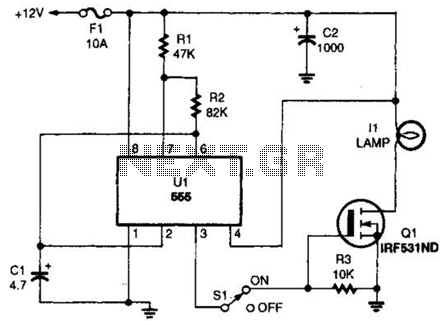
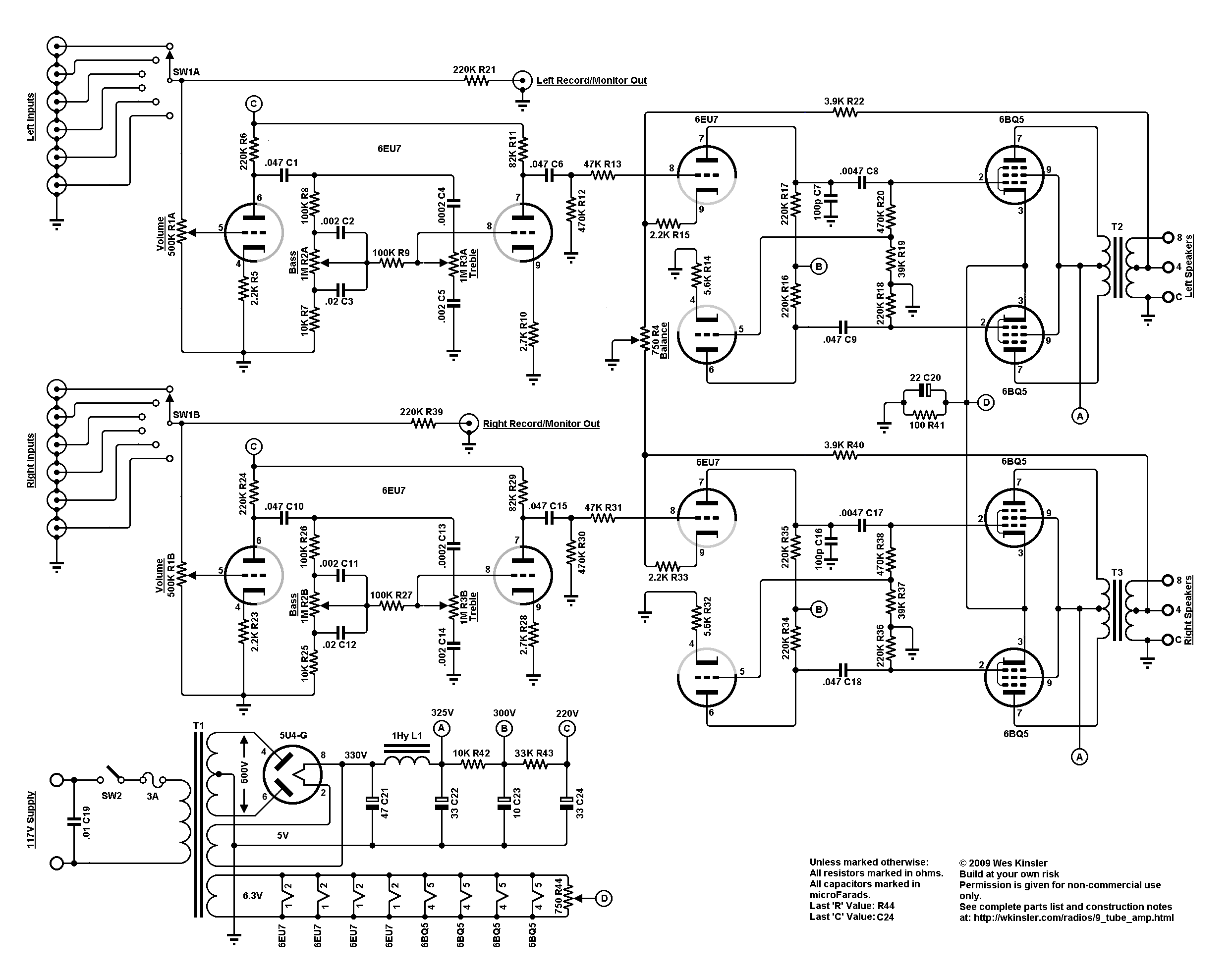
transistor power amplifier circuit diagram
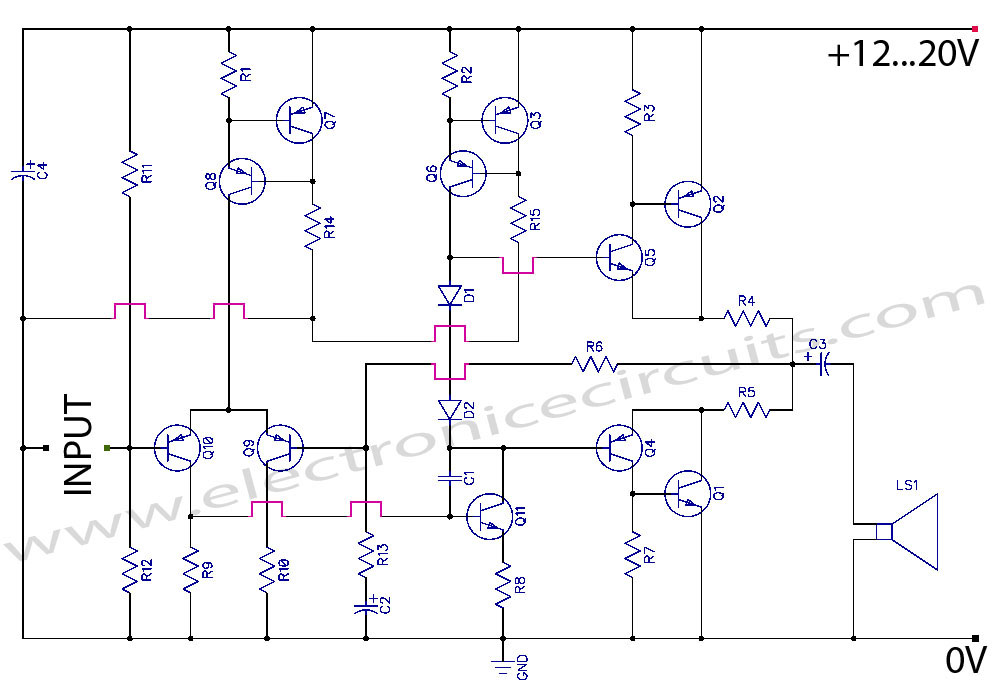
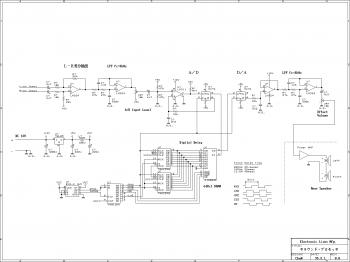
Discrete Class AB Transistor Audio Power Amplifier Circuit Diagram. This is a Class AB transistor power amplifier. It is a simple amplifier to...
A Class AB transistor audio power amplifier is designed to provide high-quality amplification for audio signals while maintaining efficiency. This circuit typically employs a complementary push-pull configuration, using both NPN and PNP transistors to enhance performance and reduce distortion.
The circuit consists of several key components: input capacitors, biasing resistors, feedback network, and output transistors. The input stage often includes a capacitor to block DC while allowing AC audio signals to pass through. This is followed by a biasing network that sets the operating point of the transistors, ensuring they operate in the linear region for optimal audio fidelity.
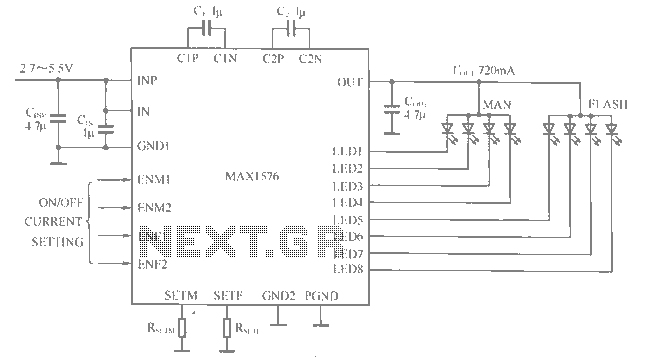
The complementary output stage, made up of NPN and PNP transistors, allows the amplifier to handle both halves of the audio waveform efficiently. This configuration minimizes crossover distortion, which is common in simpler Class B designs. The output transistors are typically driven by a driver stage that provides the necessary gain and current to drive the load, usually a speaker.
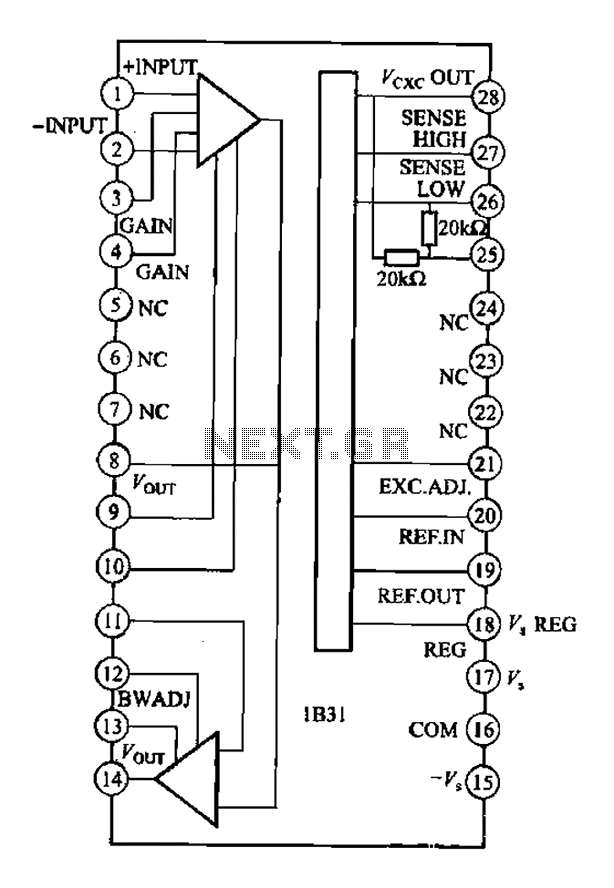
Feedback is employed in the circuit to improve linearity and reduce harmonic distortion. A portion of the output signal is fed back to the input stage, allowing for real-time adjustments to the gain and improving overall stability.
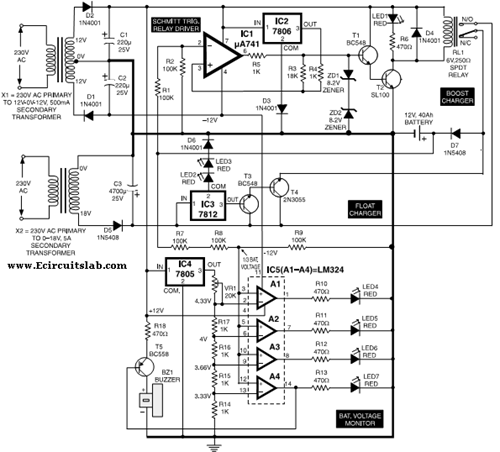
Power supply considerations are also critical in Class AB amplifiers. The circuit requires a dual power supply, providing both positive and negative voltages to the output stage. This ensures that the amplifier can reproduce the full range of audio signals without clipping.
Thermal management is another important aspect, as the output transistors can generate significant heat during operation. Heat sinks are often used to dissipate this heat and maintain the reliability of the amplifier.
Overall, the discrete Class AB transistor audio power amplifier is a versatile and efficient solution for audio amplification, providing a good balance between sound quality and power efficiency.Discrete Class AB Transistor Audio Power Amplifier Circuit Diagram This is a class AB transistor power amplifier. It is a simple amplifier to.. 🔗 External reference
A Class AB transistor audio power amplifier is designed to provide high-quality amplification for audio signals while maintaining efficiency. This circuit typically employs a complementary push-pull configuration, using both NPN and PNP transistors to enhance performance and reduce distortion.
The circuit consists of several key components: input capacitors, biasing resistors, feedback network, and output transistors. The input stage often includes a capacitor to block DC while allowing AC audio signals to pass through. This is followed by a biasing network that sets the operating point of the transistors, ensuring they operate in the linear region for optimal audio fidelity.
The complementary output stage, made up of NPN and PNP transistors, allows the amplifier to handle both halves of the audio waveform efficiently. This configuration minimizes crossover distortion, which is common in simpler Class B designs. The output transistors are typically driven by a driver stage that provides the necessary gain and current to drive the load, usually a speaker.
Feedback is employed in the circuit to improve linearity and reduce harmonic distortion. A portion of the output signal is fed back to the input stage, allowing for real-time adjustments to the gain and improving overall stability.
Power supply considerations are also critical in Class AB amplifiers. The circuit requires a dual power supply, providing both positive and negative voltages to the output stage. This ensures that the amplifier can reproduce the full range of audio signals without clipping.
Thermal management is another important aspect, as the output transistors can generate significant heat during operation. Heat sinks are often used to dissipate this heat and maintain the reliability of the amplifier.
Overall, the discrete Class AB transistor audio power amplifier is a versatile and efficient solution for audio amplification, providing a good balance between sound quality and power efficiency.Discrete Class AB Transistor Audio Power Amplifier Circuit Diagram This is a class AB transistor power amplifier. It is a simple amplifier to.. 🔗 External reference