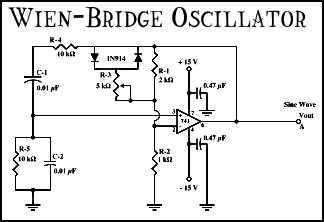
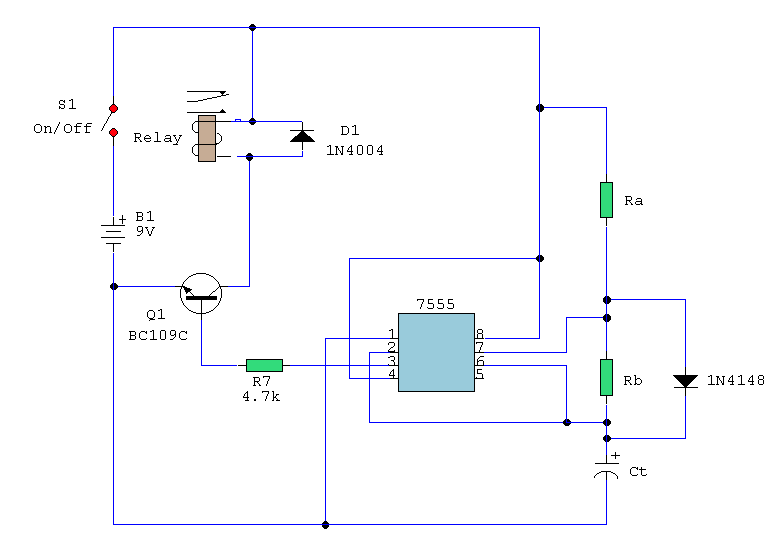
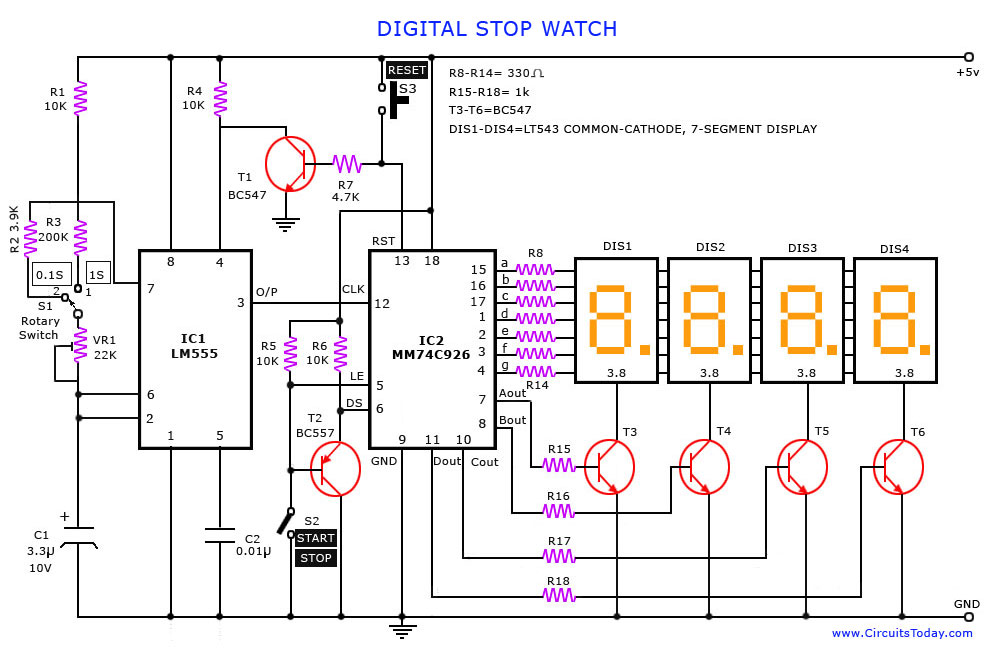
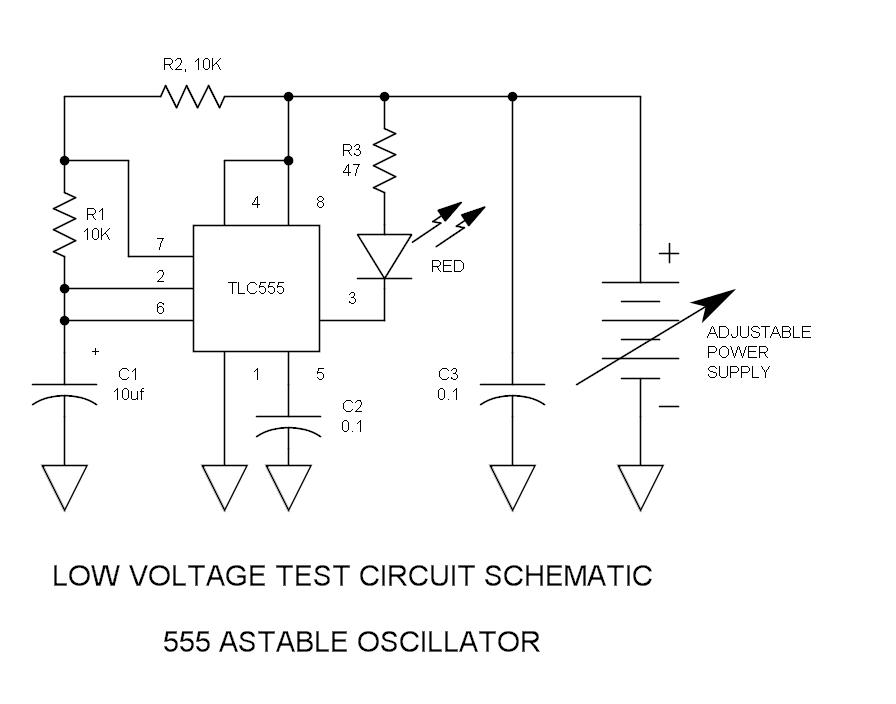
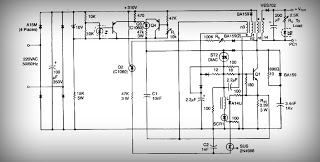
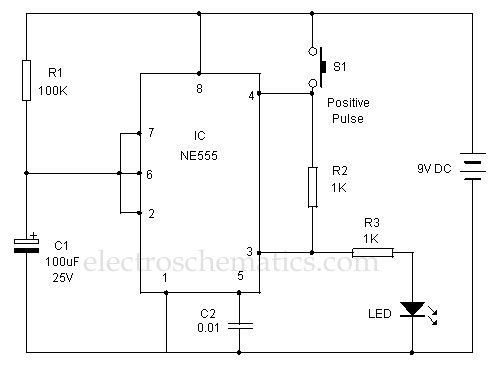
Circuit diagram for generating time delay with 555 IC
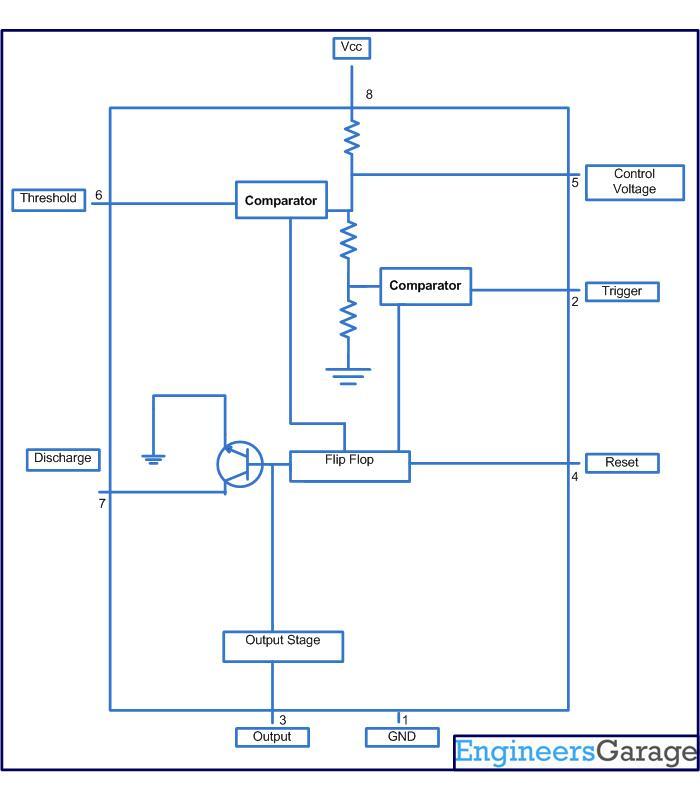
This circuit-based project demonstrates the operation of a 555 timer in astable mode to generate pulses with a time period of 0.5 seconds. These pulses can be utilized in various applications, such as blinking an LED or creating decorative blinking lights. The internal circuitry of the NE555 timer, which can be employed in both astable and monostable modes, is illustrated below. This project utilizes the NE555 timer IC to produce a constant square pulse at a desired frequency. The pulse can either be triggered or generated continuously, depending on the mode of the 555 timer being used. The two most commonly utilized modes of the 555 timer are monostable and astable. In this application, the timer operates in astable mode, with a total time period of half a second, comprising a high time of 0.333 seconds and a low time of 0.166 seconds. The total time period for the astable mode is calculated using the formula [ln(2)C*(R1+2*R2)], with the high time given by [ln(2)(R1+R2)*C] and the low time by [ln(2)(R2*C)]. In this configuration, R1 is the resistor connected between VCC and pin 7 (discharge pin), R2 is connected between pin 7 and pin 2 (trigger pin), and C1 is the capacitor connected from pin 2 to ground. For the 555 timer to function in astable mode, pins 2 and 6 (threshold) must be shorted. The reset pin is connected to VCC. The output of the 555 timer is taken from pin 3, which produces a square wave. This output is then fed into a lighting circuit that activates when the output is high and deactivates when it is low, resulting in a blinking light pattern. By adjusting the values of R1, R2, and C1, square waves of different time periods can be generated.
The NE555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used in various timing applications. In astable mode, it operates as an oscillator, generating a continuous square wave output. The frequency of this output is determined by the resistors R1 and R2, as well as the capacitor C1. The relationship between these components and the output frequency allows for a wide range of adjustable timing intervals, making the NE555 suitable for applications such as LED flashing, tone generation, and pulse width modulation.
In practical applications, the selection of R1, R2, and C1 should consider the desired frequency and duty cycle of the output signal. The duty cycle, defined as the ratio of the high time to the total time period, can be adjusted by varying the resistor values. A higher resistance value for R1 will increase the high time, whereas increasing R2 will affect both the high and low times, allowing for fine-tuning of the output waveform.
For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure that the capacitor C1 is of suitable type and value, as this will influence the stability and reliability of the output signal. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be added to the power supply lines to filter out noise, ensuring that the 555 timer operates reliably in various environments.
In summary, the 555 timer in astable mode is a powerful tool for generating precise timing signals, with applications ranging from simple LED blinking circuits to more complex timing and control systems. The flexibility in component selection allows for customization of the output characteristics to meet specific project requirements.This circuit based project demonstrates the working of 555 timer in astable mode to generate pulses of time period 0. 5 second. This pulse can be further used for anything where we need a pulse such as to blink a LED or to create fashionable blinking lights.
Image below shows internal circuitry of NE 555 timer which can be used in astable and monos table mode: This circuit of this project makes the use of timer IC NE555 which produces a constant square pulse of a desired frequency. This pulse could be either triggered or could be produced continuously depending upon the mode of 555 we are using.
The two mostly used modes of 555 are Monostable and Astable. Here it is used in the astable mode with time period of half second, with high time period of 0. 333 seconds and low time period of 0. 166 seconds. For astable mode total time period is [ln2C*(R1+2*R2)] with high time period as [ln2(R1+R2)*C]and low time period as [ln2(R2*C)]. Here R1 is the resistor connected between VCC and pin7 (discharge pin), R2 is between pin7 and pin2 (trigger pin) and C1 is the capacitor connected from pin2 to ground.
For 555 to function in astable mode pin2 and pin6 (threshold) pin must be shorted. Reset pin is connected to VCC. The output of 555 is taken at pin3 which is in the form of square wave and is then fed to lighting circuit which glows when output is high and stops when it becomes low; there by producing pattern of blinking lights. By varying the value of R1, R2 and C1 square waves of different time periods can be obtained. 🔗 External reference
The NE555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit widely used in various timing applications. In astable mode, it operates as an oscillator, generating a continuous square wave output. The frequency of this output is determined by the resistors R1 and R2, as well as the capacitor C1. The relationship between these components and the output frequency allows for a wide range of adjustable timing intervals, making the NE555 suitable for applications such as LED flashing, tone generation, and pulse width modulation.
In practical applications, the selection of R1, R2, and C1 should consider the desired frequency and duty cycle of the output signal. The duty cycle, defined as the ratio of the high time to the total time period, can be adjusted by varying the resistor values. A higher resistance value for R1 will increase the high time, whereas increasing R2 will affect both the high and low times, allowing for fine-tuning of the output waveform.
For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure that the capacitor C1 is of suitable type and value, as this will influence the stability and reliability of the output signal. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be added to the power supply lines to filter out noise, ensuring that the 555 timer operates reliably in various environments.
In summary, the 555 timer in astable mode is a powerful tool for generating precise timing signals, with applications ranging from simple LED blinking circuits to more complex timing and control systems. The flexibility in component selection allows for customization of the output characteristics to meet specific project requirements.This circuit based project demonstrates the working of 555 timer in astable mode to generate pulses of time period 0. 5 second. This pulse can be further used for anything where we need a pulse such as to blink a LED or to create fashionable blinking lights.
Image below shows internal circuitry of NE 555 timer which can be used in astable and monos table mode: This circuit of this project makes the use of timer IC NE555 which produces a constant square pulse of a desired frequency. This pulse could be either triggered or could be produced continuously depending upon the mode of 555 we are using.
The two mostly used modes of 555 are Monostable and Astable. Here it is used in the astable mode with time period of half second, with high time period of 0. 333 seconds and low time period of 0. 166 seconds. For astable mode total time period is [ln2C*(R1+2*R2)] with high time period as [ln2(R1+R2)*C]and low time period as [ln2(R2*C)]. Here R1 is the resistor connected between VCC and pin7 (discharge pin), R2 is between pin7 and pin2 (trigger pin) and C1 is the capacitor connected from pin2 to ground.
For 555 to function in astable mode pin2 and pin6 (threshold) pin must be shorted. Reset pin is connected to VCC. The output of 555 is taken at pin3 which is in the form of square wave and is then fed to lighting circuit which glows when output is high and stops when it becomes low; there by producing pattern of blinking lights. By varying the value of R1, R2 and C1 square waves of different time periods can be obtained. 🔗 External reference