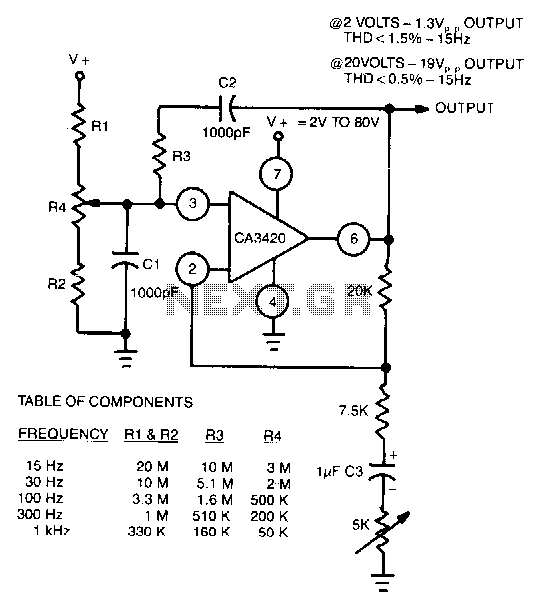
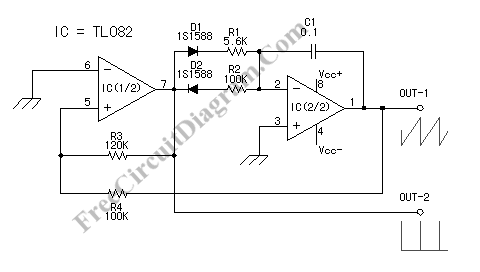
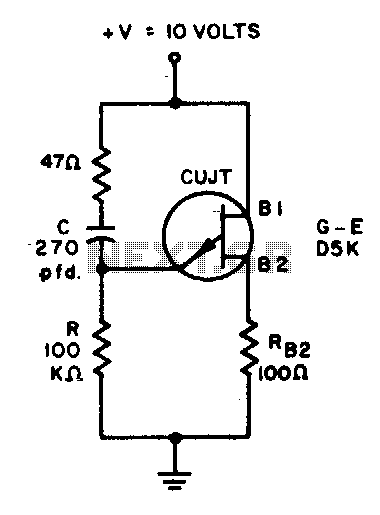
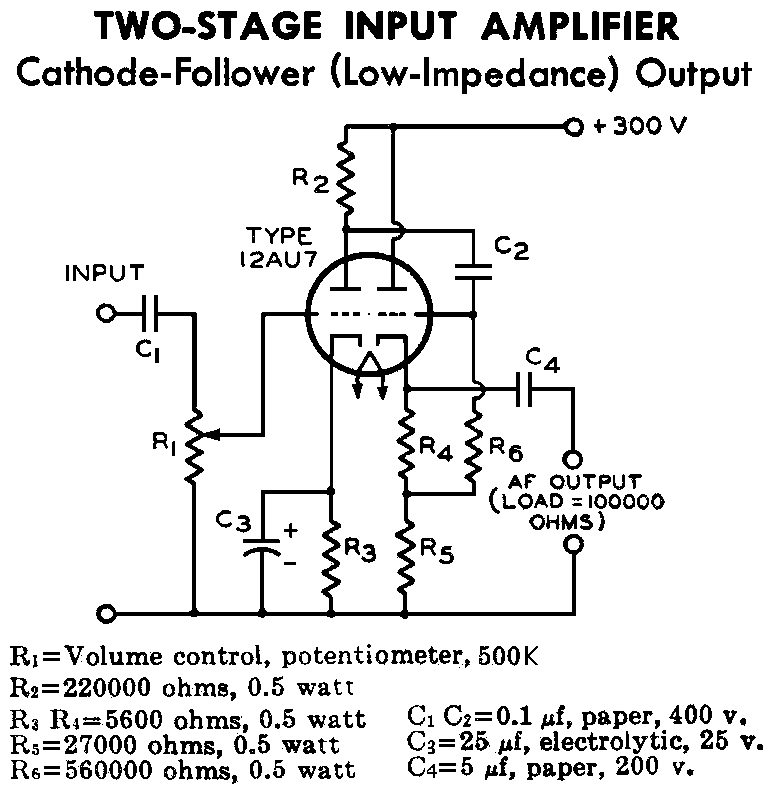
Butler emitter follower oscillator
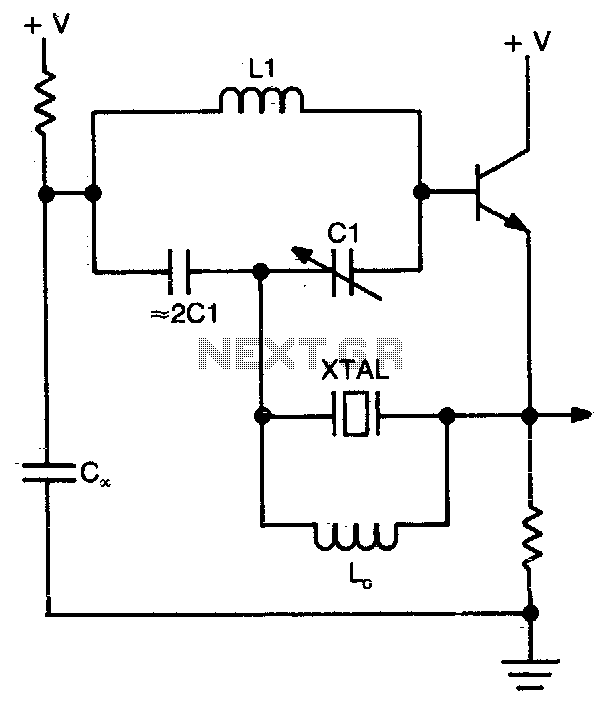
This circuit operates at or near series resonance. It is a well-designed circuit with no parasitics. It is easy to tune and has good frequency stability.
The circuit in question utilizes series resonance to achieve optimal performance. At series resonance, the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal in magnitude but opposite in phase, resulting in a purely resistive impedance. This characteristic allows for maximum current flow through the circuit at the resonant frequency, making it highly efficient for applications such as RF signal processing and filtering.
The absence of parasitic elements is a significant advantage, as parasitics can introduce unwanted losses and distortions that degrade circuit performance. This circuit's design minimizes these effects, ensuring that the desired signal characteristics are preserved.
Tuning the circuit is facilitated by adjustable components, such as variable capacitors or inductors, which enable precise control over the resonant frequency. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where frequency adjustments are necessary, such as in oscillators or tunable filters.
Moreover, the circuit exhibits good frequency stability, which is crucial for maintaining consistent performance over time and varying operating conditions. Stability is often enhanced through careful component selection and layout design, reducing susceptibility to temperature variations and other environmental factors.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for a range of applications requiring reliable performance at or near resonance, combining ease of tuning with robust frequency stability.This circuit operates at or near series resonance. It is a good circuit design with no parasitics It is easy to tune with good frequency stability. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question utilizes series resonance to achieve optimal performance. At series resonance, the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal in magnitude but opposite in phase, resulting in a purely resistive impedance. This characteristic allows for maximum current flow through the circuit at the resonant frequency, making it highly efficient for applications such as RF signal processing and filtering.
The absence of parasitic elements is a significant advantage, as parasitics can introduce unwanted losses and distortions that degrade circuit performance. This circuit's design minimizes these effects, ensuring that the desired signal characteristics are preserved.
Tuning the circuit is facilitated by adjustable components, such as variable capacitors or inductors, which enable precise control over the resonant frequency. This feature is particularly beneficial in applications where frequency adjustments are necessary, such as in oscillators or tunable filters.
Moreover, the circuit exhibits good frequency stability, which is crucial for maintaining consistent performance over time and varying operating conditions. Stability is often enhanced through careful component selection and layout design, reducing susceptibility to temperature variations and other environmental factors.
Overall, this circuit design is suitable for a range of applications requiring reliable performance at or near resonance, combining ease of tuning with robust frequency stability.This circuit operates at or near series resonance. It is a good circuit design with no parasitics It is easy to tune with good frequency stability. 🔗 External reference