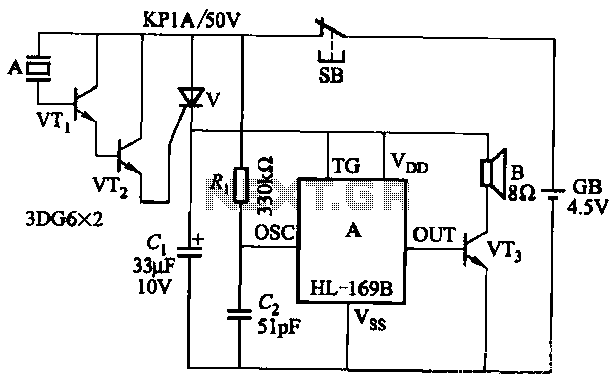
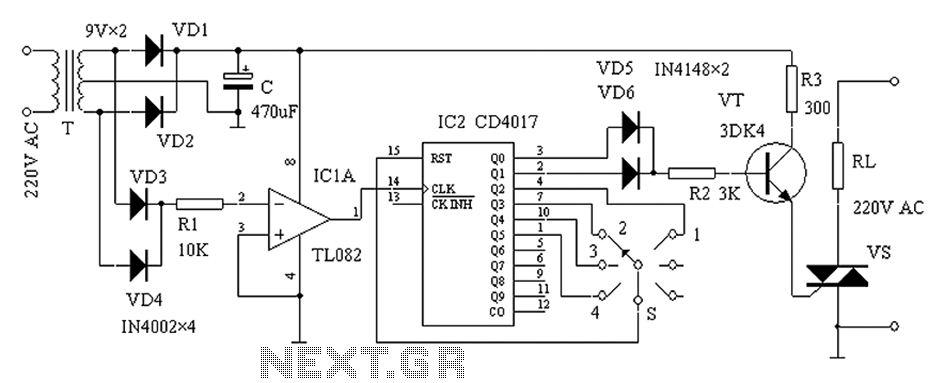
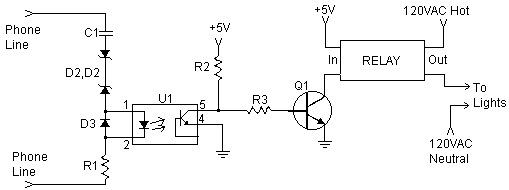
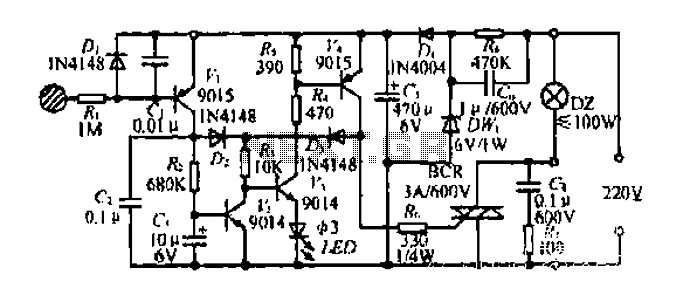
Audio Limiter Circuit
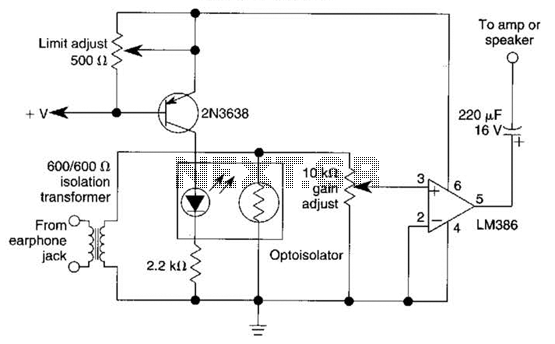
An optoisolator is utilized as an attenuator in this circuit. When the LM386 draws more current from audio signals, the 2N3638 activates, which biases the optoisolator on, thereby reducing the volume.
The circuit employs an optoisolator to achieve signal attenuation, effectively isolating the audio signal path while controlling volume levels. The LM386 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier that outputs audio signals. Under normal operating conditions, it draws a certain amount of current based on the input audio signal.
In this configuration, the 2N3638, a general-purpose NPN transistor, is used to sense the current drawn by the LM386. When the audio signal increases, the LM386's current draw also increases, causing the 2N3638 to turn on. This action results in the biasing of the optoisolator, which then modulates the signal passing through it.
The optoisolator functions by using an LED and a phototransistor within its structure. When the LED is forward-biased by the current from the 2N3638, it emits light that activates the phototransistor. This activation allows the phototransistor to conduct, thereby providing a controlled output signal that is proportional to the input signal's amplitude.
As the optoisolator is biased on, it effectively reduces the overall gain of the audio signal, leading to a decrease in volume. This method of attenuation is beneficial as it provides electrical isolation between the input and output, protecting sensitive components from high voltages or currents that may occur in the audio path.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications where volume control is required without compromising signal integrity, making it suitable for various audio processing systems. The combination of the LM386, 2N3638, and optoisolator creates a reliable and efficient means to manage audio levels dynamically. An optoisolator is used as an attenuator in this circuit. When the LM386 draws more current on audio signals, the 2N3638 turns on, which biases the optoisolator on, and reduces the volume.
The circuit employs an optoisolator to achieve signal attenuation, effectively isolating the audio signal path while controlling volume levels. The LM386 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier that outputs audio signals. Under normal operating conditions, it draws a certain amount of current based on the input audio signal.
In this configuration, the 2N3638, a general-purpose NPN transistor, is used to sense the current drawn by the LM386. When the audio signal increases, the LM386's current draw also increases, causing the 2N3638 to turn on. This action results in the biasing of the optoisolator, which then modulates the signal passing through it.
The optoisolator functions by using an LED and a phototransistor within its structure. When the LED is forward-biased by the current from the 2N3638, it emits light that activates the phototransistor. This activation allows the phototransistor to conduct, thereby providing a controlled output signal that is proportional to the input signal's amplitude.
As the optoisolator is biased on, it effectively reduces the overall gain of the audio signal, leading to a decrease in volume. This method of attenuation is beneficial as it provides electrical isolation between the input and output, protecting sensitive components from high voltages or currents that may occur in the audio path.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications where volume control is required without compromising signal integrity, making it suitable for various audio processing systems. The combination of the LM386, 2N3638, and optoisolator creates a reliable and efficient means to manage audio levels dynamically. An optoisolator is used as an attenuator in this circuit. When the LM386 draws more current on audio signals, the 2N3638 turns on, which biases the optoisolator on, and reduces the volume.