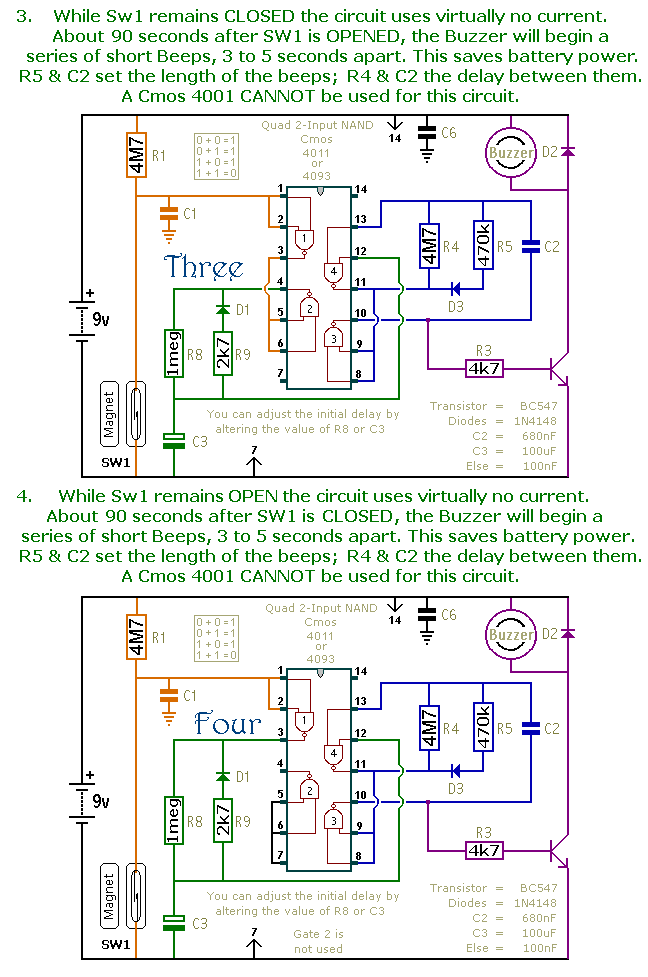
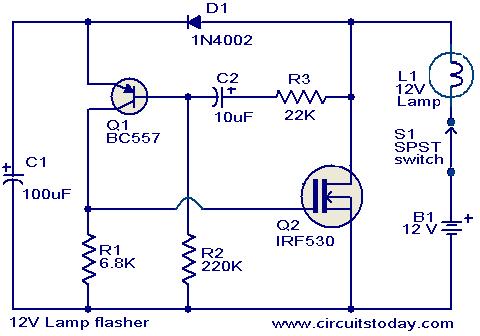
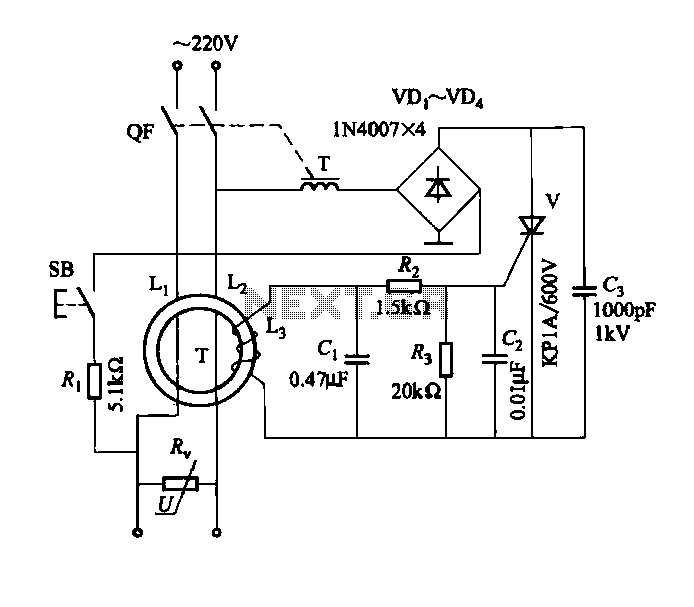
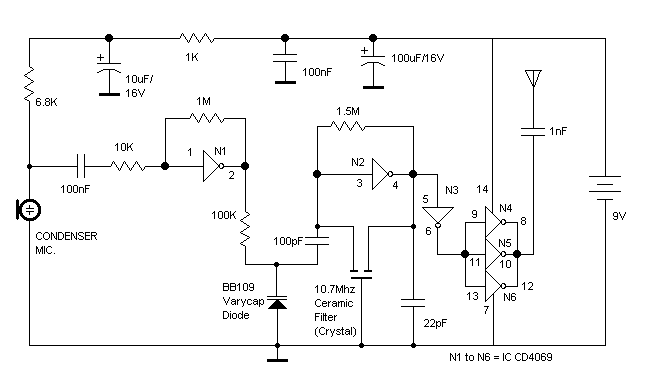
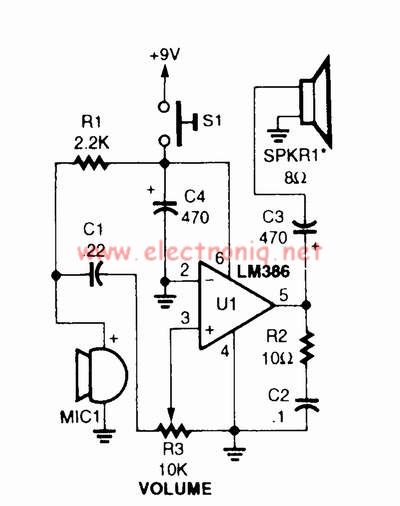
Cmos Piezo Driver Circuit
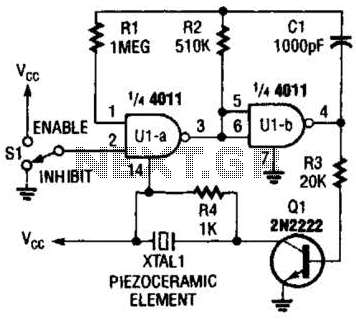
A CMOS gate and transistor buffer can be used as an effective driver for a piezoelectric transducer.
The use of a CMOS gate combined with a transistor buffer offers a robust solution for driving piezoelectric transducers. CMOS technology, known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity, provides a stable voltage level that can effectively control the operation of the transducer. The transistor buffer serves to amplify the signal generated by the CMOS gate, ensuring that the output can drive the transducer with sufficient current and voltage levels.
In a typical configuration, the CMOS gate can be employed to generate a digital signal from a microcontroller or other digital logic sources. This signal is then fed into the base of the transistor buffer, which may be configured as a common-emitter or common-collector amplifier depending on the required output characteristics. The transistor buffer amplifies the signal, providing the necessary drive capability to activate the piezoelectric transducer.
The piezoelectric transducer operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa, making it suitable for applications such as sound generation, vibration, and sensing. The combination of the CMOS gate and transistor buffer not only ensures that the transducer receives the appropriate drive signals but also enhances the overall efficiency and performance of the system.
When designing this circuit, attention must be paid to the specifications of the piezoelectric transducer, including its impedance and required drive voltage. Additionally, the choice of transistor type (BJT or MOSFET) can influence the efficiency and speed of the driving circuit. Proper biasing and protection mechanisms, such as diodes, may also be incorporated to safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes and ensure reliable operation. Overall, this configuration presents a practical approach for effectively driving piezoelectric devices in various electronic applications. A CMOS-gate and transistor buffer can be used as an effective driver for a piezoelectric transducer. 🔗 External reference
The use of a CMOS gate combined with a transistor buffer offers a robust solution for driving piezoelectric transducers. CMOS technology, known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity, provides a stable voltage level that can effectively control the operation of the transducer. The transistor buffer serves to amplify the signal generated by the CMOS gate, ensuring that the output can drive the transducer with sufficient current and voltage levels.
In a typical configuration, the CMOS gate can be employed to generate a digital signal from a microcontroller or other digital logic sources. This signal is then fed into the base of the transistor buffer, which may be configured as a common-emitter or common-collector amplifier depending on the required output characteristics. The transistor buffer amplifies the signal, providing the necessary drive capability to activate the piezoelectric transducer.
The piezoelectric transducer operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa, making it suitable for applications such as sound generation, vibration, and sensing. The combination of the CMOS gate and transistor buffer not only ensures that the transducer receives the appropriate drive signals but also enhances the overall efficiency and performance of the system.
When designing this circuit, attention must be paid to the specifications of the piezoelectric transducer, including its impedance and required drive voltage. Additionally, the choice of transistor type (BJT or MOSFET) can influence the efficiency and speed of the driving circuit. Proper biasing and protection mechanisms, such as diodes, may also be incorporated to safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes and ensure reliable operation. Overall, this configuration presents a practical approach for effectively driving piezoelectric devices in various electronic applications. A CMOS-gate and transistor buffer can be used as an effective driver for a piezoelectric transducer. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713