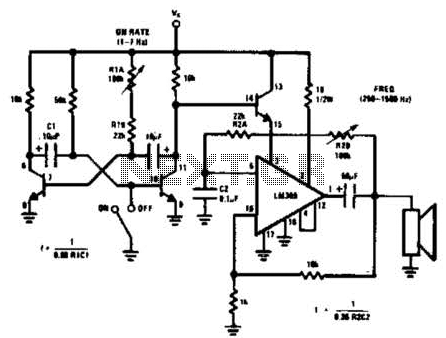
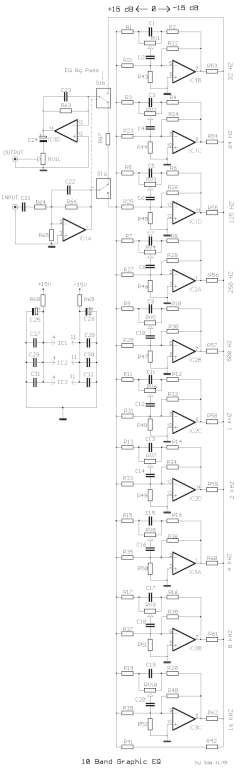
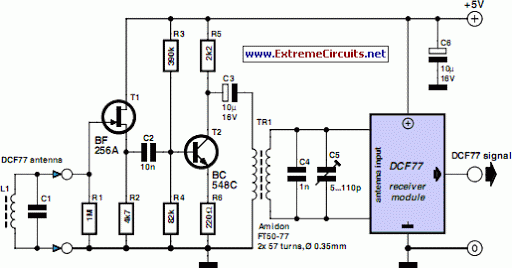
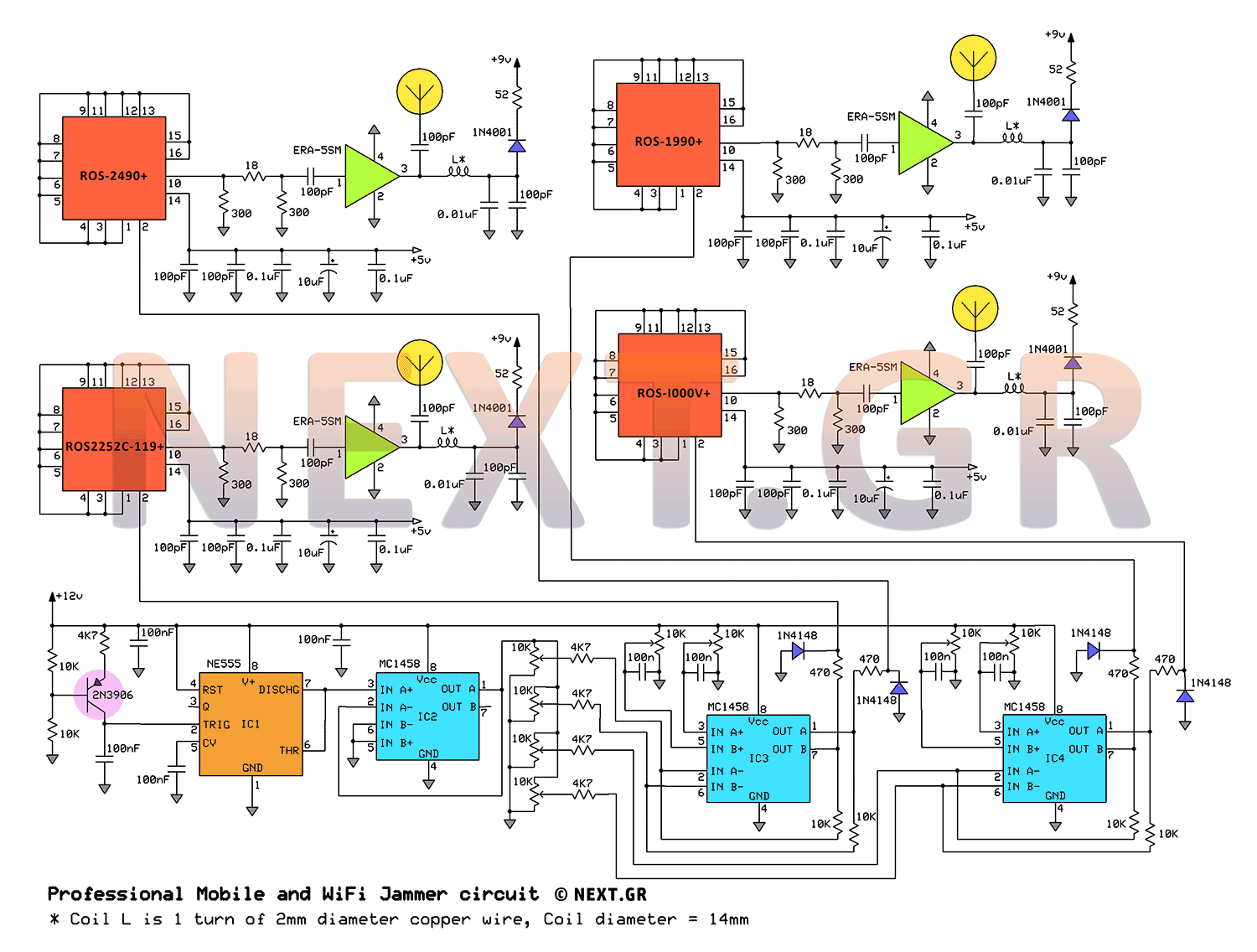
Car battery charging circuit diagram
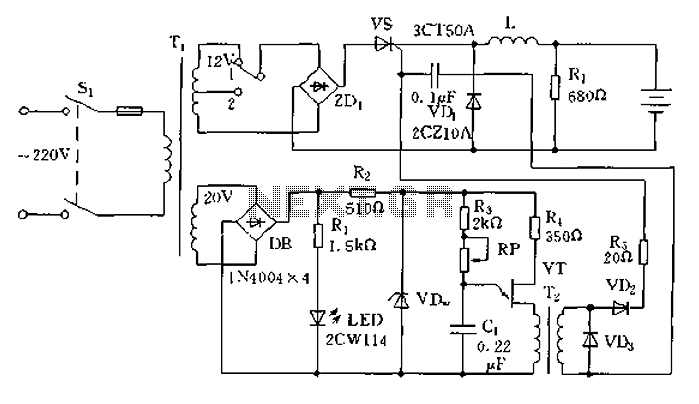
The circuit operates on the principle of a transformer, bridge rectifier, and conditioning for battery charging. The charging current can be adjusted to approximately 12V at 100A. For battery charging, a charging rate of 10 hours requires a charging current of 10A. A transformer with a secondary AC voltage of 15V and a power rating of 150VA is necessary, with a current limit of 10A. A corresponding transformer substation can provide an AC voltage of 10V, which is coupled with a full-bridge rectifier and a large capacitance to achieve a stable output of 14.14V.
The described circuit is designed to efficiently charge batteries using a transformer-based power supply. The transformer steps down the mains voltage to a secondary AC voltage of 15V, providing sufficient voltage to facilitate the charging process. The transformer must be rated at 150VA to ensure it can handle the required current without overheating.
The bridge rectifier configuration is employed to convert the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC). This is essential for charging batteries, which require a stable DC input. The full-bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing current to flow through the load during both halves of the AC cycle, thus ensuring a continuous output.
To further stabilize the output voltage and smooth out any ripple caused by the rectification process, a large capacitance is added to the circuit. This capacitor acts as a reservoir, storing charge and releasing it as needed, which helps maintain a steady voltage level of approximately 14.14V at the output. This voltage is suitable for charging lead-acid batteries, which typically require a charging voltage of around 14.4V.
The charging current can be adjusted via a variable resistor or a current limiting circuit, allowing for flexibility in the charging process. The design ensures that the maximum charging current does not exceed 10A, which is critical for safe and effective battery charging. The overall configuration of the circuit ensures that it can efficiently charge batteries while providing the necessary voltage and current regulation, thereby extending the life of the battery and improving performance. Circuit principle: circuit after transformer, bridge rectifier and conditioning on the battery charge, the charge current transformer can be adjusted simply give about 12v 100A H battery charging, charging rate by 10 hours required charging current of 10A. Need 150VA transformer secondary AC voltage of 15V, limit current is 10A. Useful corresponding transformer substation to AC 10V, with a full-bridge rectifier coupled with the large capacitance of variable stable 14.14V.
The described circuit is designed to efficiently charge batteries using a transformer-based power supply. The transformer steps down the mains voltage to a secondary AC voltage of 15V, providing sufficient voltage to facilitate the charging process. The transformer must be rated at 150VA to ensure it can handle the required current without overheating.
The bridge rectifier configuration is employed to convert the alternating current (AC) from the transformer into direct current (DC). This is essential for charging batteries, which require a stable DC input. The full-bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing current to flow through the load during both halves of the AC cycle, thus ensuring a continuous output.
To further stabilize the output voltage and smooth out any ripple caused by the rectification process, a large capacitance is added to the circuit. This capacitor acts as a reservoir, storing charge and releasing it as needed, which helps maintain a steady voltage level of approximately 14.14V at the output. This voltage is suitable for charging lead-acid batteries, which typically require a charging voltage of around 14.4V.
The charging current can be adjusted via a variable resistor or a current limiting circuit, allowing for flexibility in the charging process. The design ensures that the maximum charging current does not exceed 10A, which is critical for safe and effective battery charging. The overall configuration of the circuit ensures that it can efficiently charge batteries while providing the necessary voltage and current regulation, thereby extending the life of the battery and improving performance. Circuit principle: circuit after transformer, bridge rectifier and conditioning on the battery charge, the charge current transformer can be adjusted simply give about 12v 100A H battery charging, charging rate by 10 hours required charging current of 10A. Need 150VA transformer secondary AC voltage of 15V, limit current is 10A. Useful corresponding transformer substation to AC 10V, with a full-bridge rectifier coupled with the large capacitance of variable stable 14.14V.