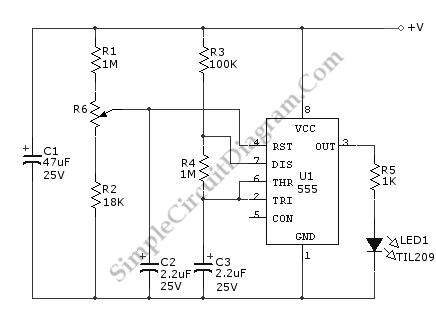
Basic UPS Power Supply
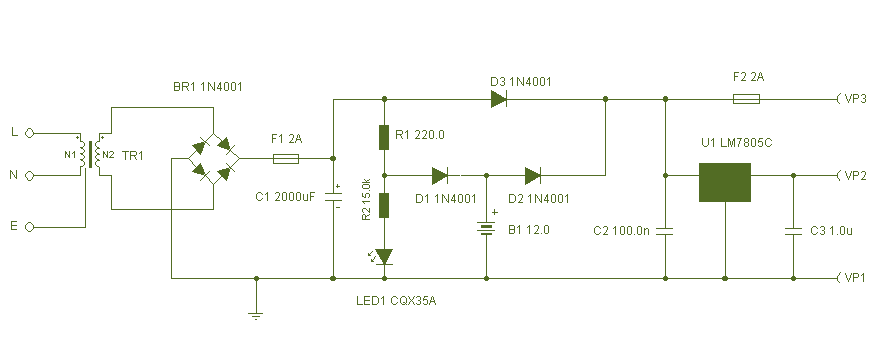
This circuit can be adapted for other regulated and unregulated voltages by using different regulators and batteries. For a 15 Volt regulated supply use two 12 Volt batteries in series and a 7815 regulator. There is a lot of flexibility in this circuit.
The described circuit is a versatile power supply that can accommodate various voltage requirements through the selection of appropriate voltage regulators and battery configurations. The primary component for achieving a regulated 15 Volt output is the 7815 voltage regulator, which is designed to provide a stable output voltage of 15 Volts with a maximum output current typically around 1.5 Amperes.
To achieve the required input voltage for the 7815 regulator, two 12 Volt lead-acid batteries are connected in series. This series configuration results in a total input voltage of 24 Volts, which is sufficient for the 7815 to function correctly, as it requires a minimum input voltage of approximately 17 Volts to maintain regulation.
The circuit design should include additional components for optimal performance and safety. A pair of decoupling capacitors (typically 0.33 µF and 0.1 µF) can be placed at the input and output terminals of the 7815 regulator to filter out high-frequency noise and ensure stability. Additionally, a larger electrolytic capacitor (e.g., 100 µF) at the output may help maintain voltage stability during transient load changes.
For applications requiring different output voltages, alternative voltage regulators can be utilized in conjunction with various battery configurations. For instance, using a 7809 regulator in a similar setup with a single 12 Volt battery would yield a regulated output of 9 Volts. The flexibility of the circuit allows for customization based on specific voltage and current requirements, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.
It is essential to consider thermal management, as voltage regulators can dissipate heat during operation. A heat sink may be necessary for the 7815 regulator to prevent overheating, especially under higher load conditions. Proper circuit layout and component selection will ensure reliable operation across different voltage configurations.This circuit can be adapted for other regulated and unregulated voltages by using different regulators and batteries. For a 15 Volt regulated supply use two 12 Volt batteries in series and a 7815 regulator. There is a lot of flexibility in this circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a versatile power supply that can accommodate various voltage requirements through the selection of appropriate voltage regulators and battery configurations. The primary component for achieving a regulated 15 Volt output is the 7815 voltage regulator, which is designed to provide a stable output voltage of 15 Volts with a maximum output current typically around 1.5 Amperes.
To achieve the required input voltage for the 7815 regulator, two 12 Volt lead-acid batteries are connected in series. This series configuration results in a total input voltage of 24 Volts, which is sufficient for the 7815 to function correctly, as it requires a minimum input voltage of approximately 17 Volts to maintain regulation.
The circuit design should include additional components for optimal performance and safety. A pair of decoupling capacitors (typically 0.33 µF and 0.1 µF) can be placed at the input and output terminals of the 7815 regulator to filter out high-frequency noise and ensure stability. Additionally, a larger electrolytic capacitor (e.g., 100 µF) at the output may help maintain voltage stability during transient load changes.
For applications requiring different output voltages, alternative voltage regulators can be utilized in conjunction with various battery configurations. For instance, using a 7809 regulator in a similar setup with a single 12 Volt battery would yield a regulated output of 9 Volts. The flexibility of the circuit allows for customization based on specific voltage and current requirements, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.
It is essential to consider thermal management, as voltage regulators can dissipate heat during operation. A heat sink may be necessary for the 7815 regulator to prevent overheating, especially under higher load conditions. Proper circuit layout and component selection will ensure reliable operation across different voltage configurations.This circuit can be adapted for other regulated and unregulated voltages by using different regulators and batteries. For a 15 Volt regulated supply use two 12 Volt batteries in series and a 7815 regulator. There is a lot of flexibility in this circuit. 🔗 External reference