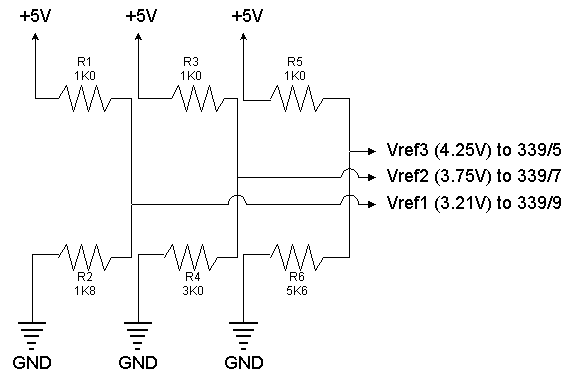
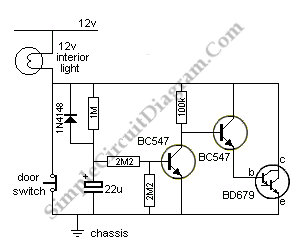
car battery charger schematics
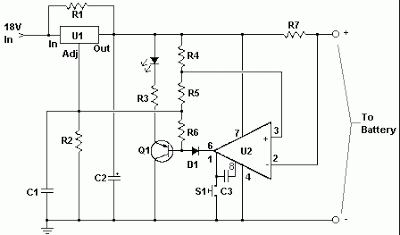
The circuit is designed to be powered directly by a power supply, which is why it does not include a transformer, rectifier, or filter capacitors in the schematic. However, the addition of these components is possible. To operate the circuit, connect it to a power supply or plug it in. Next, attach the battery intended for charging to the output terminals. Finally, activate the circuit by pressing switch S1 (the "Start" switch) and wait for the charging process to complete.
The described circuit operates as a battery charger powered by an external power source. The absence of a transformer indicates that the circuit is likely intended for low-voltage applications where the input voltage matches the required charging voltage of the battery. The lack of rectification and filtering components suggests that this design is simplified for specific use cases, where the direct current (DC) from the power supply is suitable for charging the connected battery.
The circuit's operation begins when the user connects a compatible battery to the designated output terminals. The switch S1, labeled as the "Start" switch, serves as a control mechanism that initiates the charging process. Upon activation of S1, the circuit allows current to flow from the power supply to the battery, facilitating the charging action.
To enhance the functionality and safety of the circuit, additional components may be considered. For instance, integrating a transformer could provide isolation from the power supply, while a rectifier would convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) if the power supply were AC. Filter capacitors could also be added to smooth out any voltage fluctuations, ensuring a stable charging voltage is delivered to the battery.
Furthermore, implementing a charge controller or circuitry to monitor the battery's state of charge would enhance the circuit's performance and safety. This would prevent overcharging, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan. Such enhancements would require careful consideration of component ratings and specifications to ensure compatibility with the power supply and the battery being charged.
In summary, the circuit serves as a straightforward battery charger powered by an external supply, with the potential for expansion through additional components to improve performance and safety features.The circuit was meant to be powered by a power supply, which is why there is no transformer, rectifier, or filter capacitors on the schematic. There is no reason why you cannot add these. To use the circuit, hook it up to a power supply/plug it in. Then, connect the battery to be charged to the output terminals. All you have to do now is push S1 ( the "Start" switch), and wait for the circuit to finish. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a battery charger powered by an external power source. The absence of a transformer indicates that the circuit is likely intended for low-voltage applications where the input voltage matches the required charging voltage of the battery. The lack of rectification and filtering components suggests that this design is simplified for specific use cases, where the direct current (DC) from the power supply is suitable for charging the connected battery.
The circuit's operation begins when the user connects a compatible battery to the designated output terminals. The switch S1, labeled as the "Start" switch, serves as a control mechanism that initiates the charging process. Upon activation of S1, the circuit allows current to flow from the power supply to the battery, facilitating the charging action.
To enhance the functionality and safety of the circuit, additional components may be considered. For instance, integrating a transformer could provide isolation from the power supply, while a rectifier would convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) if the power supply were AC. Filter capacitors could also be added to smooth out any voltage fluctuations, ensuring a stable charging voltage is delivered to the battery.
Furthermore, implementing a charge controller or circuitry to monitor the battery's state of charge would enhance the circuit's performance and safety. This would prevent overcharging, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan. Such enhancements would require careful consideration of component ratings and specifications to ensure compatibility with the power supply and the battery being charged.
In summary, the circuit serves as a straightforward battery charger powered by an external supply, with the potential for expansion through additional components to improve performance and safety features.The circuit was meant to be powered by a power supply, which is why there is no transformer, rectifier, or filter capacitors on the schematic. There is no reason why you cannot add these. To use the circuit, hook it up to a power supply/plug it in. Then, connect the battery to be charged to the output terminals. All you have to do now is push S1 ( the "Start" switch), and wait for the circuit to finish. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713