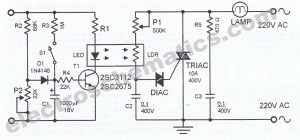
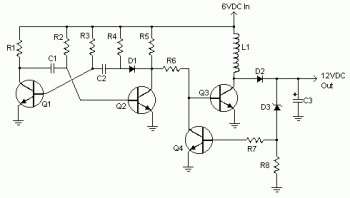
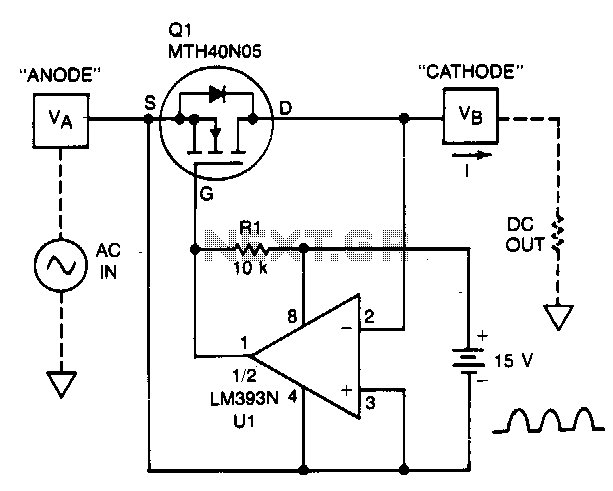
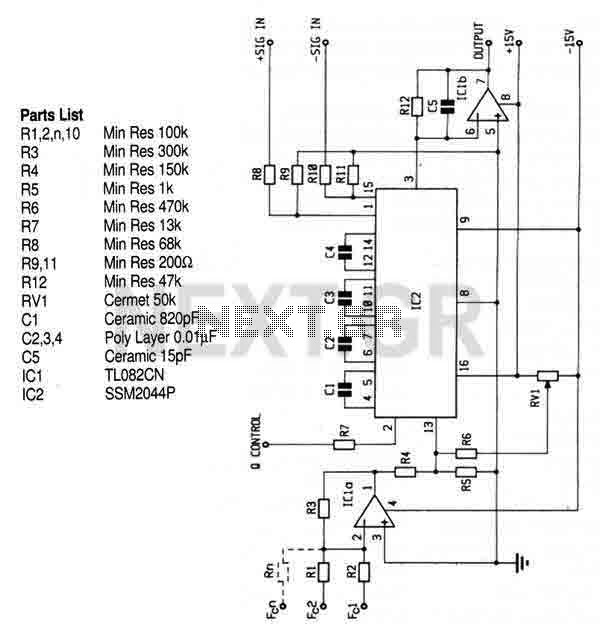
Audio Notch Filter For Shortwave Receivers Circuit
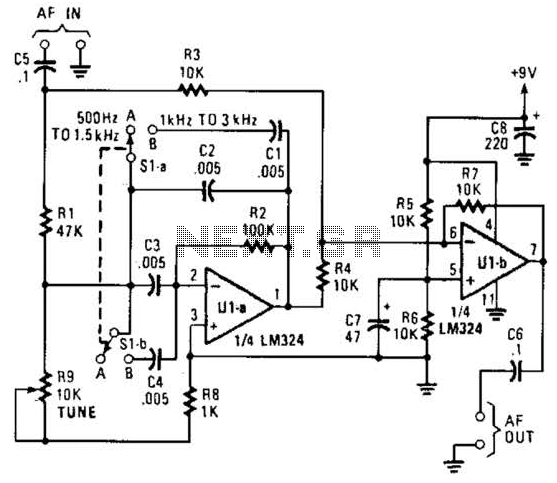
The notch filter can be integrated into nearly any receiver to attenuate a specific frequency by over 30 dB. This filter is particularly useful for diminishing heterodynes and whistles.
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop filter, is designed to selectively attenuate a narrow band of frequencies while allowing all other frequencies to pass with minimal loss. In the context of receiver applications, its primary role is to eliminate unwanted signals or noise that can interfere with the desired audio or data transmission.
The design of a notch filter typically involves the use of passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or it can be implemented using active components like operational amplifiers for improved performance. The center frequency of the notch, where the attenuation occurs, is determined by the values of the reactive components in the circuit.
For practical implementation, the notch filter can be configured in various ways, including a parallel LC circuit, where an inductor (L) and capacitor (C) are connected in parallel to ground. The resonant frequency, at which the circuit exhibits maximum attenuation, is given by the formula:
f_0 = 1 / (2π√(LC))
Where f_0 is the resonant frequency in hertz, L is the inductance in henries, and C is the capacitance in farads.
In applications where heterodynes and whistles are prevalent, such as in radio communications or audio processing, the notch filter effectively reduces these unwanted frequencies, enhancing the overall clarity and quality of the received signal. By adjusting the component values, the filter can be fine-tuned to target specific frequencies of interest, making it a versatile tool in electronic design.
The notch filter can be implemented in both analog and digital domains, with digital signal processing (DSP) techniques allowing for more complex filtering capabilities and adaptability to varying signal conditions. This flexibility makes the notch filter a vital component in modern communication systems, ensuring that the integrity of the desired signal is maintained while minimizing the impact of disruptive noise. The notch filter can be added to just about any receiver to attenuate a single frequency by more than 30 dB. This filter should be handy for reducing heterodynes and whistles. 🔗 External reference
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop filter, is designed to selectively attenuate a narrow band of frequencies while allowing all other frequencies to pass with minimal loss. In the context of receiver applications, its primary role is to eliminate unwanted signals or noise that can interfere with the desired audio or data transmission.
The design of a notch filter typically involves the use of passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or it can be implemented using active components like operational amplifiers for improved performance. The center frequency of the notch, where the attenuation occurs, is determined by the values of the reactive components in the circuit.
For practical implementation, the notch filter can be configured in various ways, including a parallel LC circuit, where an inductor (L) and capacitor (C) are connected in parallel to ground. The resonant frequency, at which the circuit exhibits maximum attenuation, is given by the formula:
f_0 = 1 / (2π√(LC))
Where f_0 is the resonant frequency in hertz, L is the inductance in henries, and C is the capacitance in farads.
In applications where heterodynes and whistles are prevalent, such as in radio communications or audio processing, the notch filter effectively reduces these unwanted frequencies, enhancing the overall clarity and quality of the received signal. By adjusting the component values, the filter can be fine-tuned to target specific frequencies of interest, making it a versatile tool in electronic design.
The notch filter can be implemented in both analog and digital domains, with digital signal processing (DSP) techniques allowing for more complex filtering capabilities and adaptability to varying signal conditions. This flexibility makes the notch filter a vital component in modern communication systems, ensuring that the integrity of the desired signal is maintained while minimizing the impact of disruptive noise. The notch filter can be added to just about any receiver to attenuate a single frequency by more than 30 dB. This filter should be handy for reducing heterodynes and whistles. 🔗 External reference