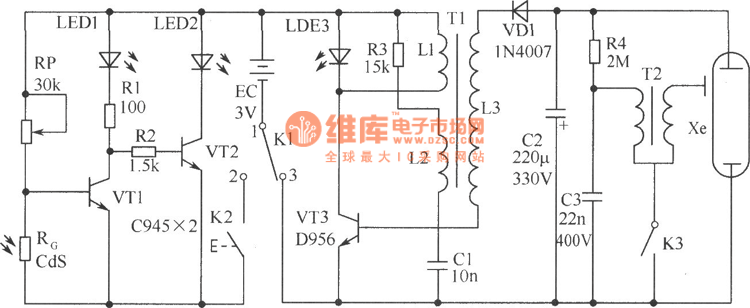
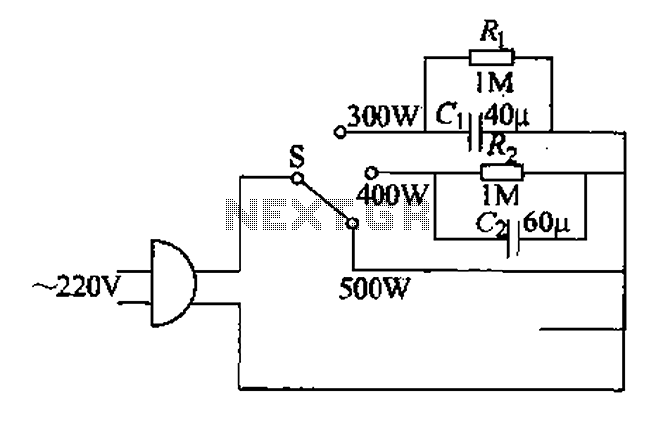
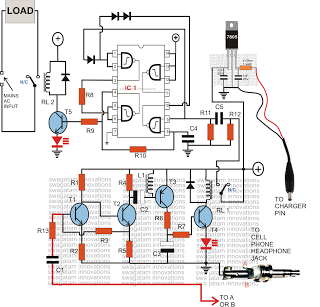
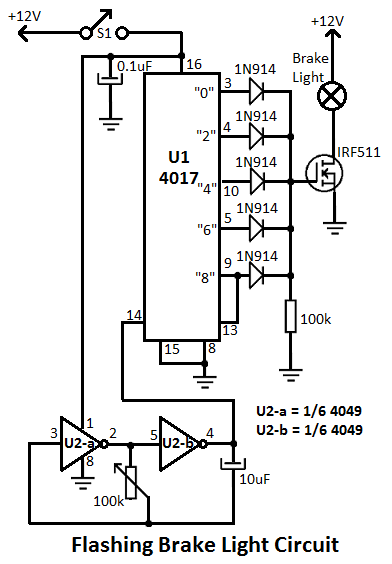
CIRCUIT ALLOWS SLEW RATE CONTROL
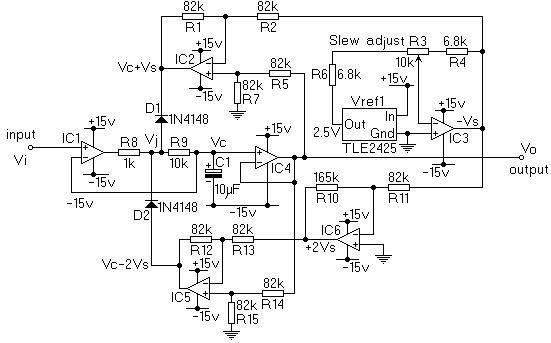
This circuit will impose a maximum slew rate on a signal; positive and negative rates can be independently controlled. The circuit is useful in servo applications where the error signal needs to be limited to be within the power rails to ensure predictable operation.
The described circuit functions as a slew rate limiter, which is critical in various electronic applications, particularly in servo control systems. The primary objective of this circuit is to restrict the rate of change of the output signal, thereby preventing abrupt changes that could lead to instability in the system.
The circuit typically consists of operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and capacitors configured in such a way that the output signal's rise and fall times are controlled. The op-amps are arranged to compare the input signal with a feedback signal derived from the output. By adjusting the feedback loop, the maximum slew rate can be set for both the positive and negative transitions of the signal independently.
For instance, the positive slew rate can be controlled by a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that determines how quickly the output can rise when the input signal transitions from a low to a high state. Similarly, a separate RC network can be used to control the negative slew rate, allowing for tailored performance based on application requirements.
In practical applications, this circuit is implemented to ensure that the servo system does not exceed the limits of the power supply rails. By limiting the slew rate, the circuit enhances the stability and predictability of the servo response, minimizing overshoot and oscillations that could occur if the system were allowed to respond too quickly to changes in the input signal.
In summary, this circuit serves an essential role in maintaining controlled signal transitions in servo applications, promoting reliable operation within the defined power limits.This circuit (figure 1) will impose a maximum slew rate on a signal; positive and negative rates can be independently controlled. The circuit is useful in servo applications where the error signal needs to be limited to be within the power rails to ensure predictable operation.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a slew rate limiter, which is critical in various electronic applications, particularly in servo control systems. The primary objective of this circuit is to restrict the rate of change of the output signal, thereby preventing abrupt changes that could lead to instability in the system.
The circuit typically consists of operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and capacitors configured in such a way that the output signal's rise and fall times are controlled. The op-amps are arranged to compare the input signal with a feedback signal derived from the output. By adjusting the feedback loop, the maximum slew rate can be set for both the positive and negative transitions of the signal independently.
For instance, the positive slew rate can be controlled by a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that determines how quickly the output can rise when the input signal transitions from a low to a high state. Similarly, a separate RC network can be used to control the negative slew rate, allowing for tailored performance based on application requirements.
In practical applications, this circuit is implemented to ensure that the servo system does not exceed the limits of the power supply rails. By limiting the slew rate, the circuit enhances the stability and predictability of the servo response, minimizing overshoot and oscillations that could occur if the system were allowed to respond too quickly to changes in the input signal.
In summary, this circuit serves an essential role in maintaining controlled signal transitions in servo applications, promoting reliable operation within the defined power limits.This circuit (figure 1) will impose a maximum slew rate on a signal; positive and negative rates can be independently controlled. The circuit is useful in servo applications where the error signal needs to be limited to be within the power rails to ensure predictable operation.
🔗 External reference