battery eliminator circuit
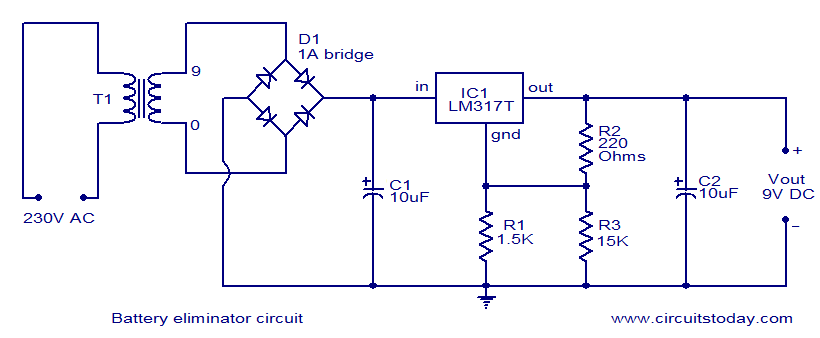
This document presents a circuit diagram of a battery eliminator circuit designed to replace 9V PP3 batteries. It can power any device that operates on a 9V battery. The transformer T1 reduces the mains voltage, while bridge rectifier D1 converts the AC voltage to DC. Capacitor C1 functions as a filter, and the IC LM317T serves as the voltage regulator. Resistors R1, R2, and R3 are selected to ensure that the output voltage of the IC remains stable at 9 volts.
The battery eliminator circuit is structured to efficiently convert mains voltage into a usable 9V DC output for various electronic devices. The transformer (T1) is pivotal in this design, as it steps down the high voltage AC from the mains to a lower AC voltage suitable for rectification. Typically, a step-down transformer with a secondary output rating of around 9V to 12V is used, depending on the load requirements.
The bridge rectifier (D1), composed of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, performs the essential function of converting the stepped-down AC voltage into pulsating DC. This pulsating DC output is not suitable for most devices, hence the need for filtering to smooth the voltage.
Capacitor C1 acts as a smoothing filter, reducing the ripple in the DC output. The value of C1 is chosen based on the load current and the acceptable ripple voltage level; larger capacitance values will yield a smoother output, but will also increase the physical size and cost of the circuit.
The voltage regulation is handled by the LM317T integrated circuit, which is a versatile adjustable voltage regulator. It is capable of providing a stable output voltage, which is crucial for sensitive electronic devices. The output voltage can be set to 9V by selecting appropriate resistor values for R1 and R2, according to the formula provided in the LM317T datasheet. The resistor R3 can be used as a current limiting resistor or to set the minimum load current necessary for proper regulation.
In summary, this battery eliminator circuit is an effective solution for powering devices that require a 9V supply, offering a reliable and stable output while eliminating the need for disposable batteries. Proper component selection and configuration ensure that the circuit operates efficiently and meets the voltage and current requirements of the connected devices.Here is the circuit diagram of a battery eliminator circuit that can be used as a replacement for 9V PP3 batteries. The circuit given here can be used to power any device that operates from a 9V battery. The transformer T1 steps down the mains voltage and bridge D1 performs the job of rectification. Capacitor C1 is a filter. IC LM317T is the regul ator here. The value of R1, R2 and R3 are so selected that the output voltage of IC1 will be steady 9 volts. 🔗 External reference
The battery eliminator circuit is structured to efficiently convert mains voltage into a usable 9V DC output for various electronic devices. The transformer (T1) is pivotal in this design, as it steps down the high voltage AC from the mains to a lower AC voltage suitable for rectification. Typically, a step-down transformer with a secondary output rating of around 9V to 12V is used, depending on the load requirements.
The bridge rectifier (D1), composed of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, performs the essential function of converting the stepped-down AC voltage into pulsating DC. This pulsating DC output is not suitable for most devices, hence the need for filtering to smooth the voltage.
Capacitor C1 acts as a smoothing filter, reducing the ripple in the DC output. The value of C1 is chosen based on the load current and the acceptable ripple voltage level; larger capacitance values will yield a smoother output, but will also increase the physical size and cost of the circuit.
The voltage regulation is handled by the LM317T integrated circuit, which is a versatile adjustable voltage regulator. It is capable of providing a stable output voltage, which is crucial for sensitive electronic devices. The output voltage can be set to 9V by selecting appropriate resistor values for R1 and R2, according to the formula provided in the LM317T datasheet. The resistor R3 can be used as a current limiting resistor or to set the minimum load current necessary for proper regulation.
In summary, this battery eliminator circuit is an effective solution for powering devices that require a 9V supply, offering a reliable and stable output while eliminating the need for disposable batteries. Proper component selection and configuration ensure that the circuit operates efficiently and meets the voltage and current requirements of the connected devices.Here is the circuit diagram of a battery eliminator circuit that can be used as a replacement for 9V PP3 batteries. The circuit given here can be used to power any device that operates from a 9V battery. The transformer T1 steps down the mains voltage and bridge D1 performs the job of rectification. Capacitor C1 is a filter. IC LM317T is the regul ator here. The value of R1, R2 and R3 are so selected that the output voltage of IC1 will be steady 9 volts. 🔗 External reference