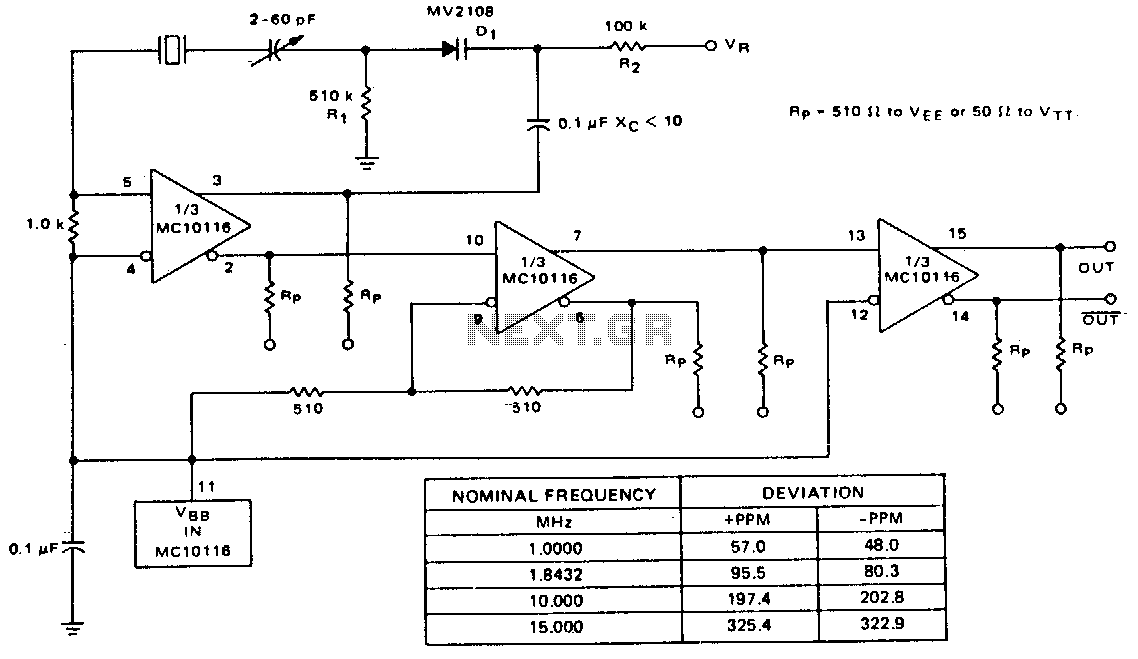
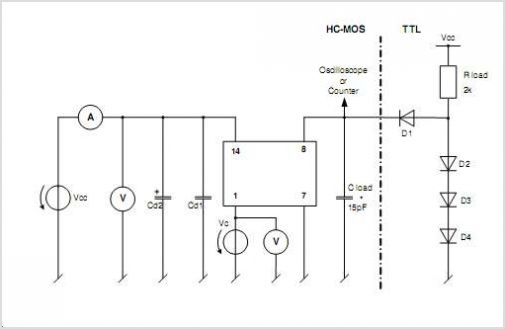
Crystal checker
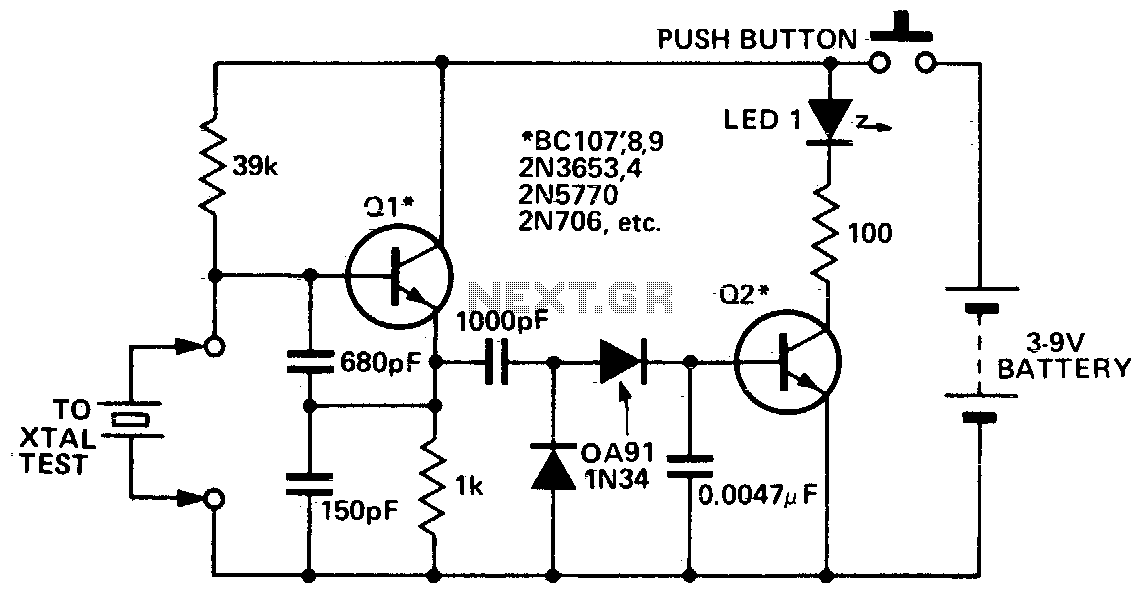
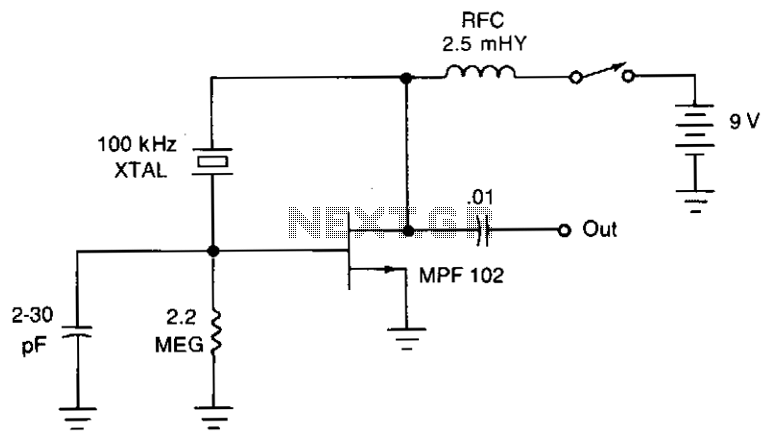
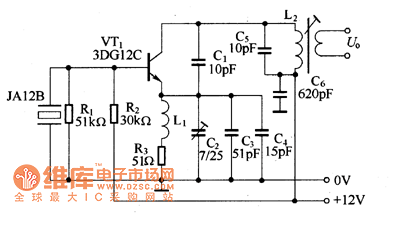
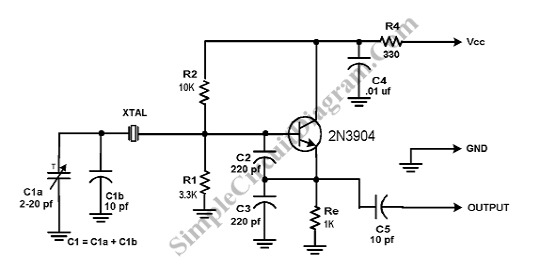
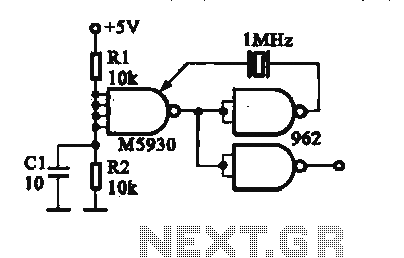
This circuit is designed to check fundamental oscillations. When Q2 conducts, the LED lights up. It operates with A3 HF crystals on a "Go-No-Go" basis. An untuned or 6V, 40mA bulb can be used in place of the Colpitts oscillator that drives a voltage multiplier, rectifier, and current amplifier.
This circuit functions primarily as an oscillator and signal verification tool, utilizing a Colpitts oscillator configuration to generate oscillations at a desired frequency. The inclusion of Q2, which acts as a switching transistor, is critical for controlling the LED indicator. When the circuit is correctly oscillating, Q2 is activated, allowing current to flow through the LED, thereby providing a visual indication of the circuit's operational status.
The circuit can be tested using A3 HF crystals, which are designed for high-frequency applications. The "Go-No-Go" testing approach implies that the circuit will indicate whether the crystal is functioning properly (Go) or not (No-Go). The use of an untuned bulb rated at 6V and 40mA is a practical alternative for applications where a more straightforward visual indication is sufficient, replacing the LED for broader visibility.
The Colpitts oscillator's output is fed into a voltage multiplier circuit, which increases the output voltage suitable for driving the LED or bulb. This voltage multiplier is essential for ensuring that the LED receives enough voltage to illuminate effectively, especially when using lower voltage sources. Additionally, the rectifier in the circuit converts the AC oscillations produced by the oscillator into DC, which is necessary for powering the LED or bulb reliably.
In summary, this circuit serves as an efficient method for testing the operational integrity of high-frequency crystals, providing both visual feedback and adaptability for different output indicators.Use this circuit for checking fundamental oscillates, Q2 conducts and the LED lights. A3 HF crystals on a "Go-No-Go" basis. An untuned or 6V, 40mA bulb could be substituted for the Colpitts oscillator drives a voltage multiplier LED rectifier and a current amplifier. If the crystal.
This circuit functions primarily as an oscillator and signal verification tool, utilizing a Colpitts oscillator configuration to generate oscillations at a desired frequency. The inclusion of Q2, which acts as a switching transistor, is critical for controlling the LED indicator. When the circuit is correctly oscillating, Q2 is activated, allowing current to flow through the LED, thereby providing a visual indication of the circuit's operational status.
The circuit can be tested using A3 HF crystals, which are designed for high-frequency applications. The "Go-No-Go" testing approach implies that the circuit will indicate whether the crystal is functioning properly (Go) or not (No-Go). The use of an untuned bulb rated at 6V and 40mA is a practical alternative for applications where a more straightforward visual indication is sufficient, replacing the LED for broader visibility.
The Colpitts oscillator's output is fed into a voltage multiplier circuit, which increases the output voltage suitable for driving the LED or bulb. This voltage multiplier is essential for ensuring that the LED receives enough voltage to illuminate effectively, especially when using lower voltage sources. Additionally, the rectifier in the circuit converts the AC oscillations produced by the oscillator into DC, which is necessary for powering the LED or bulb reliably.
In summary, this circuit serves as an efficient method for testing the operational integrity of high-frequency crystals, providing both visual feedback and adaptability for different output indicators.Use this circuit for checking fundamental oscillates, Q2 conducts and the LED lights. A3 HF crystals on a "Go-No-Go" basis. An untuned or 6V, 40mA bulb could be substituted for the Colpitts oscillator drives a voltage multiplier LED rectifier and a current amplifier. If the crystal.