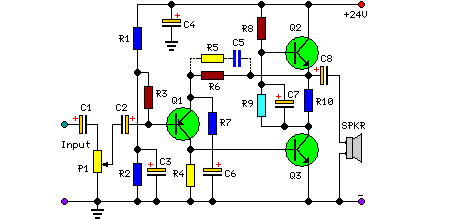
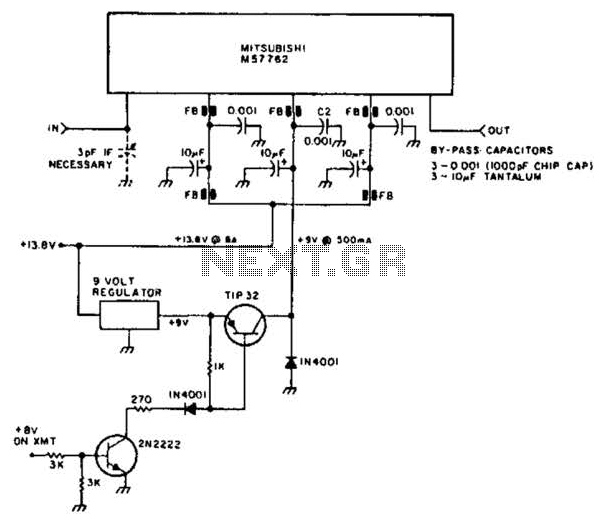
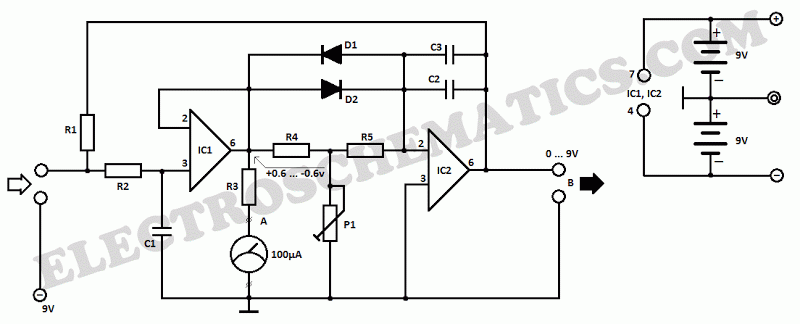
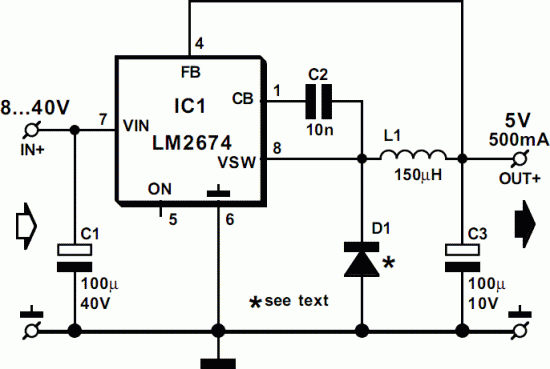
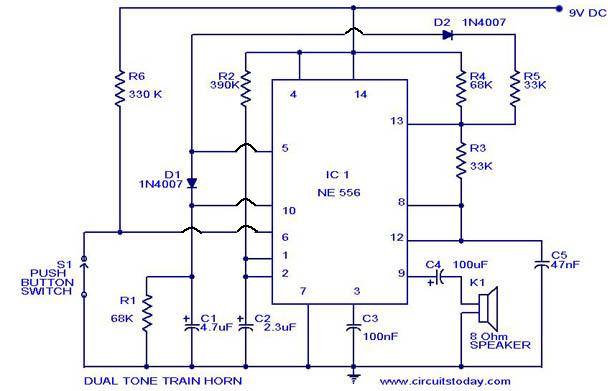
Boombox circuit diagram
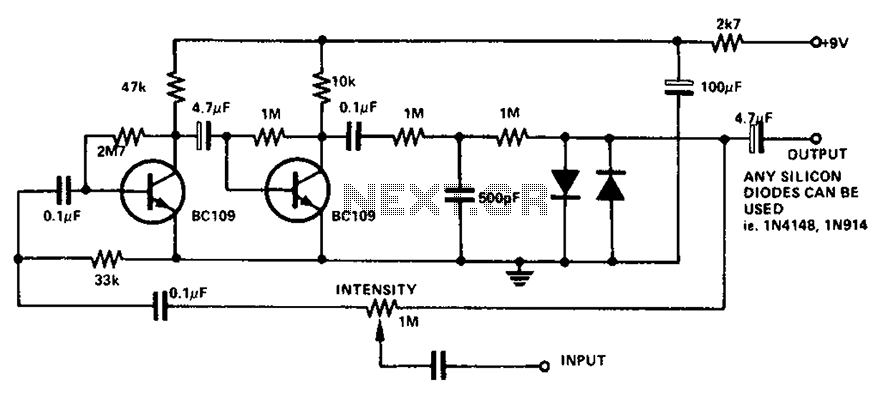
The circuit utilizes a transistor to amplify the input signal. Two diodes are employed to clamp the distorted output, while a 500 pF capacitor filters out high-frequency noise. Under normal conditions, a 1M slide rheostat is used to adjust the intensity of the noise, allowing it to vary from maximum to zero.
The circuit is designed to enhance signal integrity by utilizing a transistor as the primary amplification component. The transistor's role is to increase the amplitude of the incoming signal, making it suitable for further processing or output. The two diodes connected in the circuit serve as clamping devices, which effectively limit the voltage levels of the output signal. This clamping action prevents distortion that could occur due to excessive voltage swings, thereby preserving the quality of the amplified signal.
To address high-frequency noise, a 500 pF capacitor is integrated into the circuit. This capacitor acts as a low-pass filter, allowing lower frequency signals to pass through while attenuating higher frequency noise components. The selection of the 500 pF value is critical as it determines the cutoff frequency of the filter, ensuring that unwanted high-frequency signals are effectively removed from the output.
The inclusion of a 1M slide rheostat provides a means to adjust the noise intensity dynamically. This adjustable resistor allows the user to fine-tune the circuit's response to varying conditions, enabling a smooth transition from maximum noise to complete attenuation. This feature is particularly useful in applications where signal clarity is paramount, as it allows for real-time adjustments to accommodate different operating environments or signal conditions.
Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for amplifying signals while mitigating distortion and noise, making it suitable for various electronic applications where signal integrity is essential. Circuit Description: Transistor can amplify the input signal. Then two diodes clamp distorted output, high-frequency noise is 500 pF capacitor filter out from the circuit. Unde r normal conditions, the slide rheostat 1M adjustable intensity noise, it changed from the maximum to zero.
The circuit is designed to enhance signal integrity by utilizing a transistor as the primary amplification component. The transistor's role is to increase the amplitude of the incoming signal, making it suitable for further processing or output. The two diodes connected in the circuit serve as clamping devices, which effectively limit the voltage levels of the output signal. This clamping action prevents distortion that could occur due to excessive voltage swings, thereby preserving the quality of the amplified signal.
To address high-frequency noise, a 500 pF capacitor is integrated into the circuit. This capacitor acts as a low-pass filter, allowing lower frequency signals to pass through while attenuating higher frequency noise components. The selection of the 500 pF value is critical as it determines the cutoff frequency of the filter, ensuring that unwanted high-frequency signals are effectively removed from the output.
The inclusion of a 1M slide rheostat provides a means to adjust the noise intensity dynamically. This adjustable resistor allows the user to fine-tune the circuit's response to varying conditions, enabling a smooth transition from maximum noise to complete attenuation. This feature is particularly useful in applications where signal clarity is paramount, as it allows for real-time adjustments to accommodate different operating environments or signal conditions.
Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for amplifying signals while mitigating distortion and noise, making it suitable for various electronic applications where signal integrity is essential. Circuit Description: Transistor can amplify the input signal. Then two diodes clamp distorted output, high-frequency noise is 500 pF capacitor filter out from the circuit. Unde r normal conditions, the slide rheostat 1M adjustable intensity noise, it changed from the maximum to zero.