Digital Stop Watch and Digital Timer Circuit
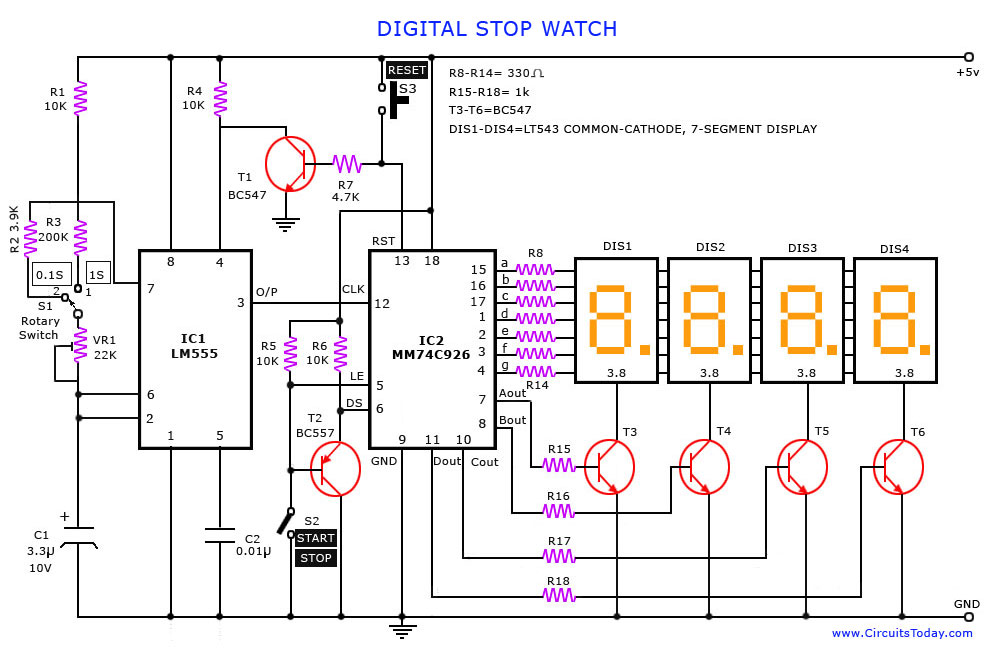
A digital stopwatch or digital timer circuit schematic is constructed using the timer IC LM555 and the 4-digit counter IC MM74C926, which is paired with a multiplexed 7-segment LED display.
The digital stopwatch circuit utilizes the LM555 timer IC configured in astable mode to generate a continuous clock pulse. The frequency of this pulse can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer. This clock pulse serves as the timing reference for the circuit, enabling it to count time intervals accurately.
The MM74C926 is a 4-digit counter IC that counts the pulses generated by the LM555 timer. It is designed to handle binary-coded decimal (BCD) counting, allowing it to display numbers from 0 to 9999. The output from the MM74C926 is connected to a multiplexed 7-segment LED display, which visually represents the counted time.
The multiplexing technique is employed to reduce the number of required pins and to simplify the circuit design. Each segment of the display is controlled by a common control line, which is switched rapidly to create the illusion of a steady display. The circuit includes additional components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure the proper functioning of the timer and counter ICs.
In summary, this digital stopwatch circuit effectively combines the LM555 timer and the MM74C926 counter to provide a user-friendly timing solution, displaying elapsed time on a multiplexed 7-segment LED display.A digital stop watch or digital timer circuit schematic built around timer IC LM555 and 4-digit counter IC MM74C926 with multiplexed 7-segment LED display.. 🔗 External reference
The digital stopwatch circuit utilizes the LM555 timer IC configured in astable mode to generate a continuous clock pulse. The frequency of this pulse can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer. This clock pulse serves as the timing reference for the circuit, enabling it to count time intervals accurately.
The MM74C926 is a 4-digit counter IC that counts the pulses generated by the LM555 timer. It is designed to handle binary-coded decimal (BCD) counting, allowing it to display numbers from 0 to 9999. The output from the MM74C926 is connected to a multiplexed 7-segment LED display, which visually represents the counted time.
The multiplexing technique is employed to reduce the number of required pins and to simplify the circuit design. Each segment of the display is controlled by a common control line, which is switched rapidly to create the illusion of a steady display. The circuit includes additional components such as resistors and capacitors to ensure the proper functioning of the timer and counter ICs.
In summary, this digital stopwatch circuit effectively combines the LM555 timer and the MM74C926 counter to provide a user-friendly timing solution, displaying elapsed time on a multiplexed 7-segment LED display.A digital stop watch or digital timer circuit schematic built around timer IC LM555 and 4-digit counter IC MM74C926 with multiplexed 7-segment LED display.. 🔗 External reference