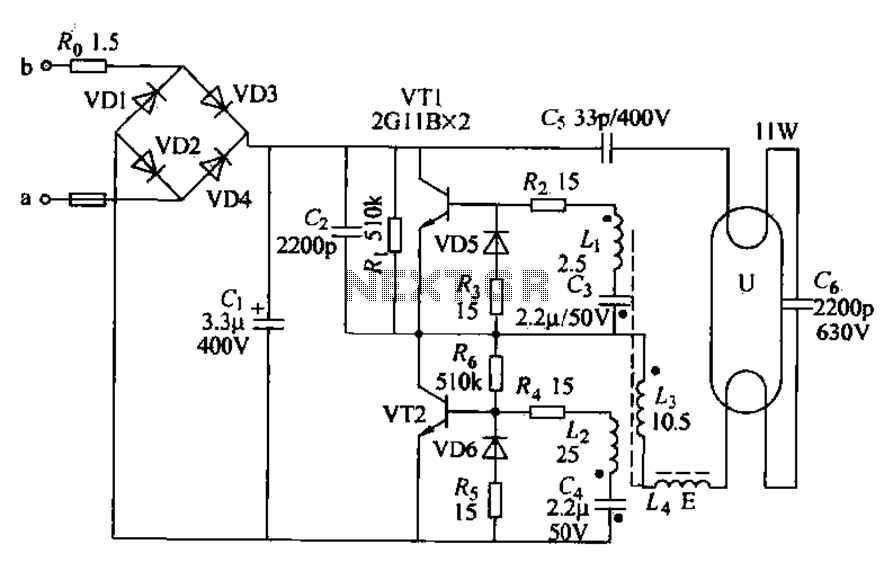
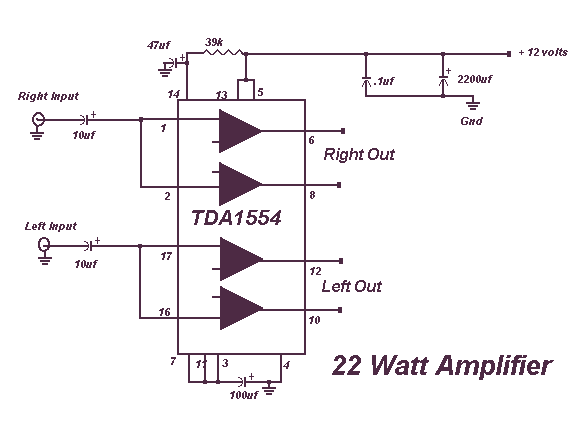
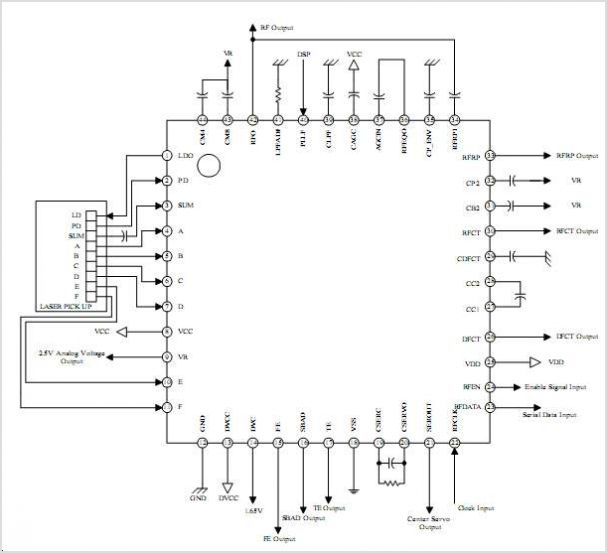
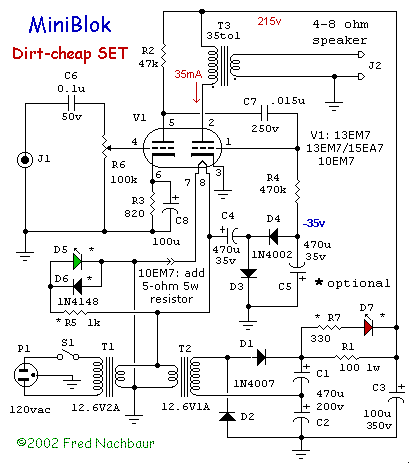
Building an B-15-inspired amp
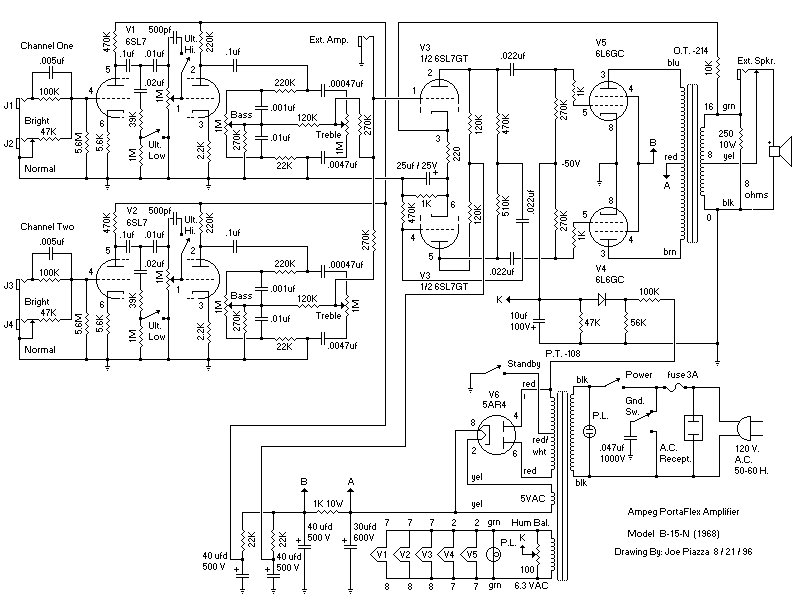
A newcomer has entered the field after completing several repairs and minor upgrades on tube amplifiers, including re-capping and addressing bias issues.
The process of repairing and upgrading tube amplifiers involves several critical steps to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Re-capping refers to the replacement of old capacitors, which can degrade over time, leading to reduced audio quality and potential circuit failures. It is essential to select capacitors that meet or exceed the original specifications to maintain the amplifier's intended performance characteristics.
Addressing bias problems is another crucial aspect of tube amplifier maintenance. Biasing involves adjusting the operating point of the output tubes to achieve the best performance while minimizing distortion. Incorrect bias settings can lead to overheating, reduced lifespan of the tubes, and suboptimal sound quality. Proper biasing techniques often require using a multimeter to measure the current flowing through the tubes and adjusting the bias potentiometer accordingly.
In addition to these tasks, various minor upgrades may include replacing outdated components with modern equivalents that offer improved performance, such as resistors with tighter tolerances or higher-quality connectors. Each modification should be carefully considered, as it can significantly impact the amplifier's overall sound and reliability.
Overall, the maintenance and upgrading of tube amplifiers require a thorough understanding of electronic principles and meticulous attention to detail to ensure that the final product meets the desired performance standards.Hello, everyone, new kid on the block here After some tube amp reparations, fixes and minor upgrades (re-capping, fixing bias problems, various.. 🔗 External reference
The process of repairing and upgrading tube amplifiers involves several critical steps to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Re-capping refers to the replacement of old capacitors, which can degrade over time, leading to reduced audio quality and potential circuit failures. It is essential to select capacitors that meet or exceed the original specifications to maintain the amplifier's intended performance characteristics.
Addressing bias problems is another crucial aspect of tube amplifier maintenance. Biasing involves adjusting the operating point of the output tubes to achieve the best performance while minimizing distortion. Incorrect bias settings can lead to overheating, reduced lifespan of the tubes, and suboptimal sound quality. Proper biasing techniques often require using a multimeter to measure the current flowing through the tubes and adjusting the bias potentiometer accordingly.
In addition to these tasks, various minor upgrades may include replacing outdated components with modern equivalents that offer improved performance, such as resistors with tighter tolerances or higher-quality connectors. Each modification should be carefully considered, as it can significantly impact the amplifier's overall sound and reliability.
Overall, the maintenance and upgrading of tube amplifiers require a thorough understanding of electronic principles and meticulous attention to detail to ensure that the final product meets the desired performance standards.Hello, everyone, new kid on the block here After some tube amp reparations, fixes and minor upgrades (re-capping, fixing bias problems, various.. 🔗 External reference