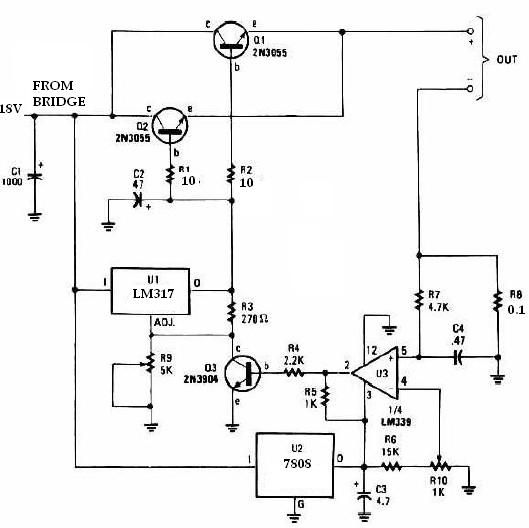
Audio-To-Adc Interface Circuit
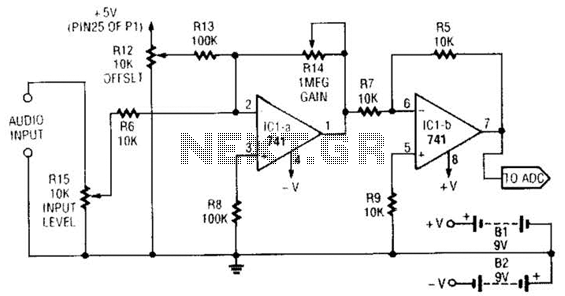
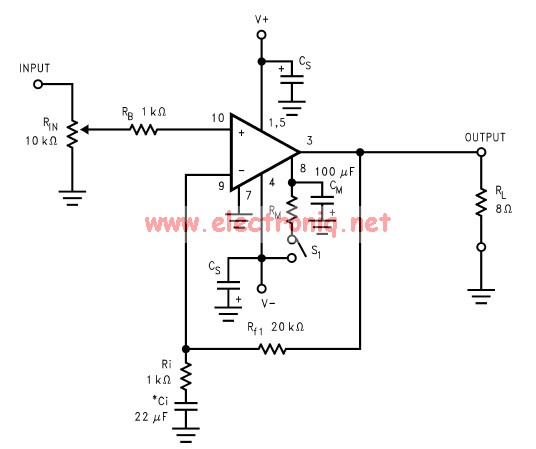
This simple general-purpose driver for an analog/digital converter uses two 741 IC devices with adjustable gain and offset. Other op-amps might be substituted, but some circuit adjustments might be needed.
The circuit consists of two operational amplifiers (op-amps) from the 741 series, which are configured to provide adjustable gain and offset for the input signal. The first op-amp is configured as a non-inverting amplifier, allowing for the amplification of the input voltage while maintaining its phase. The gain of this amplifier can be adjusted using a feedback resistor network, which typically includes a variable resistor (potentiometer) to facilitate fine-tuning.
The output from the first op-amp is then fed into the second op-amp, which serves as a summing amplifier. This configuration allows for the addition of a DC offset to the amplified signal, enabling the adjustment of the output voltage range to match the requirements of the analog/digital converter. The offset can be introduced by connecting a reference voltage to one of the input terminals of the second op-amp, again utilizing a potentiometer for precise control.
It is important to note that while the 741 op-amps are suitable for many applications, other op-amps with similar specifications may be used in this circuit. However, substituting different op-amps may necessitate recalibrating the gain and offset settings to ensure optimal performance. Proper attention should be given to the power supply requirements and frequency response characteristics of the chosen op-amps to maintain the integrity of the signal processing.
Overall, this driver circuit provides a flexible solution for interfacing analog signals with digital converters, facilitating a range of applications in signal conditioning and data acquisition systems. This simple general-purpose driver for an analog/digital converter uses two 741 IC devices with adjustable gain and offset, Other op amps might be substituted, but some circuit adjustments might be needed.
The circuit consists of two operational amplifiers (op-amps) from the 741 series, which are configured to provide adjustable gain and offset for the input signal. The first op-amp is configured as a non-inverting amplifier, allowing for the amplification of the input voltage while maintaining its phase. The gain of this amplifier can be adjusted using a feedback resistor network, which typically includes a variable resistor (potentiometer) to facilitate fine-tuning.
The output from the first op-amp is then fed into the second op-amp, which serves as a summing amplifier. This configuration allows for the addition of a DC offset to the amplified signal, enabling the adjustment of the output voltage range to match the requirements of the analog/digital converter. The offset can be introduced by connecting a reference voltage to one of the input terminals of the second op-amp, again utilizing a potentiometer for precise control.
It is important to note that while the 741 op-amps are suitable for many applications, other op-amps with similar specifications may be used in this circuit. However, substituting different op-amps may necessitate recalibrating the gain and offset settings to ensure optimal performance. Proper attention should be given to the power supply requirements and frequency response characteristics of the chosen op-amps to maintain the integrity of the signal processing.
Overall, this driver circuit provides a flexible solution for interfacing analog signals with digital converters, facilitating a range of applications in signal conditioning and data acquisition systems. This simple general-purpose driver for an analog/digital converter uses two 741 IC devices with adjustable gain and offset, Other op amps might be substituted, but some circuit adjustments might be needed.