12V Lamp flasher circuit
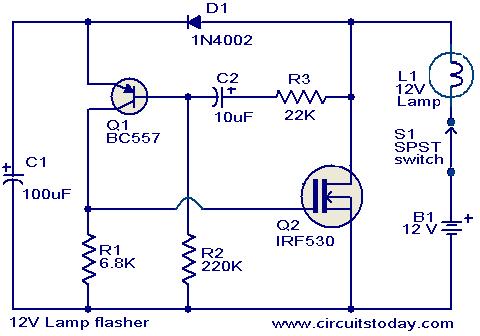
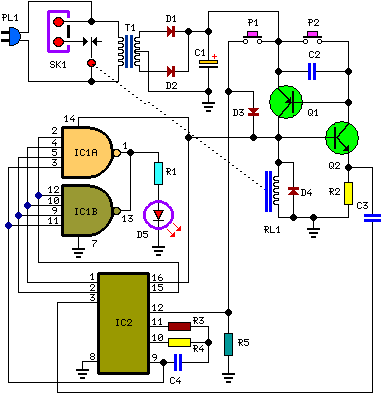
This circuit is a straightforward yet effective solution for flashing 12V lamps, particularly those utilized in automobiles. The flashing mechanism relies on transistor Q1 (BC557) and MOSFET Q2 (IRF530), with Q2 delivering the required drive for the lamp. The circuit can accommodate multiple bulbs, as long as the total load does not surpass 2 Watts.
The circuit operates by utilizing a BC557 transistor as a switching element, which is responsible for controlling the ON and OFF states of the circuit. The transistor is connected to a control circuit that dictates the flashing frequency, allowing for customizable blinking patterns. The IRF530 MOSFET is employed to handle higher current loads, providing efficient drive capability for the connected lamps.
In terms of component connections, the base of the BC557 transistor is typically connected to a resistor that limits the base current, ensuring that the transistor operates within its safe limits. The emitter is connected to the ground, while the collector is linked to the gate of the IRF530 MOSFET. The source of the MOSFET connects to the ground, and the drain is connected to the load, which in this case are the 12V lamps.
To ensure that the total load does not exceed 2 Watts, the circuit designer should calculate the number of bulbs based on their individual wattage ratings. For example, if using 1W bulbs, a maximum of two bulbs can be connected in parallel. Additionally, appropriate heat sinking may be required for the MOSFET, depending on the total current drawn by the lamps, to prevent thermal overload.
The circuit can be powered from a standard 12V automotive battery, making it suitable for various automotive applications. Overall, this design provides a reliable method for creating flashing light effects in vehicles, enhancing visibility and safety.Here is a simple yet powerful circuit that can be used for flashing 12V lamps especially that is used on automobiles. The flashing circuit is based on transistor Q1(BC557) and MOSFET Q2 (IRF530) where the Q2 provides the necessary drive for the lamp.
Any number of bulbs can be flashed using this circuit provided that the total load must not exceed 4 2 Watts. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a BC557 transistor as a switching element, which is responsible for controlling the ON and OFF states of the circuit. The transistor is connected to a control circuit that dictates the flashing frequency, allowing for customizable blinking patterns. The IRF530 MOSFET is employed to handle higher current loads, providing efficient drive capability for the connected lamps.
In terms of component connections, the base of the BC557 transistor is typically connected to a resistor that limits the base current, ensuring that the transistor operates within its safe limits. The emitter is connected to the ground, while the collector is linked to the gate of the IRF530 MOSFET. The source of the MOSFET connects to the ground, and the drain is connected to the load, which in this case are the 12V lamps.
To ensure that the total load does not exceed 2 Watts, the circuit designer should calculate the number of bulbs based on their individual wattage ratings. For example, if using 1W bulbs, a maximum of two bulbs can be connected in parallel. Additionally, appropriate heat sinking may be required for the MOSFET, depending on the total current drawn by the lamps, to prevent thermal overload.
The circuit can be powered from a standard 12V automotive battery, making it suitable for various automotive applications. Overall, this design provides a reliable method for creating flashing light effects in vehicles, enhancing visibility and safety.Here is a simple yet powerful circuit that can be used for flashing 12V lamps especially that is used on automobiles. The flashing circuit is based on transistor Q1(BC557) and MOSFET Q2 (IRF530) where the Q2 provides the necessary drive for the lamp.
Any number of bulbs can be flashed using this circuit provided that the total load must not exceed 4 2 Watts. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713