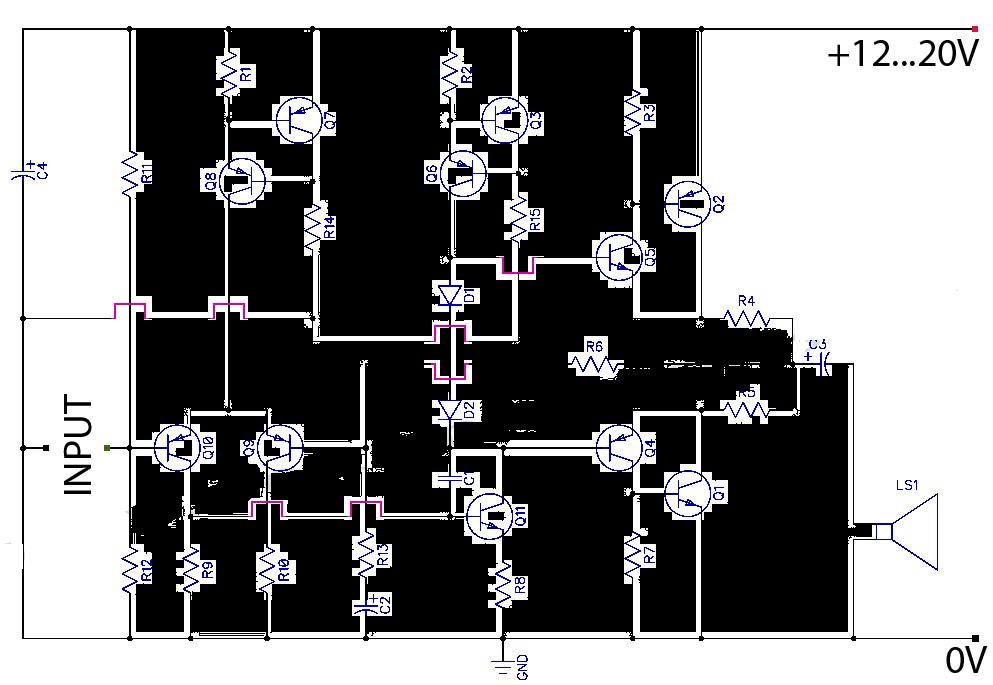
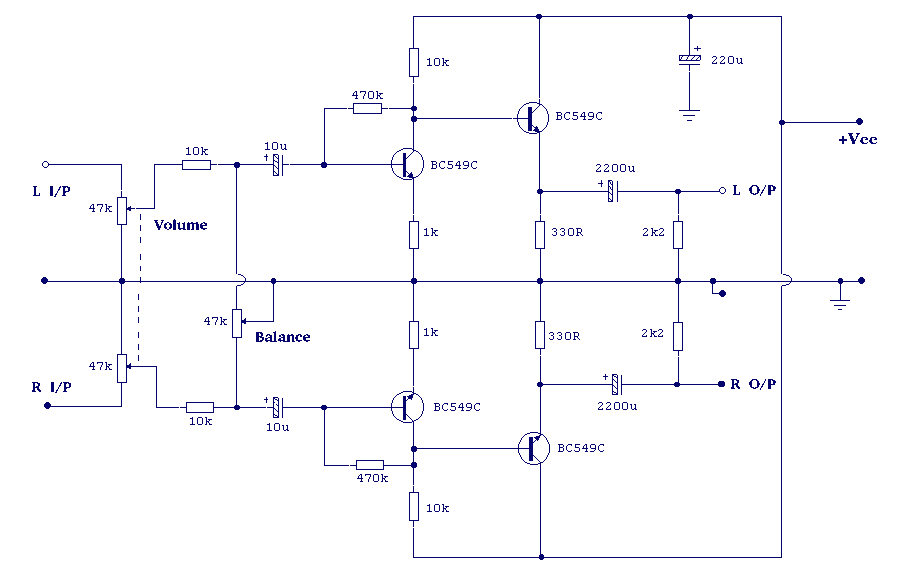
Bridge amplifier
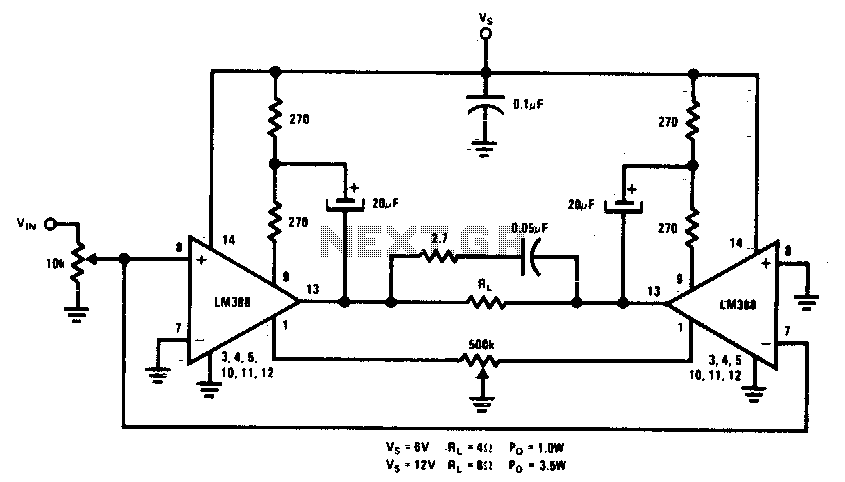
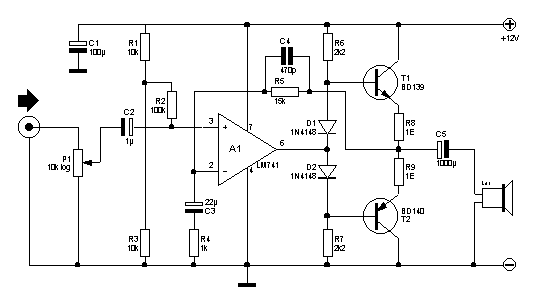
This circuit is designed for low voltage applications that demand high power outputs. Typical output power levels are low into 4 ohms from 6 V and 3 V into 8 ohms from 12 V. Coupling capacitors are not required since the output DC levels will be within a few tenths of a volt of each other. In cases where critical matching is necessary, a 500 K potentiometer is included and can be adjusted to ensure zero DC current flow through the load.
This low voltage high power output circuit is primarily utilized in applications where efficient power delivery is crucial, such as in audio amplification or driving low impedance loads. The circuit operates effectively at voltages of 6 V and 12 V, providing adequate power levels while maintaining low distortion and high fidelity.
The design eliminates the need for coupling capacitors, which simplifies the circuit and reduces component count. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where space and weight are critical, such as portable devices. The close matching of output DC levels minimizes the risk of DC offset, which can adversely affect performance and lead to potential damage in sensitive components.
The inclusion of a 500 K potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the circuit. By adjusting this potentiometer, the user can achieve precise matching of output characteristics and eliminate any DC current that may flow through the load. This adjustment capability enhances the circuit's versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications requiring different load conditions.
Overall, the circuit's design emphasizes simplicity, efficiency, and adaptability, making it an ideal choice for low voltage, high power output applications. Proper implementation of this circuit can lead to significant improvements in performance and reliability in various electronic systems.This circuit is for low voltage applications requiring high power outputs. Output power levels of LO W into 4 ohm from 6 V and 3 V into 8 ohm from 12 V are typical. Coupling capacitors are not necessary since the output dc levels will-be within a few tenths of a volt of each other Where critical matching is required the 500 K potentiometer is added and adjusted for zero dc current flow through the load.
This low voltage high power output circuit is primarily utilized in applications where efficient power delivery is crucial, such as in audio amplification or driving low impedance loads. The circuit operates effectively at voltages of 6 V and 12 V, providing adequate power levels while maintaining low distortion and high fidelity.
The design eliminates the need for coupling capacitors, which simplifies the circuit and reduces component count. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where space and weight are critical, such as portable devices. The close matching of output DC levels minimizes the risk of DC offset, which can adversely affect performance and lead to potential damage in sensitive components.
The inclusion of a 500 K potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the circuit. By adjusting this potentiometer, the user can achieve precise matching of output characteristics and eliminate any DC current that may flow through the load. This adjustment capability enhances the circuit's versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications requiring different load conditions.
Overall, the circuit's design emphasizes simplicity, efficiency, and adaptability, making it an ideal choice for low voltage, high power output applications. Proper implementation of this circuit can lead to significant improvements in performance and reliability in various electronic systems.This circuit is for low voltage applications requiring high power outputs. Output power levels of LO W into 4 ohm from 6 V and 3 V into 8 ohm from 12 V are typical. Coupling capacitors are not necessary since the output dc levels will-be within a few tenths of a volt of each other Where critical matching is required the 500 K potentiometer is added and adjusted for zero dc current flow through the load.