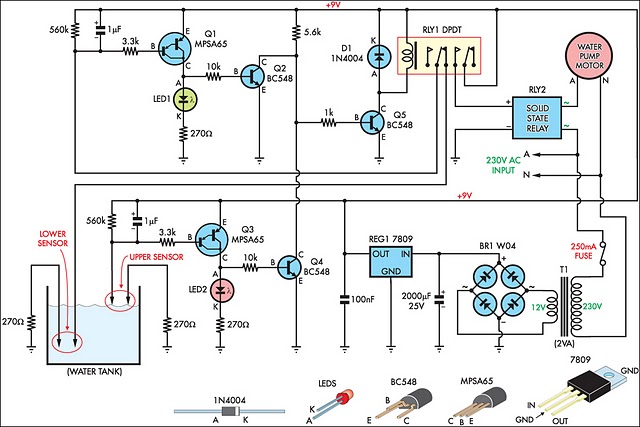
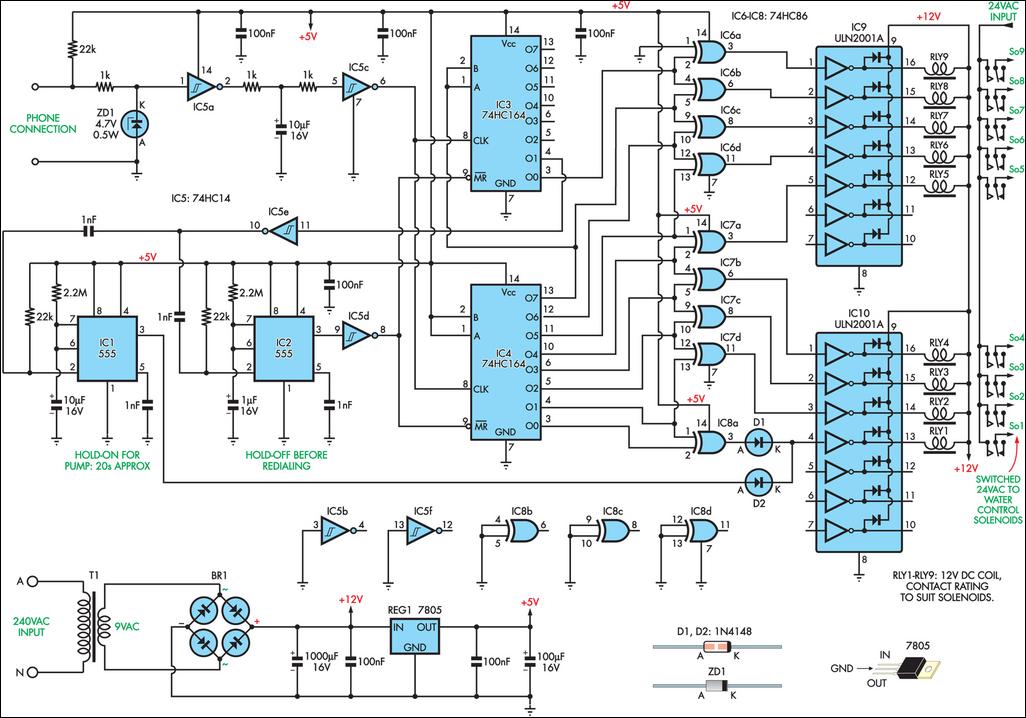
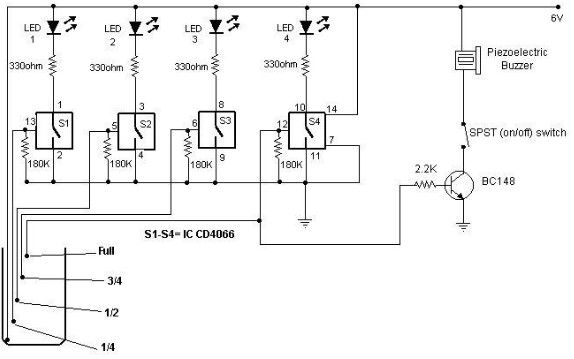
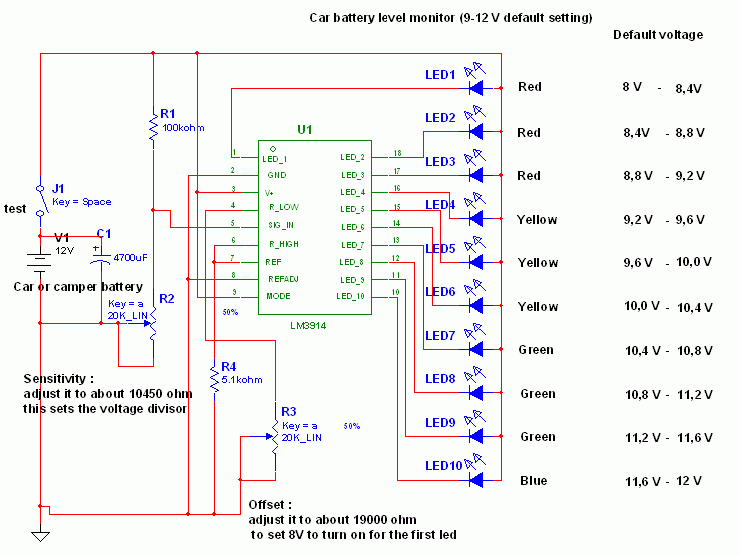
Car water Temperature monitor
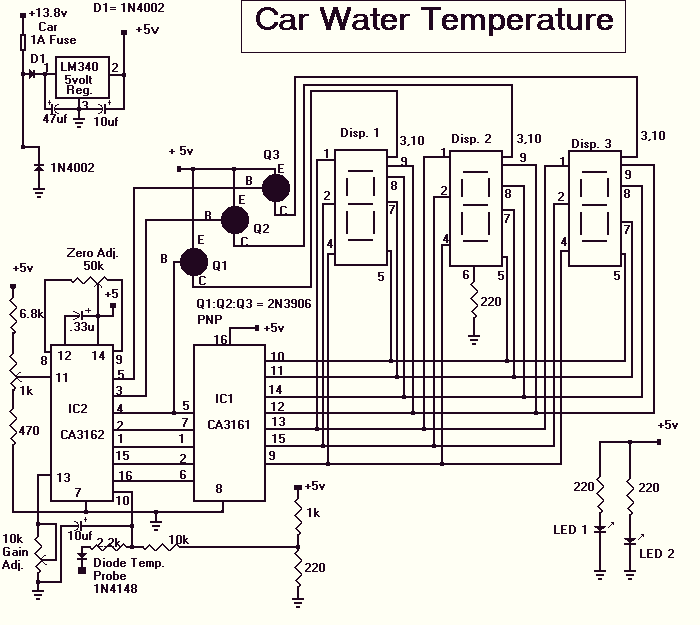
The Car Temperature Gauge is basically the same circuit as March's project with some minor changes to the input circuit. This circuit will display the water temperature to 1 degree resolution.
The Car Temperature Gauge circuit is designed to measure and display the engine coolant temperature with high precision, specifically to a resolution of 1 degree Celsius. The core components of this circuit include a temperature sensor, typically a thermistor or an LM35 temperature sensor, which converts the temperature into an electrical signal.
The circuit utilizes an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to translate the analog voltage signal from the sensor into a digital format suitable for processing. The ADC's output is then fed into a microcontroller, which processes the data and drives a display module, such as an LCD or LED display, to present the temperature reading.
In terms of the input circuit modifications referenced, these may involve adjustments to the sensor interface, such as adding filtering capacitors to reduce noise, or implementing a voltage divider to ensure that the sensor's output voltage remains within the ADC's input range. The microcontroller may also include calibration routines to account for sensor inaccuracies, ensuring that the displayed temperature is accurate.
Power supply considerations are crucial in this design, as the circuit should operate reliably under varying conditions. Typically, a voltage regulator may be employed to provide a stable voltage supply to the microcontroller and sensor, protecting the components from voltage fluctuations.
Overall, this Car Temperature Gauge circuit is a practical implementation of temperature measurement in automotive applications, providing real-time feedback to the driver and contributing to vehicle safety and performance monitoring.The Car Temperature Gauge is basically the same circuit as March's project with some minor changes to the input circuit. This circuit will display the water temperature to 1 degree resolution. 🔗 External reference
The Car Temperature Gauge circuit is designed to measure and display the engine coolant temperature with high precision, specifically to a resolution of 1 degree Celsius. The core components of this circuit include a temperature sensor, typically a thermistor or an LM35 temperature sensor, which converts the temperature into an electrical signal.
The circuit utilizes an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to translate the analog voltage signal from the sensor into a digital format suitable for processing. The ADC's output is then fed into a microcontroller, which processes the data and drives a display module, such as an LCD or LED display, to present the temperature reading.
In terms of the input circuit modifications referenced, these may involve adjustments to the sensor interface, such as adding filtering capacitors to reduce noise, or implementing a voltage divider to ensure that the sensor's output voltage remains within the ADC's input range. The microcontroller may also include calibration routines to account for sensor inaccuracies, ensuring that the displayed temperature is accurate.
Power supply considerations are crucial in this design, as the circuit should operate reliably under varying conditions. Typically, a voltage regulator may be employed to provide a stable voltage supply to the microcontroller and sensor, protecting the components from voltage fluctuations.
Overall, this Car Temperature Gauge circuit is a practical implementation of temperature measurement in automotive applications, providing real-time feedback to the driver and contributing to vehicle safety and performance monitoring.The Car Temperature Gauge is basically the same circuit as March's project with some minor changes to the input circuit. This circuit will display the water temperature to 1 degree resolution. 🔗 External reference