Cmos crystal oscillator
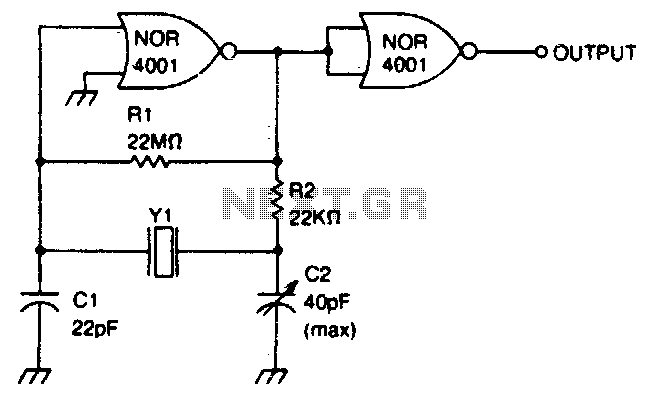
This circuit operates within a frequency range of 0 MHz to 2 MHz. The frequency can be finely adjusted to a specific value using the trimmer capacitor C2. Additionally, the second NOR gate functions as an output buffer.
The circuit design includes a frequency generator capable of producing signals within the specified range of 0 MHz to 2 MHz. The primary component responsible for frequency adjustment is the trimmer capacitor C2, which allows for precise tuning of the output frequency. This feature is crucial for applications requiring specific frequency outputs, such as in communication systems or signal processing.
The inclusion of a second NOR gate as an output buffer enhances the circuit's performance by isolating the frequency generation stage from the load. This buffering action prevents loading effects that could alter the frequency or amplitude of the output signal. The NOR gate configuration also provides a robust output stage, ensuring that the circuit can drive subsequent stages effectively without distortion.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various electronic devices where adjustable frequency signals are necessary. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it suitable for educational purposes as well as in professional environments where precise frequency control is required. The careful selection of components, including the trimmer capacitor and NOR gates, contributes to the overall reliability and functionality of the circuit.This circuit has a frequency range of 0 MHz to 2 MHz. Frequency can be adjusted to a precise value with trimmer capacitor C2 The second NOR gate serves as an output buffer. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design includes a frequency generator capable of producing signals within the specified range of 0 MHz to 2 MHz. The primary component responsible for frequency adjustment is the trimmer capacitor C2, which allows for precise tuning of the output frequency. This feature is crucial for applications requiring specific frequency outputs, such as in communication systems or signal processing.
The inclusion of a second NOR gate as an output buffer enhances the circuit's performance by isolating the frequency generation stage from the load. This buffering action prevents loading effects that could alter the frequency or amplitude of the output signal. The NOR gate configuration also provides a robust output stage, ensuring that the circuit can drive subsequent stages effectively without distortion.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various electronic devices where adjustable frequency signals are necessary. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it suitable for educational purposes as well as in professional environments where precise frequency control is required. The careful selection of components, including the trimmer capacitor and NOR gates, contributes to the overall reliability and functionality of the circuit.This circuit has a frequency range of 0 MHz to 2 MHz. Frequency can be adjusted to a precise value with trimmer capacitor C2 The second NOR gate serves as an output buffer. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713