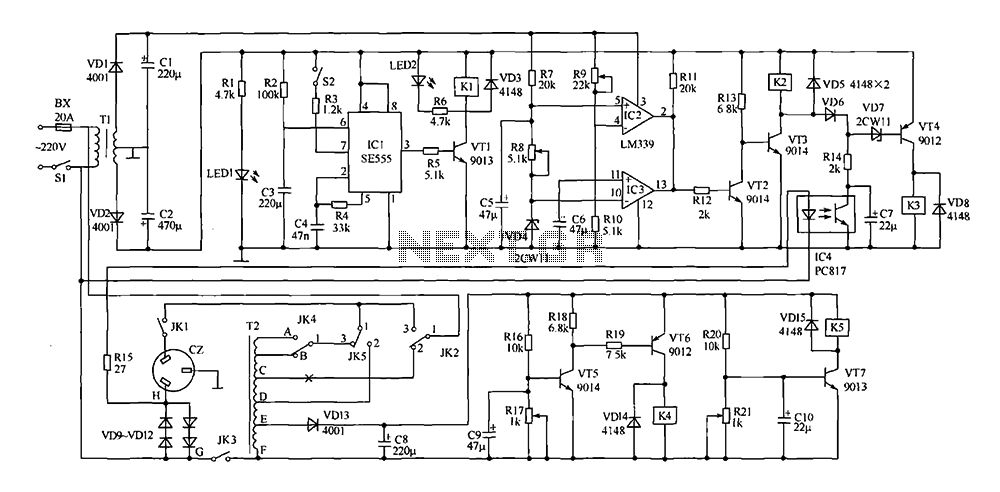
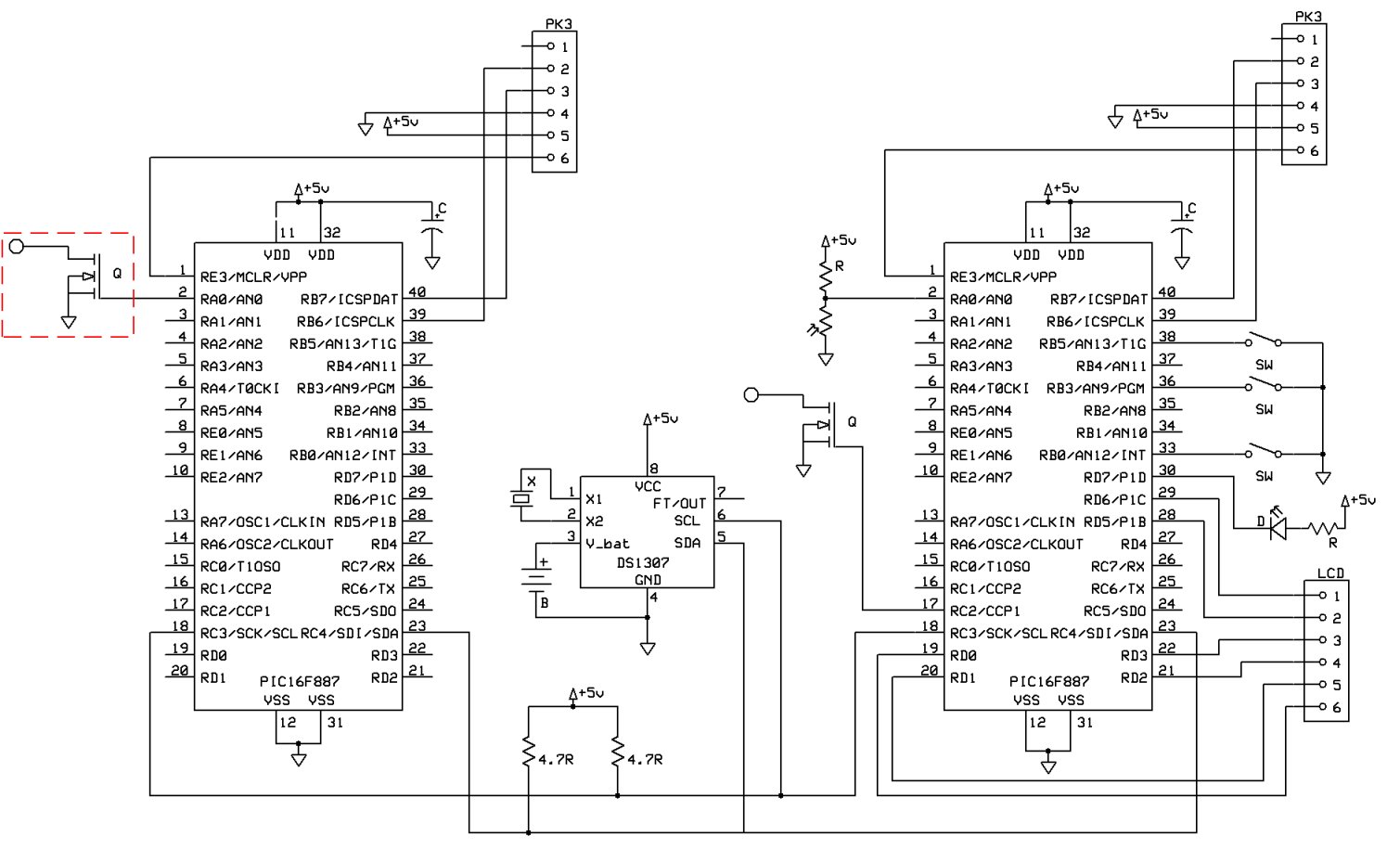
Circuit of RIIA phono pre-amplifier op-27
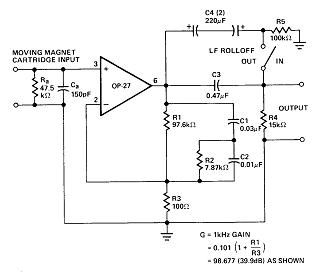
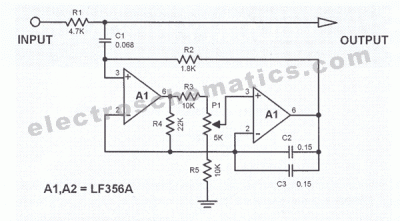
The circuit contributes 3.2 nV/√Hz of voltage noise and 0.45 pA/√Hz of current noise. To minimize noise from other sources, resistor R3 is configured to 100 ohms, resulting in an additional voltage noise of only 1.3 nV/√Hz. Resistors R1, R2, C1, and C@ form a highly precise RIAA network using standard components, providing the necessary time constants of 3180 µs, 318 µs, and 75 µs. For initial equalization and stability, metal-film resistors and film capacitors made of polystyrene or polypropylene are recommended. Capacitor C3 and resistor R4 create a simple -6 dB/octave filter with a cutoff frequency of 22 Hz. This circuit is capable of maintaining very low distortion at the input signal, typically below 0.01%. At 3V of total harmonic output, the produced distortion is less than 0.03% at frequencies above 20 kHz.
The described circuit is a sophisticated audio processing unit designed to ensure high fidelity and minimal noise interference. The low voltage and current noise specifications indicate a high level of precision in component selection and circuit design. The choice of 100-ohm resistor R3 effectively reduces additional noise, demonstrating a thoughtful approach to noise management.
The RIAA network formed by resistors R1, R2 and capacitors C1 and C@ is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of audio signal reproduction. The specified time constants of 3180 µs, 318 µs, and 75 µs are indicative of the circuit's ability to accurately process audio signals across a wide frequency range, ensuring that the bass, midrange, and treble frequencies are reproduced correctly.
The use of metal-film resistors and film capacitors made from polystyrene or polypropylene is a critical design choice that enhances the circuit's stability and equalization characteristics. These components are known for their low noise and high stability, which contribute to the overall performance of the circuit.
The filter created by capacitor C3 and resistor R4 is designed to attenuate frequencies above 22 Hz, effectively reducing unwanted low-frequency noise and ensuring that the audio signal remains clear and defined. The -6 dB/octave slope indicates a gradual roll-off, minimizing phase distortion and maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The circuit's performance is impressive, with distortion levels below 0.01% at the input and less than 0.03% at the output when operating at 3V and frequencies above 20 kHz. This low distortion is essential for high-quality audio applications, making the circuit suitable for professional audio equipment where clarity and fidelity are paramount. Overall, the design reflects a comprehensive understanding of audio electronics, optimizing both performance and reliability.He only contributes with 3. 2nV/ HZ of noise tension and 0. 45pA/ HZ of current noise to the circuit. To minimize the noise of other sources, R3 it is configured for 100 ©. That generates tension of noise additional of only 1. 3nV/ HZ. R1, R2, c1, and c @ form a net RIAA of a lot of precision with standard components supplying the necessary constant of time of 3180, 318 and 75 µsec. For initial equalization and stability, resistors metal-film and capacitors of film of polystyrene or polypropylene are recommended. Capacitor C3 and resistor R4 forms a simple filter of -6dB for octave, with cut to 22Hz. That circuit is capable of very low distortion on the entrance sign, usually below 0. 01%. To 3v of total harmonic exit produced distortion is smaller than 0. 03% in the frequencies above 20KHZ. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a sophisticated audio processing unit designed to ensure high fidelity and minimal noise interference. The low voltage and current noise specifications indicate a high level of precision in component selection and circuit design. The choice of 100-ohm resistor R3 effectively reduces additional noise, demonstrating a thoughtful approach to noise management.
The RIAA network formed by resistors R1, R2 and capacitors C1 and C@ is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of audio signal reproduction. The specified time constants of 3180 µs, 318 µs, and 75 µs are indicative of the circuit's ability to accurately process audio signals across a wide frequency range, ensuring that the bass, midrange, and treble frequencies are reproduced correctly.
The use of metal-film resistors and film capacitors made from polystyrene or polypropylene is a critical design choice that enhances the circuit's stability and equalization characteristics. These components are known for their low noise and high stability, which contribute to the overall performance of the circuit.
The filter created by capacitor C3 and resistor R4 is designed to attenuate frequencies above 22 Hz, effectively reducing unwanted low-frequency noise and ensuring that the audio signal remains clear and defined. The -6 dB/octave slope indicates a gradual roll-off, minimizing phase distortion and maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The circuit's performance is impressive, with distortion levels below 0.01% at the input and less than 0.03% at the output when operating at 3V and frequencies above 20 kHz. This low distortion is essential for high-quality audio applications, making the circuit suitable for professional audio equipment where clarity and fidelity are paramount. Overall, the design reflects a comprehensive understanding of audio electronics, optimizing both performance and reliability.He only contributes with 3. 2nV/ HZ of noise tension and 0. 45pA/ HZ of current noise to the circuit. To minimize the noise of other sources, R3 it is configured for 100 ©. That generates tension of noise additional of only 1. 3nV/ HZ. R1, R2, c1, and c @ form a net RIAA of a lot of precision with standard components supplying the necessary constant of time of 3180, 318 and 75 µsec. For initial equalization and stability, resistors metal-film and capacitors of film of polystyrene or polypropylene are recommended. Capacitor C3 and resistor R4 forms a simple filter of -6dB for octave, with cut to 22Hz. That circuit is capable of very low distortion on the entrance sign, usually below 0. 01%. To 3v of total harmonic exit produced distortion is smaller than 0. 03% in the frequencies above 20KHZ. 🔗 External reference