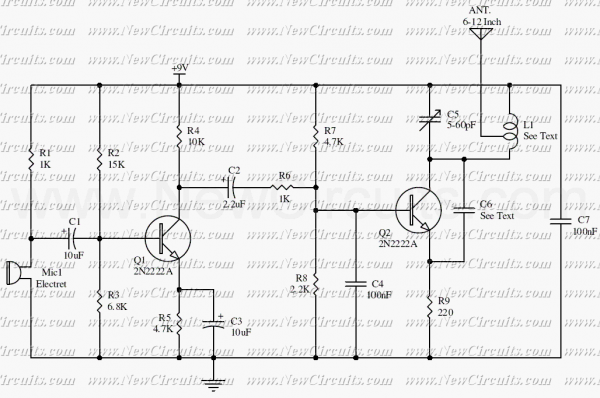
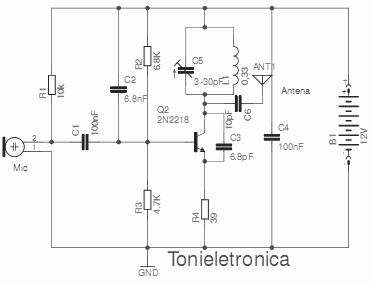
Carrier Current Transmitter For Data Transmission
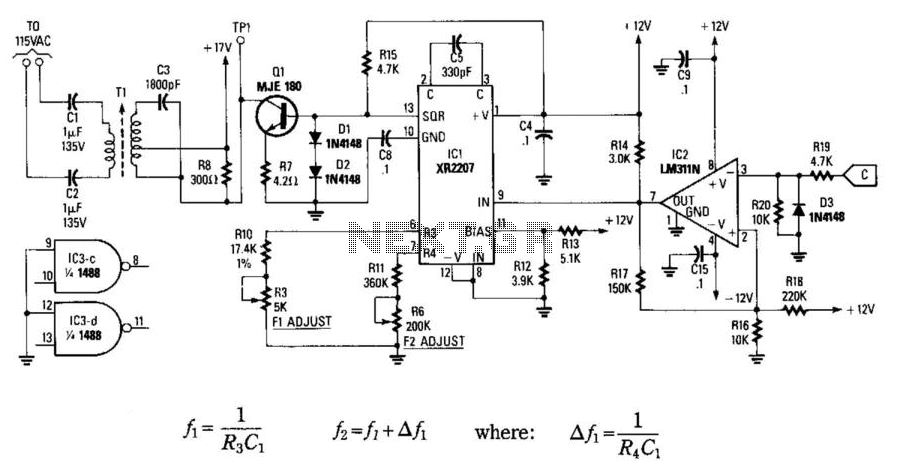
In this circuit, data at input C is amplified by IC2 and then fed to modulator IC1. IC1 generates two frequencies, depending on the values of C5, I10, R5, Rn, and R6. The frequency f1 is generated if pin 9 of IC1 is low and f2 if pin 9 of IC1 is high. A square wave appears at pin 13 of IC1 and is fed to Q1, an amplifier stage, that is coupled via tuned transformer T to the AC line through C1 and C2. It is important to note that, for safety reasons, C1 and C2 must be specifically rated for the AC line voltage.
In this circuit design, the operational flow begins with the input signal at point C, which is processed by operational amplifier IC2. The purpose of IC2 is to amplify the input data to a sufficient level before it is sent to modulator IC1. The modulation process within IC1 is controlled by the logic level present at pin 9; a low signal generates frequency f1, while a high signal produces frequency f2. The specific frequencies generated are influenced by the passive components connected to IC1, including capacitors C5 and I10, and resistors R5, Rn, and R6.
The output from IC1 at pin 13 is a square wave signal, which serves as the input to the next stage, Q1. This transistor amplifier stage is crucial for driving the subsequent load. The output of Q1 is coupled to the AC line through a tuned transformer T, which ensures that the signal is properly matched and transferred to the line without distortion.
Additionally, capacitors C1 and C2 play a vital role in this circuit. They function as coupling capacitors that isolate the AC line from the rest of the circuit, preventing any DC offset from affecting the operation of the components. It is essential that these capacitors are rated appropriately for the AC line voltage to ensure safety and reliability in operation. Failure to use correctly rated components could lead to circuit failure or hazardous conditions.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a typical application of modulation techniques in electronic design, where frequency generation and amplification are key to achieving the desired output signal characteristics. In this circuit, data at input C is amplified by IC2 and then fed to modulator IC1. IC1 g enerates two frequencies, depending on the values of C5, ii0, R$, Rn, and R6. The frequency/, is generated if pin 9IC1 is low and fa if pin 9IC1 is high. A square wave appears at pin 13 of IC1 and is fed to Ql, an amplifier stage, that is coupled via tuned transformer T, to the ac line via CI and C2. Notice that, for safety reasons, CI and C2 must be specifically rated for the ac line voltage.
In this circuit design, the operational flow begins with the input signal at point C, which is processed by operational amplifier IC2. The purpose of IC2 is to amplify the input data to a sufficient level before it is sent to modulator IC1. The modulation process within IC1 is controlled by the logic level present at pin 9; a low signal generates frequency f1, while a high signal produces frequency f2. The specific frequencies generated are influenced by the passive components connected to IC1, including capacitors C5 and I10, and resistors R5, Rn, and R6.
The output from IC1 at pin 13 is a square wave signal, which serves as the input to the next stage, Q1. This transistor amplifier stage is crucial for driving the subsequent load. The output of Q1 is coupled to the AC line through a tuned transformer T, which ensures that the signal is properly matched and transferred to the line without distortion.
Additionally, capacitors C1 and C2 play a vital role in this circuit. They function as coupling capacitors that isolate the AC line from the rest of the circuit, preventing any DC offset from affecting the operation of the components. It is essential that these capacitors are rated appropriately for the AC line voltage to ensure safety and reliability in operation. Failure to use correctly rated components could lead to circuit failure or hazardous conditions.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a typical application of modulation techniques in electronic design, where frequency generation and amplification are key to achieving the desired output signal characteristics. In this circuit, data at input C is amplified by IC2 and then fed to modulator IC1. IC1 g enerates two frequencies, depending on the values of C5, ii0, R$, Rn, and R6. The frequency/, is generated if pin 9IC1 is low and fa if pin 9IC1 is high. A square wave appears at pin 13 of IC1 and is fed to Ql, an amplifier stage, that is coupled via tuned transformer T, to the ac line via CI and C2. Notice that, for safety reasons, CI and C2 must be specifically rated for the ac line voltage.