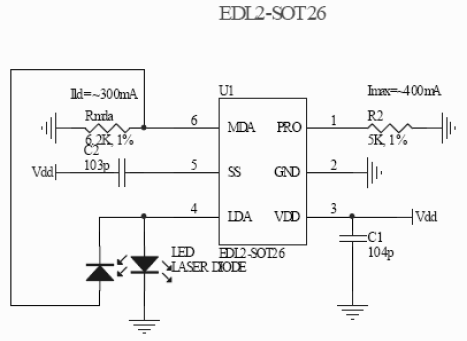
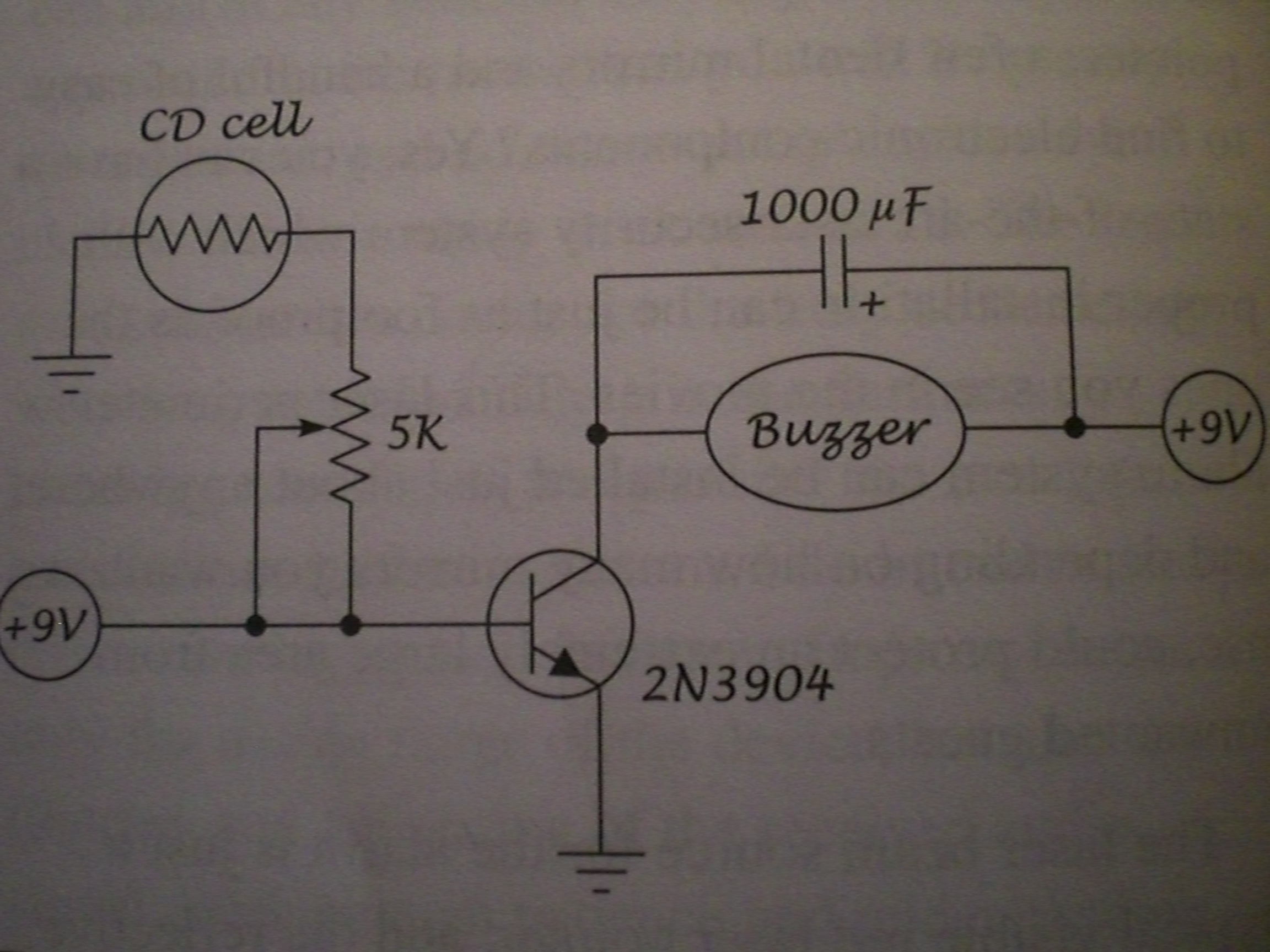
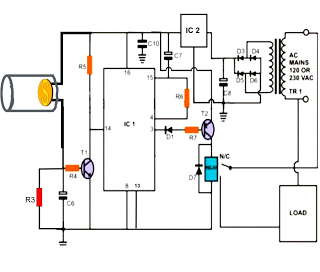
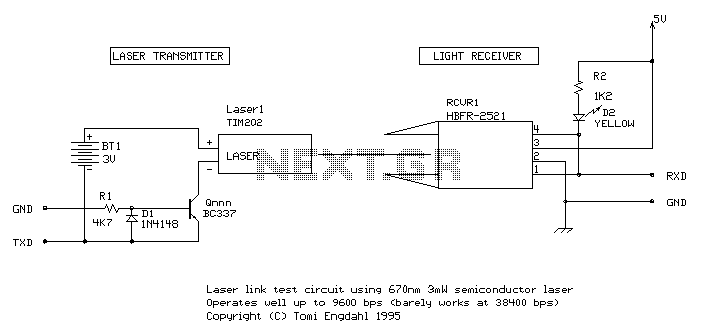
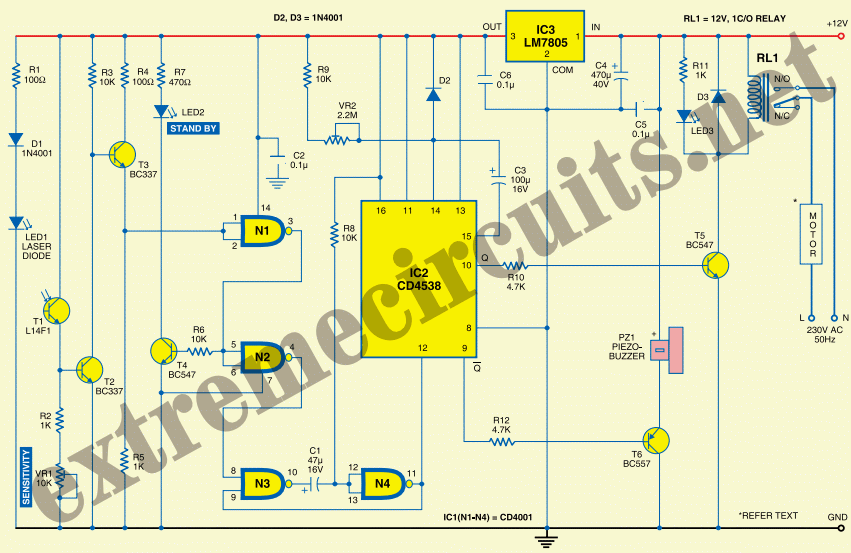
ch laser
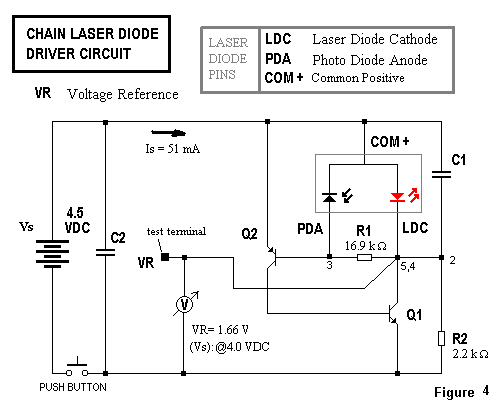
The laser diode will be forward biased, and its cathode (LDC) will connect to a driver transistor and/or network to regulate the laser diode current based on the photodiode current within a feedback network.
In this circuit configuration, the laser diode operates under forward bias conditions, which allows it to emit coherent light when current flows through it. The cathode of the laser diode (LDC) is connected to a driver transistor that plays a crucial role in regulating the current supplied to the laser diode. This regulation is essential for maintaining optimal performance and preventing damage due to overcurrent conditions.
The feedback network, which includes a photodiode, is integral to the operation of this circuit. The photodiode monitors the output light intensity from the laser diode and generates a corresponding current proportional to the light detected. This current is fed back into the driver transistor's control mechanism, allowing for real-time adjustments to the laser diode's operating current.
The driver transistor can be configured in various ways, such as using a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET), depending on the specific requirements of the application. The choice of transistor impacts the overall efficiency, response time, and stability of the feedback loop.
In summary, this configuration ensures that the laser diode operates efficiently and safely by continuously adjusting its current in response to changes in output light intensity, thus maintaining consistent performance across varying conditions. The design of the feedback network is critical, as it must be capable of responding quickly to changes in the photodiode's output to prevent fluctuations in the laser output.The laser diode will be forward biased and its cathode (LDC) will connect to a driver transistor &/or network to regulate the LD current based on the photodiode current (feedback network). 🔗 External reference
In this circuit configuration, the laser diode operates under forward bias conditions, which allows it to emit coherent light when current flows through it. The cathode of the laser diode (LDC) is connected to a driver transistor that plays a crucial role in regulating the current supplied to the laser diode. This regulation is essential for maintaining optimal performance and preventing damage due to overcurrent conditions.
The feedback network, which includes a photodiode, is integral to the operation of this circuit. The photodiode monitors the output light intensity from the laser diode and generates a corresponding current proportional to the light detected. This current is fed back into the driver transistor's control mechanism, allowing for real-time adjustments to the laser diode's operating current.
The driver transistor can be configured in various ways, such as using a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET), depending on the specific requirements of the application. The choice of transistor impacts the overall efficiency, response time, and stability of the feedback loop.
In summary, this configuration ensures that the laser diode operates efficiently and safely by continuously adjusting its current in response to changes in output light intensity, thus maintaining consistent performance across varying conditions. The design of the feedback network is critical, as it must be capable of responding quickly to changes in the photodiode's output to prevent fluctuations in the laser output.The laser diode will be forward biased and its cathode (LDC) will connect to a driver transistor &/or network to regulate the LD current based on the photodiode current (feedback network). 🔗 External reference