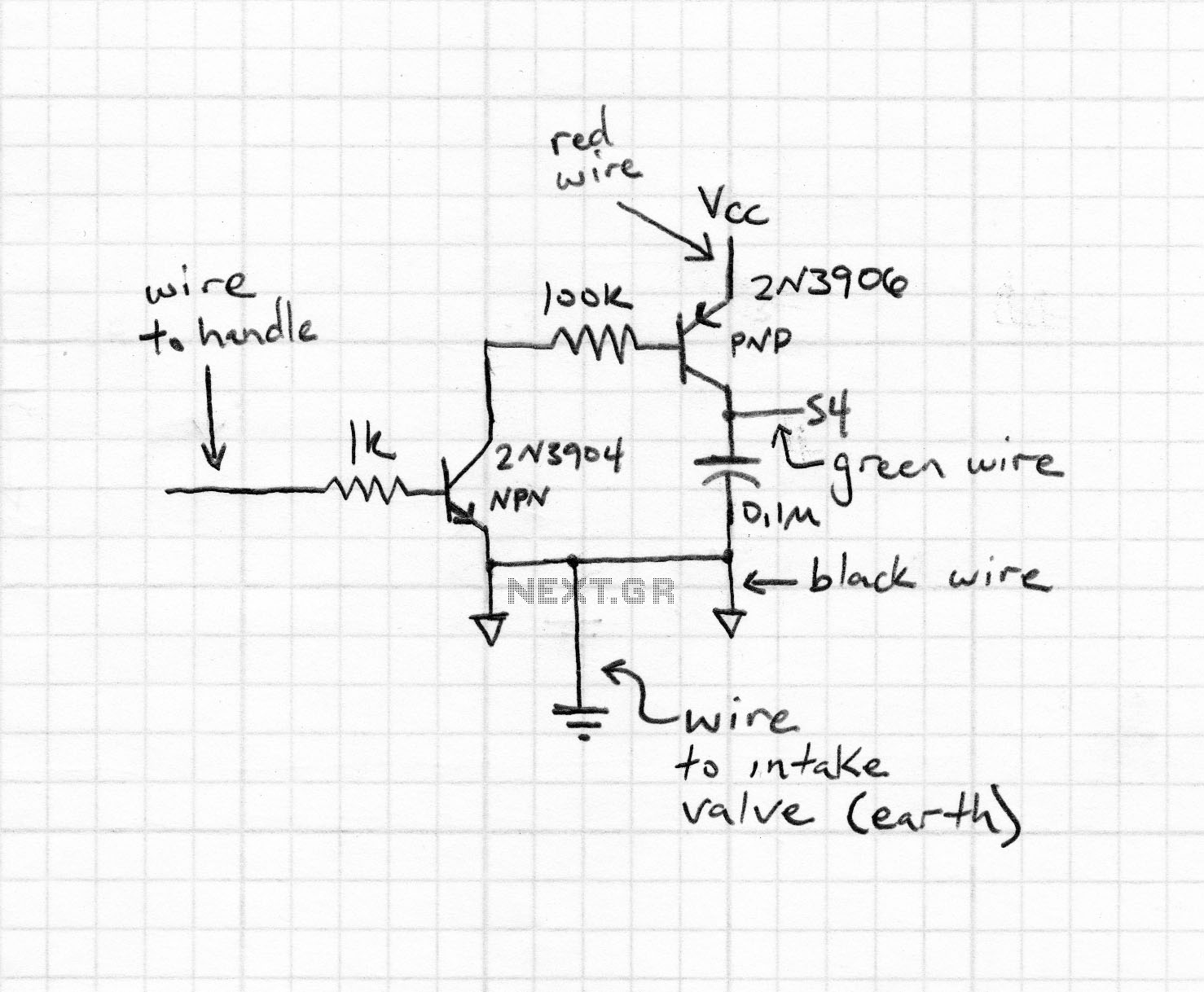
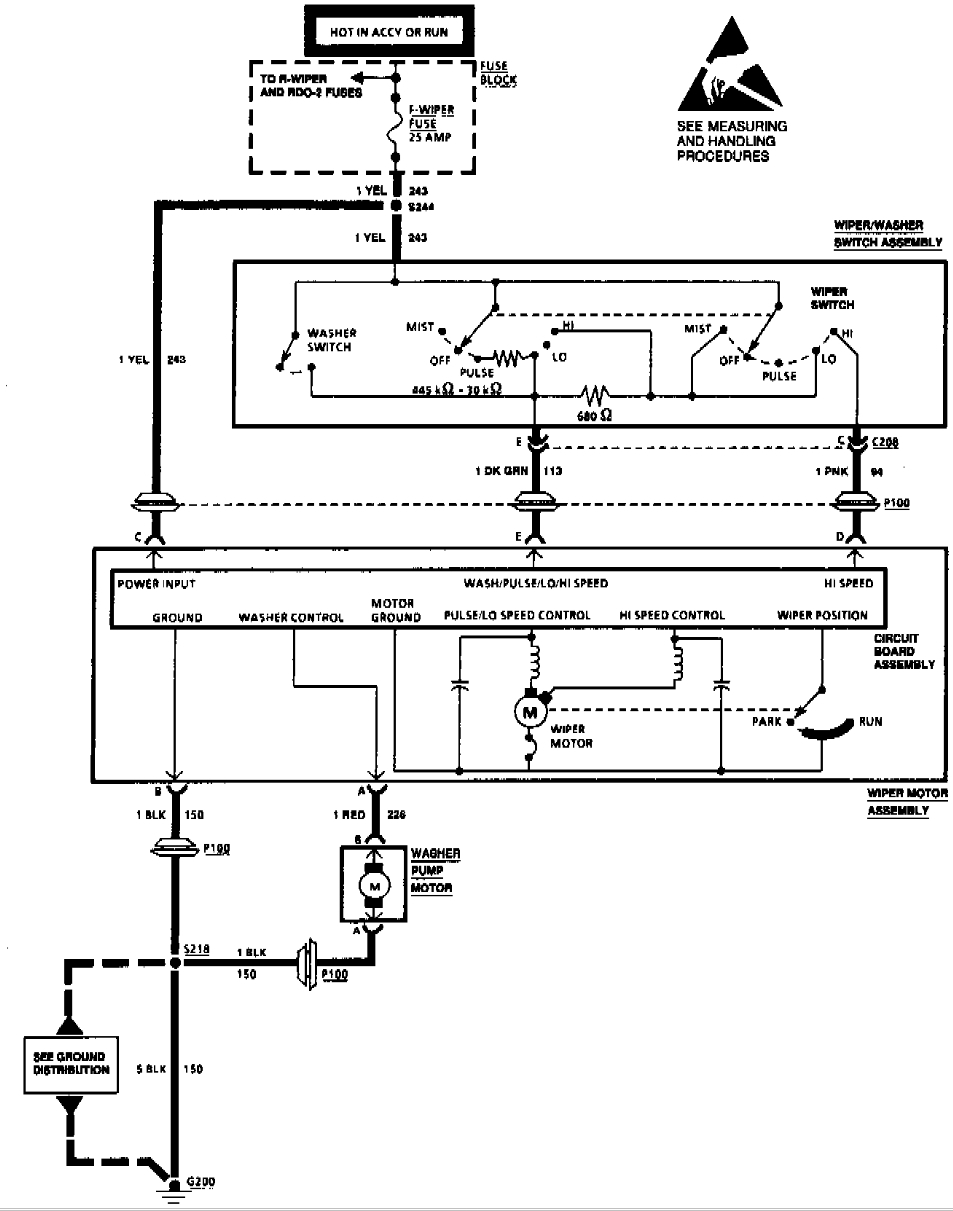
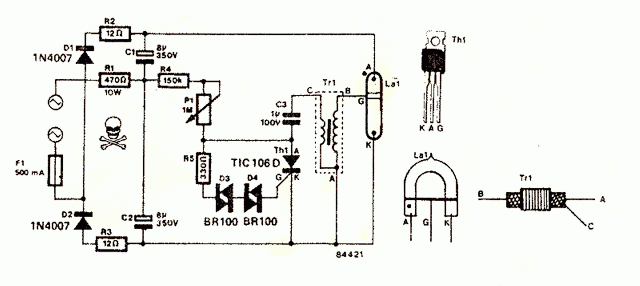
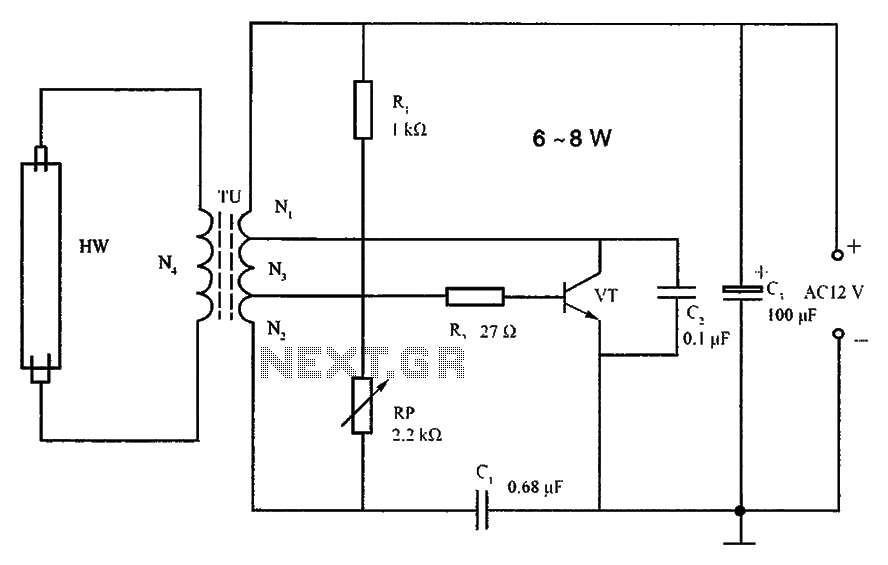
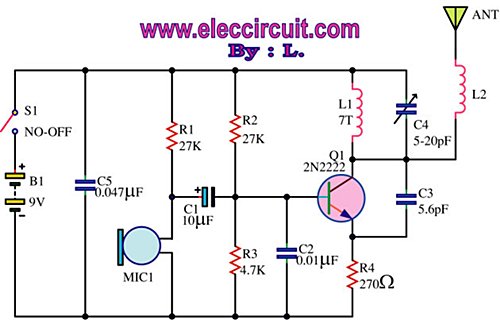
Bipolar Stepper Motor Driver Circuit
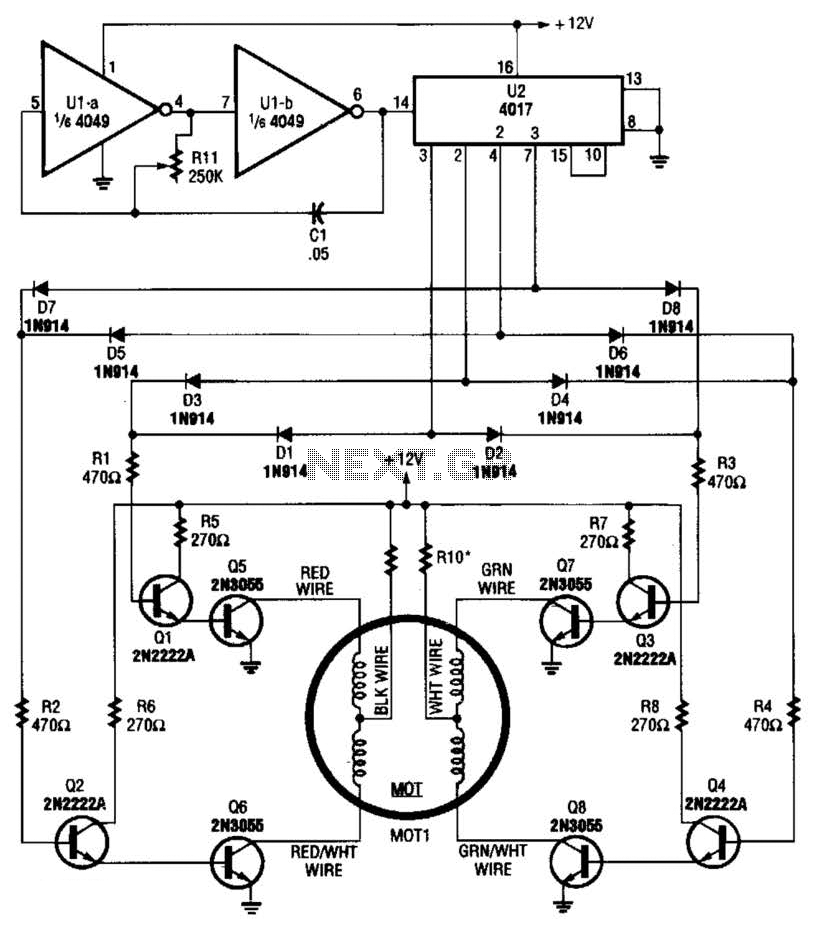
A 4017 decade counter/divider, driven by a low-frequency oscillator (U1-a and U1-b), is employed to control transistor switches that sequence the motor windings as required. The motor (MOT1) is a 12-V stepper motor. Resistors R9 and R10 are chosen based on the motor's current rating. A 3.3-Hz signal from U1 will result in the motor operating at 1 rpm, while a 33-Hz signal will lead to a speed of 10 rpm, and so forth.
The circuit utilizes a 4017 decade counter to sequentially activate transistor switches that control the windings of a 12-V stepper motor (MOT1). The low-frequency oscillator, comprising operational amplifiers U1-a and U1-b, generates the clock signals necessary for the counter's operation. The output of the 4017 activates the transistors in a specific sequence, allowing for precise control of the motor's movement.
Resistors R9 and R10 are critical components selected to match the current requirements of the stepper motor. These resistors ensure that the transistors operate within their safe limits, preventing overheating or damage due to excessive current. The choice of these resistors is based on the motor's specifications, particularly its rated current.
The frequency of the oscillator directly influences the speed of the stepper motor. For instance, a 3.3-Hz clock signal results in a motor speed of 1 rpm, while increasing the frequency to 33 Hz allows the motor to operate at 10 rpm. This relationship between frequency and motor speed can be utilized to achieve various operational speeds by adjusting the oscillator's frequency output. The design provides flexibility in controlling the motor's speed, making it suitable for applications requiring precise movement and positioning.
Overall, this circuit design effectively integrates a decade counter, low-frequency oscillator, and transistor switches to control a stepper motor, demonstrating a practical approach to motor control in electronic applications. A 4017 decade counter/divider driven from a low-frequency oscillator (Ul-a and Ul-b) is used to drive transistor switches to sequence the windings, as is needed. MOT1 is a 12-V stepper motor. R9 and RIO are selected for the motor`s current rating. A 3.3-Hz signal from Ul will cause the motor to run at 1 rpm, a 33-Hz signal will result in 10 rpm, etc. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a 4017 decade counter to sequentially activate transistor switches that control the windings of a 12-V stepper motor (MOT1). The low-frequency oscillator, comprising operational amplifiers U1-a and U1-b, generates the clock signals necessary for the counter's operation. The output of the 4017 activates the transistors in a specific sequence, allowing for precise control of the motor's movement.
Resistors R9 and R10 are critical components selected to match the current requirements of the stepper motor. These resistors ensure that the transistors operate within their safe limits, preventing overheating or damage due to excessive current. The choice of these resistors is based on the motor's specifications, particularly its rated current.
The frequency of the oscillator directly influences the speed of the stepper motor. For instance, a 3.3-Hz clock signal results in a motor speed of 1 rpm, while increasing the frequency to 33 Hz allows the motor to operate at 10 rpm. This relationship between frequency and motor speed can be utilized to achieve various operational speeds by adjusting the oscillator's frequency output. The design provides flexibility in controlling the motor's speed, making it suitable for applications requiring precise movement and positioning.
Overall, this circuit design effectively integrates a decade counter, low-frequency oscillator, and transistor switches to control a stepper motor, demonstrating a practical approach to motor control in electronic applications. A 4017 decade counter/divider driven from a low-frequency oscillator (Ul-a and Ul-b) is used to drive transistor switches to sequence the windings, as is needed. MOT1 is a 12-V stepper motor. R9 and RIO are selected for the motor`s current rating. A 3.3-Hz signal from Ul will cause the motor to run at 1 rpm, a 33-Hz signal will result in 10 rpm, etc. 🔗 External reference