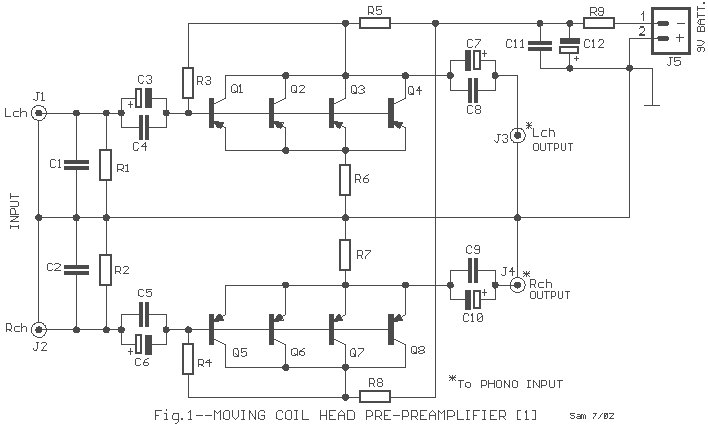
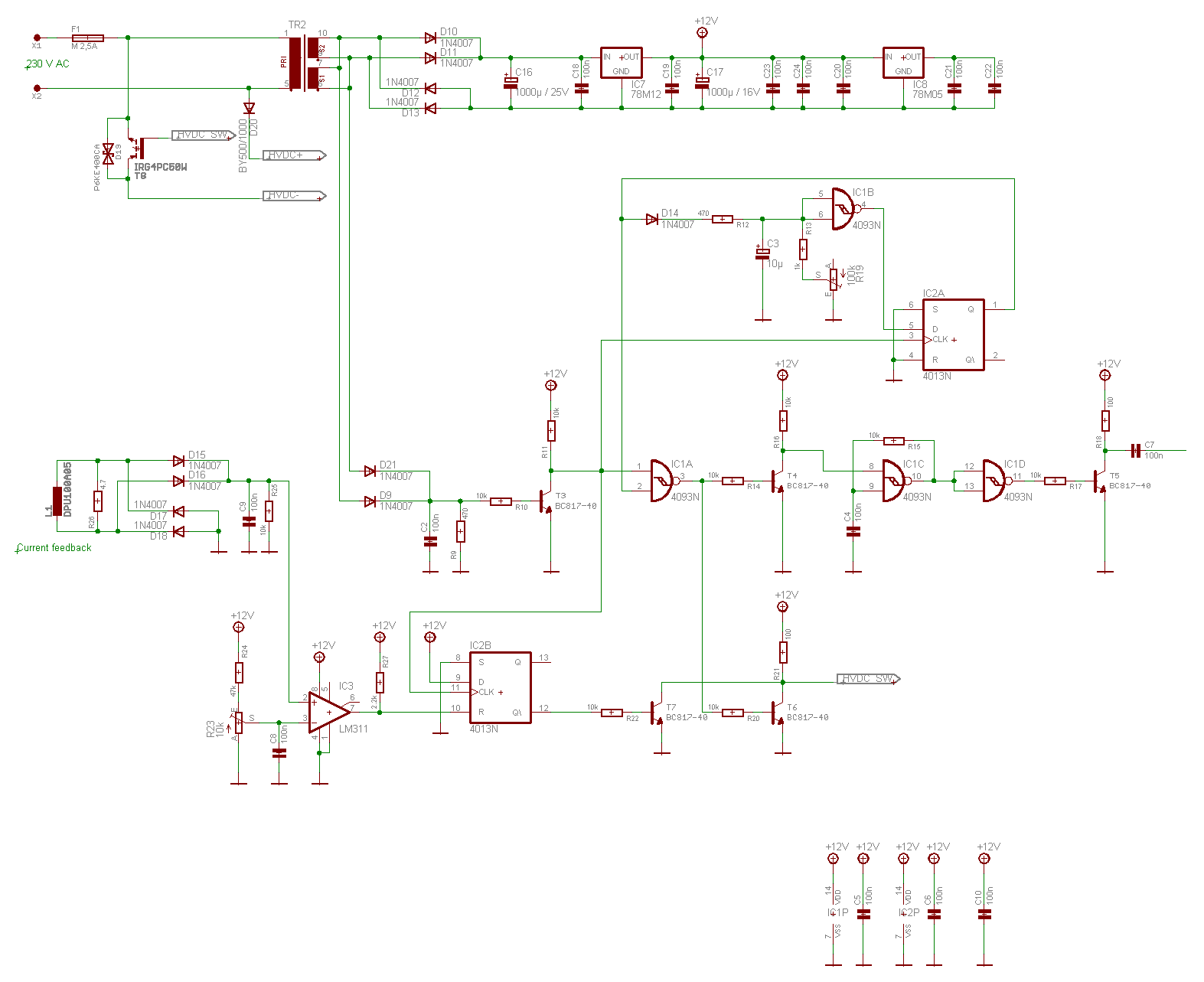
baby Tesla coil

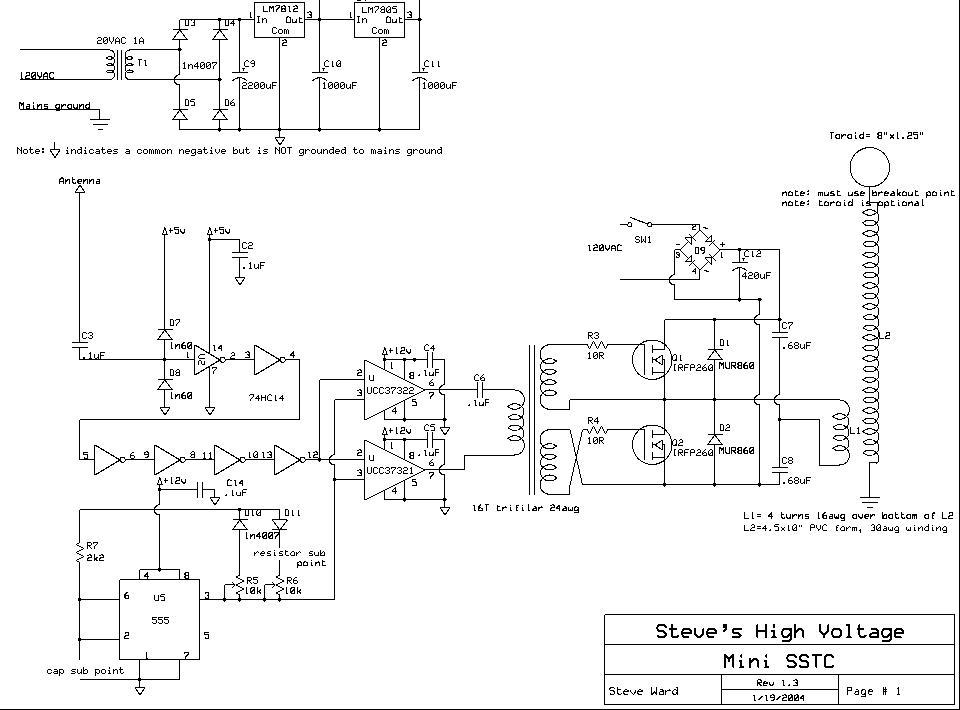
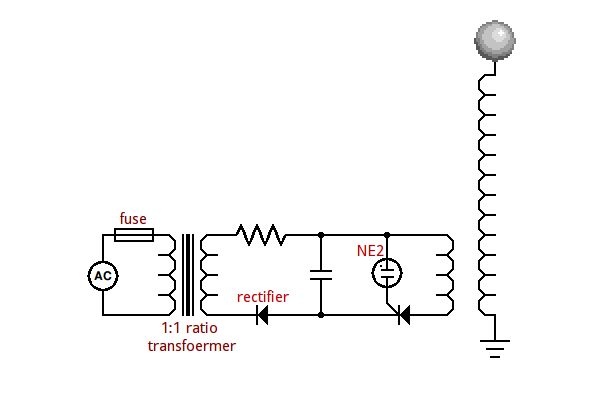
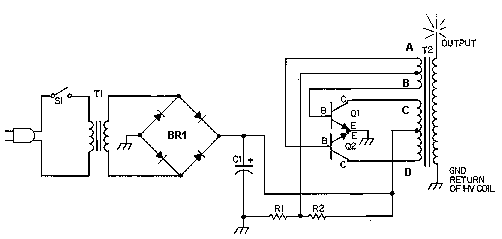
An inverter circuit is designed to power electroluminescent (EL) backlights and fluorescent tubes, producing an output of approximately 127 VAC. However, the objective is to achieve an output of 1 kV or more to generate at least 1 mm of purple plasma, similar to that produced by a Tesla coil, which requires approximately 30 kV to create a plasma arc of 1 cm in length. The circuit utilizes a MOSFET IRF840 as the switching transistor, although any IRF-series MOSFET, such as the IRF741 or IRF630, can be employed. A transformer salvaged from a battery charger is used to step up the voltage to exceed 1 kV. The resistor R2 is specified to be 464 kOhm or higher, allowing for experimentation with different values. This resistor influences the frequency of operation, resulting in varying sound pitches from the plasma, which emits a buzzing sound depending on its operating frequency.
The inverter circuit operates by converting DC voltage into high-frequency AC voltage, which is then transformed to a higher voltage level. The use of a MOSFET like the IRF840 is crucial due to its capability to handle high switching speeds, essential for efficiently driving the transformer. The circuit typically consists of a DC power source, the MOSFET, a transformer, and the output components, including the resistor R2 which plays a vital role in tuning the frequency of the inverter.
The transformer used in this application should be capable of handling high voltages and must be designed to operate at the frequency generated by the MOSFET. The output from the transformer can be rectified and filtered if necessary, depending on the application requirements. The selection of the transformer is critical; it must be capable of stepping up the voltage safely and efficiently.
R2 functions as a feedback resistor that influences the oscillation frequency of the inverter circuit. By adjusting its value, the user can modify the operating frequency, which in turn affects the pitch of the sound produced by the plasma. The buzzing sound is a direct result of the rapid switching of the MOSFET and the resonant behavior of the circuit.
Safety precautions should be taken when working with high voltages, as the output can be lethal. Proper insulation, protective equipment, and adherence to safety standards are essential when constructing and testing this inverter circuit. Additionally, experimentation with different MOSFETs and transformer configurations can yield varying results, allowing for optimization of the plasma generation characteristics.Inverter circuit to power EL backlights and fluorescent tubes, so the output is about 127 VAC as he claimed. But I want 1kV or more to make at least 1mm purple plasma as Tesla coil usually produce! (30kV is required to make 1cm length plasma). Therefore i use MOSFET IRF 840 as a transistor for high switching rate (also any IRF-named MOSFET will do, such
as IRF741 and 630) and also transformer i use before from cracking open a battery charger to step up the voltage to more than 1kV. R2: 464kOhm or more, up to you ( you experiment it yourself). This resistor controls the frequency so different values produce different sound pitches of the plasma ( it produces buzzing sound depending on its operating frequency)
🔗 External reference
The inverter circuit operates by converting DC voltage into high-frequency AC voltage, which is then transformed to a higher voltage level. The use of a MOSFET like the IRF840 is crucial due to its capability to handle high switching speeds, essential for efficiently driving the transformer. The circuit typically consists of a DC power source, the MOSFET, a transformer, and the output components, including the resistor R2 which plays a vital role in tuning the frequency of the inverter.
The transformer used in this application should be capable of handling high voltages and must be designed to operate at the frequency generated by the MOSFET. The output from the transformer can be rectified and filtered if necessary, depending on the application requirements. The selection of the transformer is critical; it must be capable of stepping up the voltage safely and efficiently.
R2 functions as a feedback resistor that influences the oscillation frequency of the inverter circuit. By adjusting its value, the user can modify the operating frequency, which in turn affects the pitch of the sound produced by the plasma. The buzzing sound is a direct result of the rapid switching of the MOSFET and the resonant behavior of the circuit.
Safety precautions should be taken when working with high voltages, as the output can be lethal. Proper insulation, protective equipment, and adherence to safety standards are essential when constructing and testing this inverter circuit. Additionally, experimentation with different MOSFETs and transformer configurations can yield varying results, allowing for optimization of the plasma generation characteristics.Inverter circuit to power EL backlights and fluorescent tubes, so the output is about 127 VAC as he claimed. But I want 1kV or more to make at least 1mm purple plasma as Tesla coil usually produce! (30kV is required to make 1cm length plasma). Therefore i use MOSFET IRF 840 as a transistor for high switching rate (also any IRF-named MOSFET will do, such
as IRF741 and 630) and also transformer i use before from cracking open a battery charger to step up the voltage to more than 1kV. R2: 464kOhm or more, up to you ( you experiment it yourself). This resistor controls the frequency so different values produce different sound pitches of the plasma ( it produces buzzing sound depending on its operating frequency)
🔗 External reference