807 Tube Triode Connected
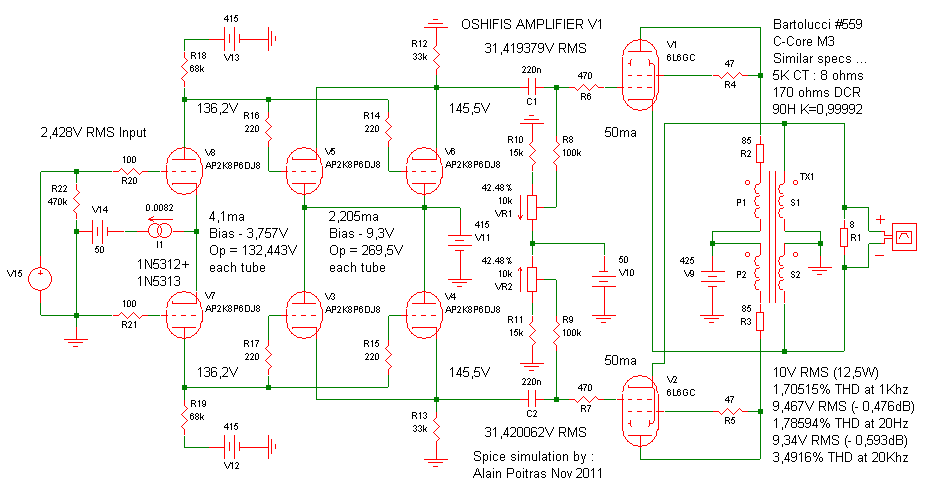
This is an effective amplifier design that is challenging to enhance. The results validate the 6DJ8 and 6L6GC Spice models, as the 6L6GC and 807 exhibit similar characteristics, yielding results closely aligned with the schematic. Utilizing the 1N5312 and 1N5313 diodes as a current limiter for the phase splitter current mirror is a sound approach; however, the absence of their Spice models necessitated the use of the built-in SIMetrix current source, which performs equivalently. It is advisable to address this matter promptly, considering the high cost of the 6DJ8 tubes. The operational point of the phase splitter tubes appears satisfactory, leading to the creation of a revised version with a closely matched operational point for the driver, maintaining a safe Va below 130V. Modifications include replacing the 33K cathode resistors with 18K (R12 and R13) and adding two 4.7K 2W resistors (R23 and R24) along with a 47uF filter capacitor (C3) to achieve a 268.8V supply for the driver tubes. While this adjustment introduces slightly more distortion, it is unlikely to be perceptible. An alternative enhancement involves employing adjustable current mirrors for the plates using a high-voltage TO220 DN2540 power depletion MOSFET as a current limiter. This modification reduces distortion and increases gain, remaining cost-effective, as the DN2540 is priced around $2.50 and has a long lifespan. In contrast, replacing four 6DJ8 drivers incurs a cost exceeding $100. The phase splitter requires a supply of approximately 200V or slightly more if needed, allowing for an adequately filtered supply for this stage. A 48V headroom is maintained for signals up to 34V RMS plus 15.8V for the DN2540 Vds, which is ample. Providing a small heatsink for each MOSFET can help manage heat dissipation.
The amplifier circuit comprises several key components that work together to achieve optimal performance. The input stage typically includes the 6DJ8 tubes configured as a differential amplifier. These tubes are known for their low noise and high gain characteristics, making them ideal for audio applications. The phase splitter configuration allows for the conversion of a single-ended input signal into a balanced output, which is essential for driving the push-pull stage effectively.
The inclusion of the 1N5312 and 1N5313 diodes as current limiters in the phase splitter enhances the stability of the circuit by preventing excessive current flow that could damage the tubes. The SIMetrix current source serves as an adequate substitute for the missing Spice model, ensuring that the design remains functional and reliable.
The proposed modifications to the resistor values and the addition of the filter capacitor are critical in optimizing the performance of the amplifier. By adjusting the cathode resistors from 33K to 18K, the biasing of the tubes is altered, allowing for improved linearity and reduced distortion. The introduction of the 4.7K resistors and the 47uF capacitor further stabilizes the voltage supply to the driver tubes, ensuring consistent operation under varying load conditions.
Utilizing the DN2540 MOSFET as an adjustable current mirror for the plates of the phase splitter presents a modern approach to enhancing amplifier performance. This component's high voltage rating and low on-resistance contribute to lower distortion levels and increased gain, making it a valuable addition to the design. The careful consideration of headroom and power supply design ensures that the amplifier can handle dynamic audio signals without clipping or distortion.
Overall, this amplifier design exemplifies a thoughtful integration of traditional tube technology with modern electronic components, resulting in a robust and high-performing audio amplifier suitable for various applications. This is a very nice amplifier design and it is very difficult to improve it. I am glad about the results because that's a very good way to verify my 6DJ8 and 6L6GC Spice models, like I tell you before, the 6L6GC and 807 have very close caracteristics and I get very close results to what you schematic said It is a really good idea to use the 1N5312 and 1N5313 diodes current limiter for the phase splitter current mirror but I don't have their Spice model so I just use the incorporated SIMetrix current source, it does exactly the same thing . This is something you should take care of as soon as possible because I know the 6DJ8 are very expensives ... The phase splitter tubes operation point look very good to me so I draw a corrected version with a close operation point for the driver too and a safe Va under 130V.
Like you can see, you just have to change the 33K cathode resistors for 18K (R12 and R13) and add two 4,7K 2W (or more) resistor (R23 and R24) and a 47uF filter capacitor (C3) to get a 268,8V supply for the driver tubes. There is just a little bit more distortion this way but nobody will notice any differences for sure. Of course, the distortion is a little bit higher but it is so simple ... However, there is a simple way to improve it, since you already use a current mirror for the splitter cathodes, why not use adjustable ones for their plates, using a good "TO220 high voltage DN2540 power depletion MOSFET" as current limiter ...
It improve the distortion and the gain ... It is still very simple and cheap, a DN2540 cost about 2,50$ and last for life but each time you replace your four 6DJ8 drivers, it cost you over 100$, think about it ... A phase splitter like that just need a 200V supply or a little more if necessary so you can get a better filtered supply for this stage.
I left a 48V "headroom" for a signal up to 34V RMS plus 15,8V for the DN2540 Vds, it is plenty enough, just provide a very small heatsink for each of them will help if they get too hot. 🔗 External reference
The amplifier circuit comprises several key components that work together to achieve optimal performance. The input stage typically includes the 6DJ8 tubes configured as a differential amplifier. These tubes are known for their low noise and high gain characteristics, making them ideal for audio applications. The phase splitter configuration allows for the conversion of a single-ended input signal into a balanced output, which is essential for driving the push-pull stage effectively.
The inclusion of the 1N5312 and 1N5313 diodes as current limiters in the phase splitter enhances the stability of the circuit by preventing excessive current flow that could damage the tubes. The SIMetrix current source serves as an adequate substitute for the missing Spice model, ensuring that the design remains functional and reliable.
The proposed modifications to the resistor values and the addition of the filter capacitor are critical in optimizing the performance of the amplifier. By adjusting the cathode resistors from 33K to 18K, the biasing of the tubes is altered, allowing for improved linearity and reduced distortion. The introduction of the 4.7K resistors and the 47uF capacitor further stabilizes the voltage supply to the driver tubes, ensuring consistent operation under varying load conditions.
Utilizing the DN2540 MOSFET as an adjustable current mirror for the plates of the phase splitter presents a modern approach to enhancing amplifier performance. This component's high voltage rating and low on-resistance contribute to lower distortion levels and increased gain, making it a valuable addition to the design. The careful consideration of headroom and power supply design ensures that the amplifier can handle dynamic audio signals without clipping or distortion.
Overall, this amplifier design exemplifies a thoughtful integration of traditional tube technology with modern electronic components, resulting in a robust and high-performing audio amplifier suitable for various applications. This is a very nice amplifier design and it is very difficult to improve it. I am glad about the results because that's a very good way to verify my 6DJ8 and 6L6GC Spice models, like I tell you before, the 6L6GC and 807 have very close caracteristics and I get very close results to what you schematic said It is a really good idea to use the 1N5312 and 1N5313 diodes current limiter for the phase splitter current mirror but I don't have their Spice model so I just use the incorporated SIMetrix current source, it does exactly the same thing . This is something you should take care of as soon as possible because I know the 6DJ8 are very expensives ... The phase splitter tubes operation point look very good to me so I draw a corrected version with a close operation point for the driver too and a safe Va under 130V.
Like you can see, you just have to change the 33K cathode resistors for 18K (R12 and R13) and add two 4,7K 2W (or more) resistor (R23 and R24) and a 47uF filter capacitor (C3) to get a 268,8V supply for the driver tubes. There is just a little bit more distortion this way but nobody will notice any differences for sure. Of course, the distortion is a little bit higher but it is so simple ... However, there is a simple way to improve it, since you already use a current mirror for the splitter cathodes, why not use adjustable ones for their plates, using a good "TO220 high voltage DN2540 power depletion MOSFET" as current limiter ...
It improve the distortion and the gain ... It is still very simple and cheap, a DN2540 cost about 2,50$ and last for life but each time you replace your four 6DJ8 drivers, it cost you over 100$, think about it ... A phase splitter like that just need a 200V supply or a little more if necessary so you can get a better filtered supply for this stage.
I left a 48V "headroom" for a signal up to 34V RMS plus 15,8V for the DN2540 Vds, it is plenty enough, just provide a very small heatsink for each of them will help if they get too hot. 🔗 External reference