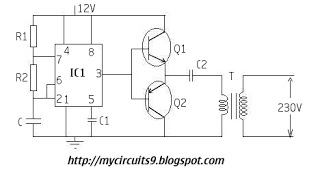
Welder no-load power saver circuit diagarm 5
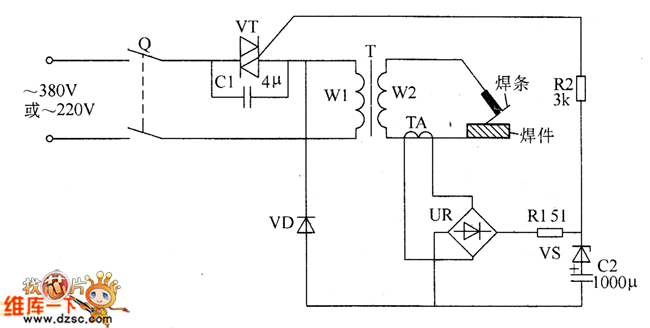
The welder no-load power saver circuit consists of a current detection control circuit and a power saving control circuit, as illustrated in the accompanying chart. The current detection control circuit includes a current transformer (TA), a bridge rectifier (UR), a resistor (R1), a Zener diode (VS), a capacitor (C2), and a diode (VD). The power control circuit comprises additional resistors.
The welder no-load power saver circuit is designed to minimize energy consumption when the welder is not actively engaged in welding tasks. The current detection control circuit plays a crucial role in monitoring the current flowing through the welder. The current transformer (TA) is employed to sense the current and convert it into a proportional lower current suitable for processing.
The bridge rectifier (UR) converts the alternating current (AC) output from the current transformer into direct current (DC). This DC signal is then filtered and stabilized using the resistor (R1) and the Zener diode (VS), ensuring that the voltage remains within a specified range. The capacitor (C2) serves to smooth out any fluctuations in the rectified voltage, while the diode (VD) protects the circuit from reverse polarity.
The power saving control circuit is responsible for regulating the power supplied to the welder during idle periods. By utilizing resistors in this circuit, the system can effectively limit the power draw, thereby reducing overall energy consumption. This circuit operates in conjunction with the current detection control circuit to ensure that power is only consumed when necessary, thus enhancing the efficiency of the welder.
Overall, the welder no-load power saver circuit is an essential component for modern welding equipment, contributing to energy efficiency and operational cost savings. Its design incorporates various electronic components that work together to detect current usage and regulate power consumption, thereby providing a sustainable solution for welding applications.The welder no-load power saver circuit is composed of the current detection control circuit and power saving control circuit, and the circuit is shown as the chart. Current detection control circuit is composed of the current transformer TA, bridge rectifier UR, resistor R1, Zener diode VS, capacitor C2 and diode VD.
Power control circuit consists of resisto.. 🔗 External reference
The welder no-load power saver circuit is designed to minimize energy consumption when the welder is not actively engaged in welding tasks. The current detection control circuit plays a crucial role in monitoring the current flowing through the welder. The current transformer (TA) is employed to sense the current and convert it into a proportional lower current suitable for processing.
The bridge rectifier (UR) converts the alternating current (AC) output from the current transformer into direct current (DC). This DC signal is then filtered and stabilized using the resistor (R1) and the Zener diode (VS), ensuring that the voltage remains within a specified range. The capacitor (C2) serves to smooth out any fluctuations in the rectified voltage, while the diode (VD) protects the circuit from reverse polarity.
The power saving control circuit is responsible for regulating the power supplied to the welder during idle periods. By utilizing resistors in this circuit, the system can effectively limit the power draw, thereby reducing overall energy consumption. This circuit operates in conjunction with the current detection control circuit to ensure that power is only consumed when necessary, thus enhancing the efficiency of the welder.
Overall, the welder no-load power saver circuit is an essential component for modern welding equipment, contributing to energy efficiency and operational cost savings. Its design incorporates various electronic components that work together to detect current usage and regulate power consumption, thereby providing a sustainable solution for welding applications.The welder no-load power saver circuit is composed of the current detection control circuit and power saving control circuit, and the circuit is shown as the chart. Current detection control circuit is composed of the current transformer TA, bridge rectifier UR, resistor R1, Zener diode VS, capacitor C2 and diode VD.
Power control circuit consists of resisto.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713