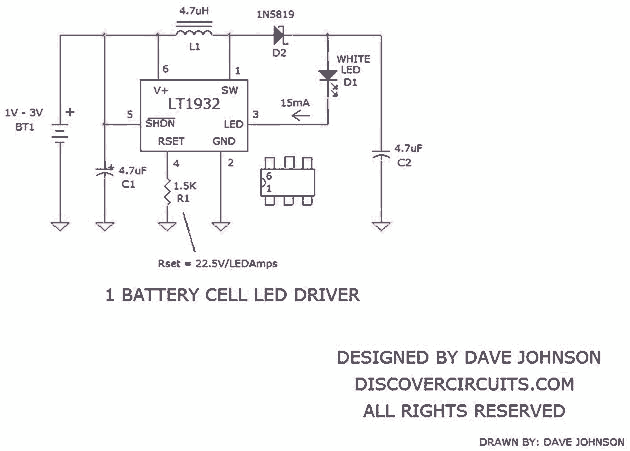
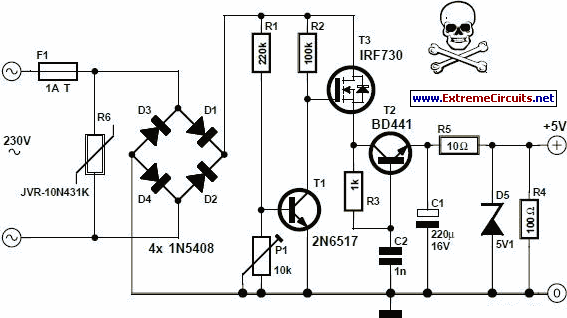
Audio power amplifier
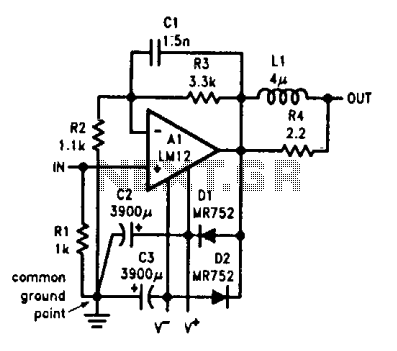
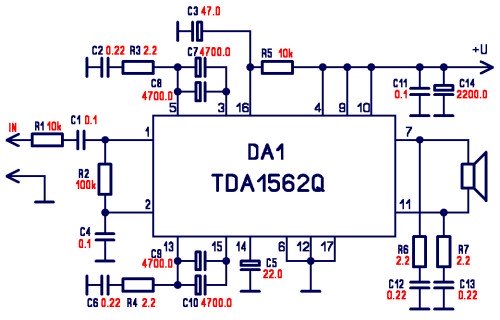
Output-clamp diodes are essential due to the inductive nature of loudspeakers. Output LR isolation is employed as audio amplifiers are typically designed to manage load capacitance of up to 2 µF. Large supply-bypass capacitors placed near the integrated circuit (IC) are utilized to prevent the rectified load current in the supply leads from returning to the amplifier, which can lead to increased high-frequency distortion. Additionally, single-point grounding for all internal leads, along with the signal source and load, is advised to prevent ground loops that may contribute to distortion.
Output-clamp diodes play a critical role in audio amplifier circuits, particularly when interfacing with inductive loads such as loudspeakers. The inductive characteristics of these loads can generate back EMF (electromotive force) during transient events, potentially damaging the amplifier or causing distortion in the output signal. By incorporating output-clamp diodes, any reverse voltage generated by the loudspeaker is safely redirected, protecting the amplifier and maintaining signal integrity.
The concept of output LR (inductance-resistance) isolation is significant in audio amplifier design. This isolation ensures that the amplifier can handle capacitive loads effectively, with a maximum capacitance of up to 2 µF. This specification is critical for maintaining stability and performance, particularly in high-frequency applications where capacitive effects can lead to oscillations or distortion.
Supply-bypass capacitors are another essential component in this circuit design. These capacitors are strategically placed close to the IC to minimize the impedance of the power supply path. During operation, the rectified load current can create fluctuations in the supply voltage. If these fluctuations are allowed to propagate back into the amplifier, they can introduce high-frequency noise and distortion. By using large supply-bypass capacitors, the circuit can provide a stable voltage supply, ensuring that the amplifier operates efficiently and with minimal distortion.
Furthermore, implementing a single-point grounding scheme is crucial for minimizing ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise and distortion into the audio signal. In this configuration, all internal leads, along with the signal source and load, are connected to a common ground point. This approach reduces the potential for ground loops that may arise from multiple grounding paths, thereby enhancing the overall performance and fidelity of the audio amplifier circuit.
In summary, the careful selection and implementation of output-clamp diodes, output LR isolation, supply-bypass capacitors, and single-point grounding are vital practices in the design of audio amplifiers to ensure high fidelity and reliability in performance.Output-clamp diodes are mandatory because loudspeakers are inductive loads. Output LR isolation is also used because audio amplifiers are usually expected to handle up to 2 µ¥ load capacitance. Large, supply-bypass capacitors located close to the IC are used so that the rectified load current in the supply leads does not get back into the amplifier, increasing high-frequency distortion.
Single-point grounding for all internal leads plus the signal source and load is recommended to avoid ground loops that can increase distortion. 🔗 External reference
Output-clamp diodes play a critical role in audio amplifier circuits, particularly when interfacing with inductive loads such as loudspeakers. The inductive characteristics of these loads can generate back EMF (electromotive force) during transient events, potentially damaging the amplifier or causing distortion in the output signal. By incorporating output-clamp diodes, any reverse voltage generated by the loudspeaker is safely redirected, protecting the amplifier and maintaining signal integrity.
The concept of output LR (inductance-resistance) isolation is significant in audio amplifier design. This isolation ensures that the amplifier can handle capacitive loads effectively, with a maximum capacitance of up to 2 µF. This specification is critical for maintaining stability and performance, particularly in high-frequency applications where capacitive effects can lead to oscillations or distortion.
Supply-bypass capacitors are another essential component in this circuit design. These capacitors are strategically placed close to the IC to minimize the impedance of the power supply path. During operation, the rectified load current can create fluctuations in the supply voltage. If these fluctuations are allowed to propagate back into the amplifier, they can introduce high-frequency noise and distortion. By using large supply-bypass capacitors, the circuit can provide a stable voltage supply, ensuring that the amplifier operates efficiently and with minimal distortion.
Furthermore, implementing a single-point grounding scheme is crucial for minimizing ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise and distortion into the audio signal. In this configuration, all internal leads, along with the signal source and load, are connected to a common ground point. This approach reduces the potential for ground loops that may arise from multiple grounding paths, thereby enhancing the overall performance and fidelity of the audio amplifier circuit.
In summary, the careful selection and implementation of output-clamp diodes, output LR isolation, supply-bypass capacitors, and single-point grounding are vital practices in the design of audio amplifiers to ensure high fidelity and reliability in performance.Output-clamp diodes are mandatory because loudspeakers are inductive loads. Output LR isolation is also used because audio amplifiers are usually expected to handle up to 2 µ¥ load capacitance. Large, supply-bypass capacitors located close to the IC are used so that the rectified load current in the supply leads does not get back into the amplifier, increasing high-frequency distortion.
Single-point grounding for all internal leads plus the signal source and load is recommended to avoid ground loops that can increase distortion. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713