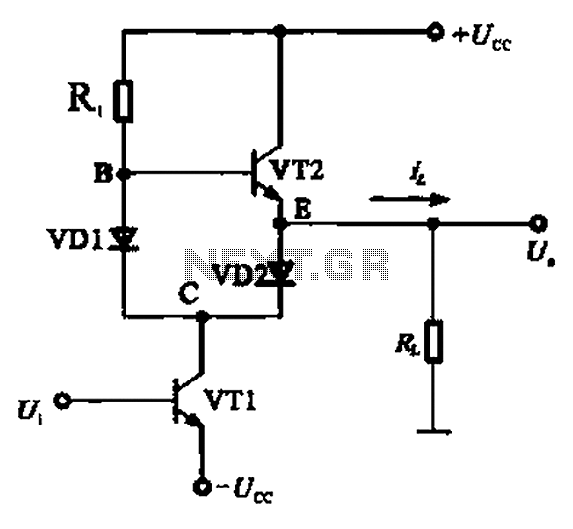
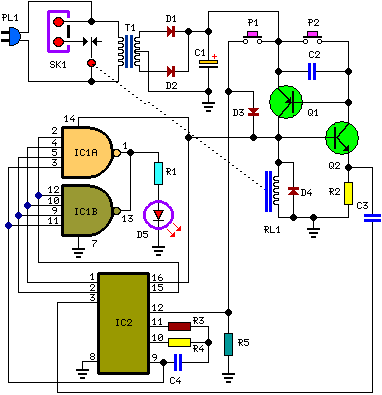
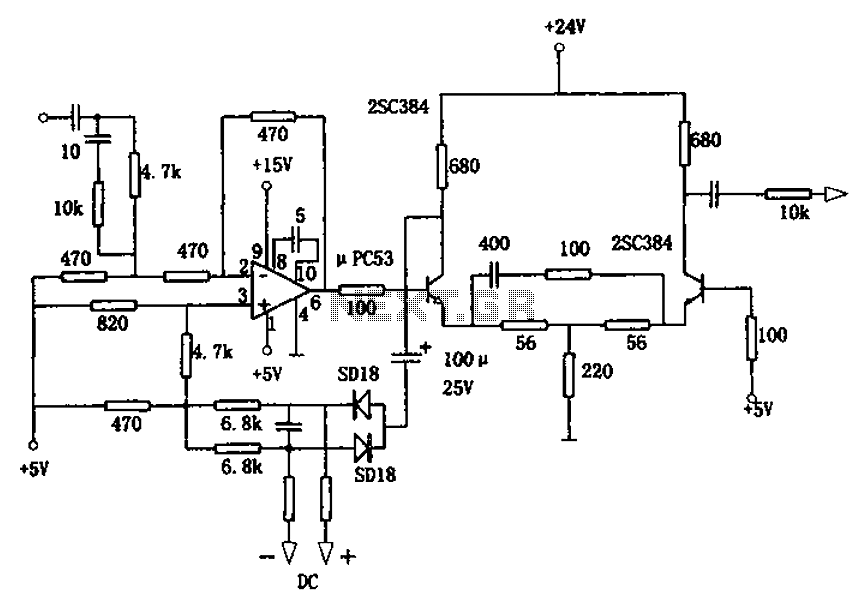
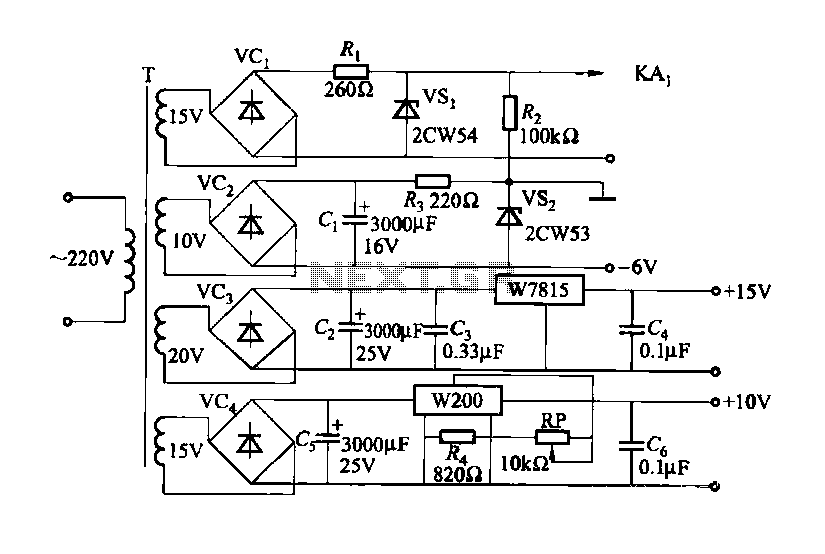
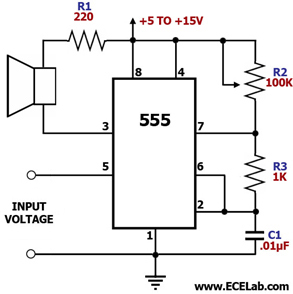
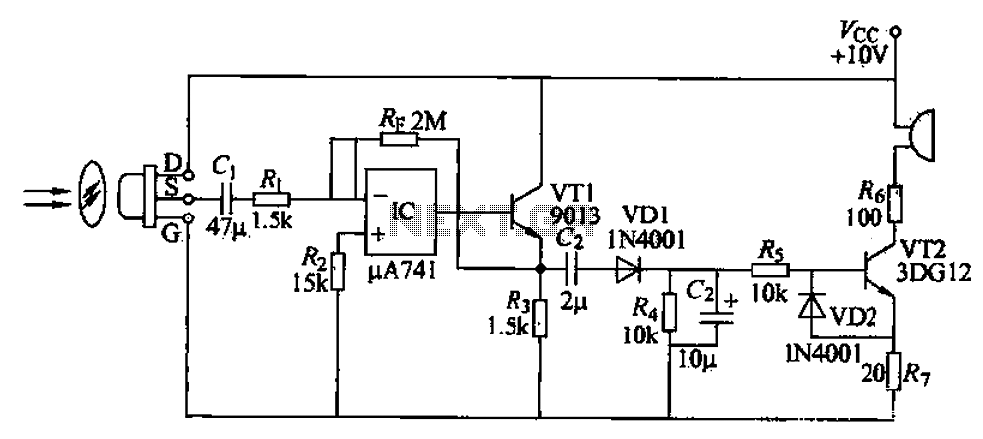
Charging circuit from the DC power supply switching power supply control
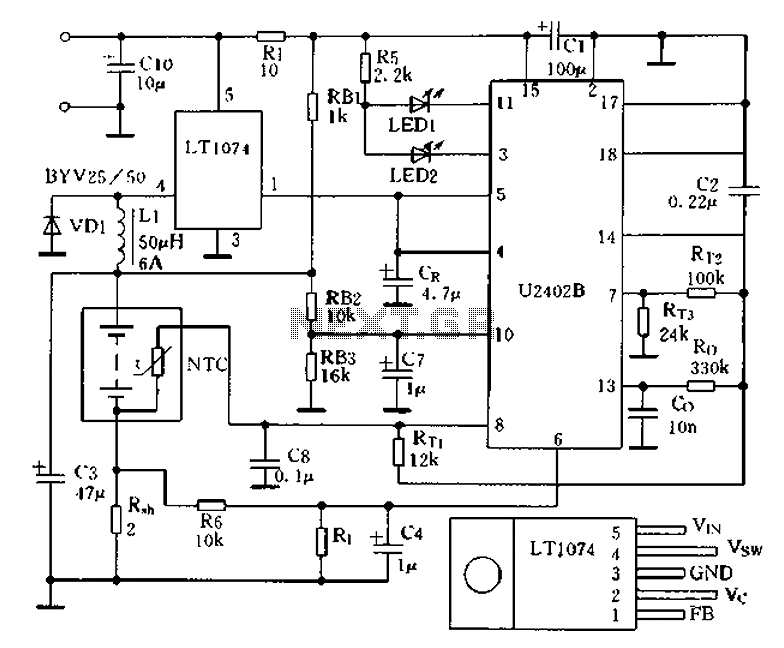
Charging circuit from the DC power supply switching power supply control
The charging circuit described is designed to operate with a DC power supply, utilizing a switching power supply control mechanism. This type of circuit is commonly employed in applications where efficient energy transfer and regulation are critical, such as in battery charging systems.
The circuit typically consists of several key components, including a switching regulator, input and output capacitors, diodes, and control logic. The switching regulator is responsible for converting the input DC voltage to a regulated output voltage suitable for charging a battery or powering a load. It operates by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, which allows for efficient energy conversion and minimal heat generation.
Input capacitors are used to filter the incoming voltage, ensuring a stable supply to the switching regulator. Output capacitors are crucial for smoothing the output voltage and minimizing voltage ripple, which is essential for sensitive electronic components and batteries.
Diodes may be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the power supply and connected devices from potential damage. The control logic, which may consist of operational amplifiers or microcontrollers, regulates the switching frequency and duty cycle of the regulator, adjusting the output based on the load requirements and battery state.
Overall, this charging circuit is characterized by its ability to efficiently manage power delivery from a DC source, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. Proper design and implementation of the circuit components are essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability. Charging circuit from the DC power supply switching power supply control
The charging circuit described is designed to operate with a DC power supply, utilizing a switching power supply control mechanism. This type of circuit is commonly employed in applications where efficient energy transfer and regulation are critical, such as in battery charging systems.
The circuit typically consists of several key components, including a switching regulator, input and output capacitors, diodes, and control logic. The switching regulator is responsible for converting the input DC voltage to a regulated output voltage suitable for charging a battery or powering a load. It operates by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, which allows for efficient energy conversion and minimal heat generation.
Input capacitors are used to filter the incoming voltage, ensuring a stable supply to the switching regulator. Output capacitors are crucial for smoothing the output voltage and minimizing voltage ripple, which is essential for sensitive electronic components and batteries.
Diodes may be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, protecting the power supply and connected devices from potential damage. The control logic, which may consist of operational amplifiers or microcontrollers, regulates the switching frequency and duty cycle of the regulator, adjusting the output based on the load requirements and battery state.
Overall, this charging circuit is characterized by its ability to efficiently manage power delivery from a DC source, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. Proper design and implementation of the circuit components are essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability. Charging circuit from the DC power supply switching power supply control