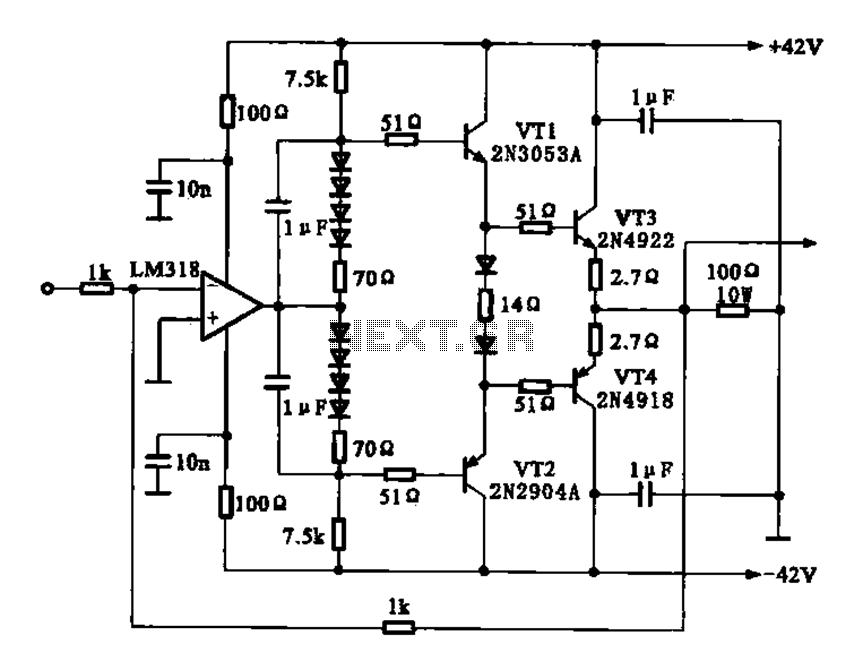
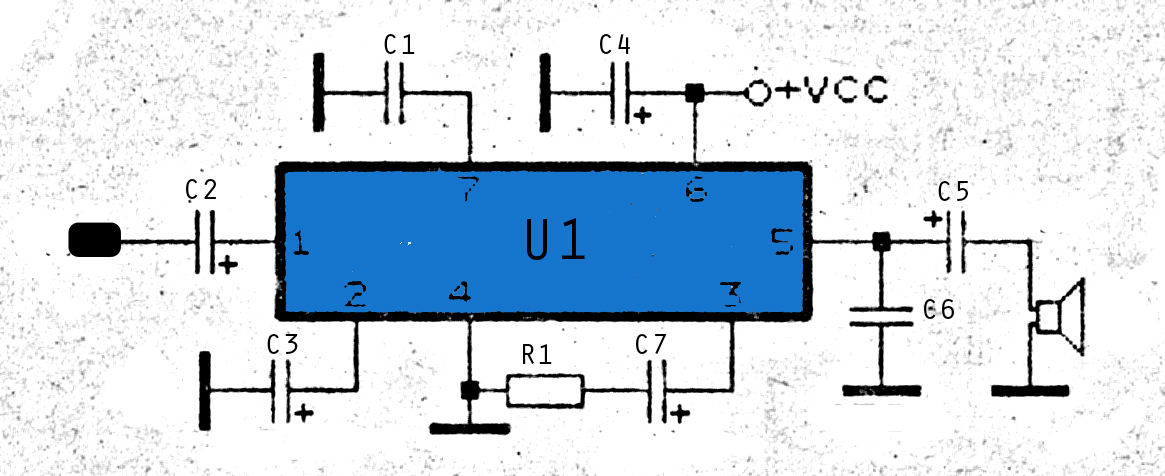
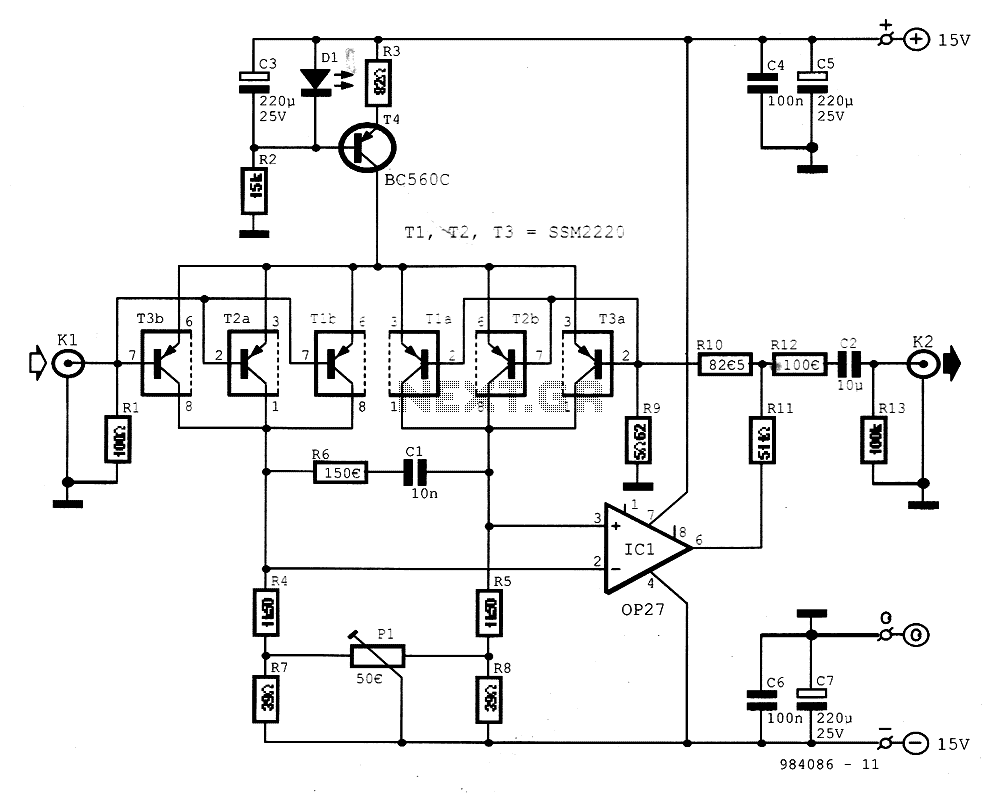
Buffer amplifier
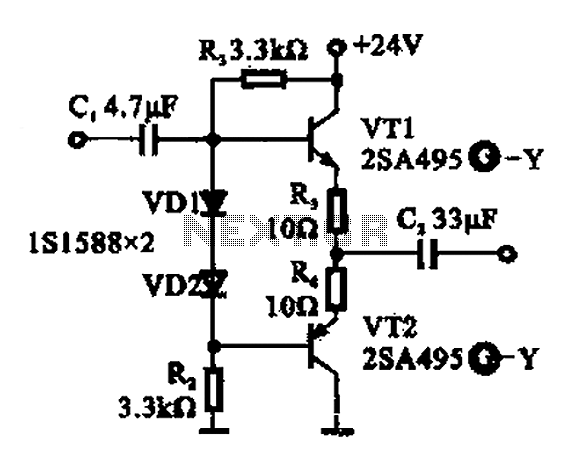
A buffer amplifier is utilized as a transistor emitter follower buffer amplifier for applications that necessitate a high input impedance. The circuit employs a complementary push-pull configuration. The signal input is connected to the base of transistor VT1, which features a base bias resistor divider. The base of the transistor is indirectly influenced by two forward-biased diodes to ensure stability in the base voltage. Given that this circuit employs a dual emitter output, it exhibits low output impedance and a robust output capability.
The buffer amplifier described functions primarily as an impedance matching device, allowing signals from high impedance sources to drive lower impedance loads without signal degradation. The configuration of the amplifier as an emitter follower ensures that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage while providing a significant increase in current drive capability.
In this circuit, the transistor VT1 acts as the main amplifying element. The high input impedance is achieved through the use of a resistor divider network that biases the base of VT1, allowing minimal loading on the input signal source. The inclusion of the two forward-biased diodes serves to stabilize the base voltage against fluctuations, enhancing the performance of the amplifier under varying conditions.
The complementary push-pull arrangement typically involves a second transistor, which can be configured to handle the negative half of the signal cycle, thereby improving linearity and reducing distortion. This configuration allows the circuit to efficiently drive loads while maintaining signal integrity.
The output stage of the buffer amplifier, characterized by its dual emitter output, results in low output impedance. This is advantageous for driving capacitive loads or long cable runs, as it minimizes signal loss and ensures that the load receives a faithful representation of the input signal. The overall design is particularly suited for applications in audio amplification, sensor interfacing, and other scenarios where signal fidelity and impedance matching are critical. Buffer amplifier Shown in use as a transistor emitter follower buffer amplifier for applications that require high input impedance of the amplifier. Complementary push-pull cir cuit the circuit configuration, the signal input from the base of VT1, two transistor base bias resistor divider type, the base of the transistor both indirect two forward biased diodes, to maintain the base voltage static stability, since the circuit dual emitter output circuit, because the output impedance and low output has strong ability.
The buffer amplifier described functions primarily as an impedance matching device, allowing signals from high impedance sources to drive lower impedance loads without signal degradation. The configuration of the amplifier as an emitter follower ensures that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage while providing a significant increase in current drive capability.
In this circuit, the transistor VT1 acts as the main amplifying element. The high input impedance is achieved through the use of a resistor divider network that biases the base of VT1, allowing minimal loading on the input signal source. The inclusion of the two forward-biased diodes serves to stabilize the base voltage against fluctuations, enhancing the performance of the amplifier under varying conditions.
The complementary push-pull arrangement typically involves a second transistor, which can be configured to handle the negative half of the signal cycle, thereby improving linearity and reducing distortion. This configuration allows the circuit to efficiently drive loads while maintaining signal integrity.
The output stage of the buffer amplifier, characterized by its dual emitter output, results in low output impedance. This is advantageous for driving capacitive loads or long cable runs, as it minimizes signal loss and ensures that the load receives a faithful representation of the input signal. The overall design is particularly suited for applications in audio amplification, sensor interfacing, and other scenarios where signal fidelity and impedance matching are critical. Buffer amplifier Shown in use as a transistor emitter follower buffer amplifier for applications that require high input impedance of the amplifier. Complementary push-pull cir cuit the circuit configuration, the signal input from the base of VT1, two transistor base bias resistor divider type, the base of the transistor both indirect two forward biased diodes, to maintain the base voltage static stability, since the circuit dual emitter output circuit, because the output impedance and low output has strong ability.