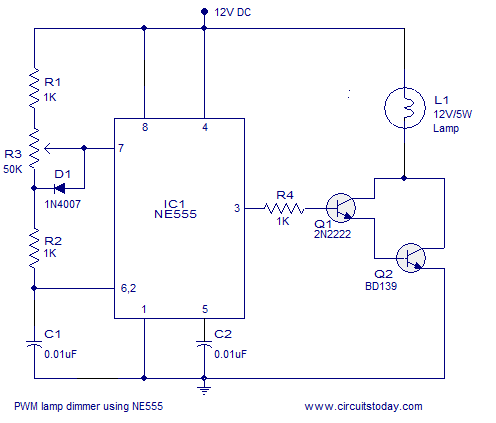
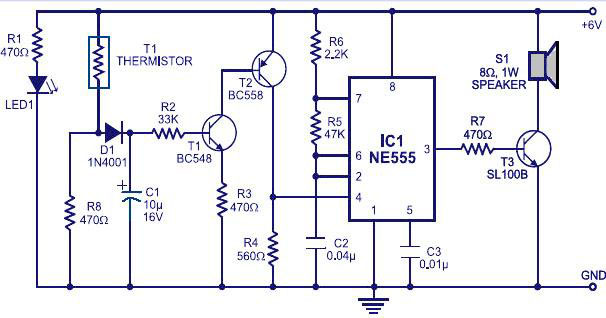
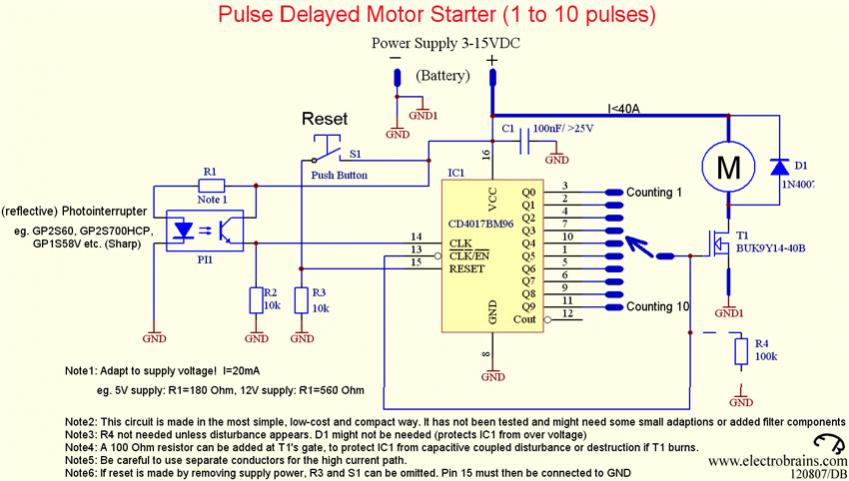
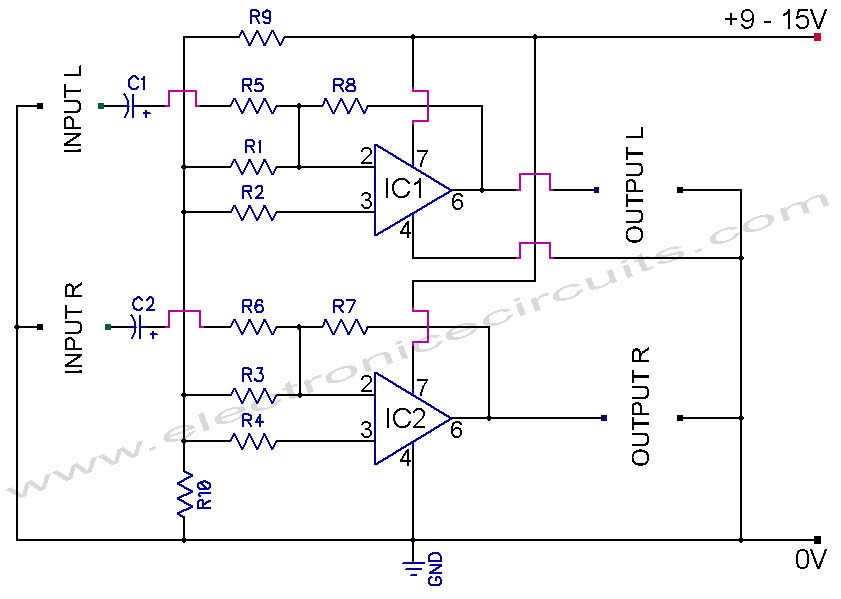
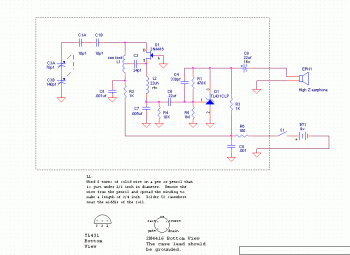
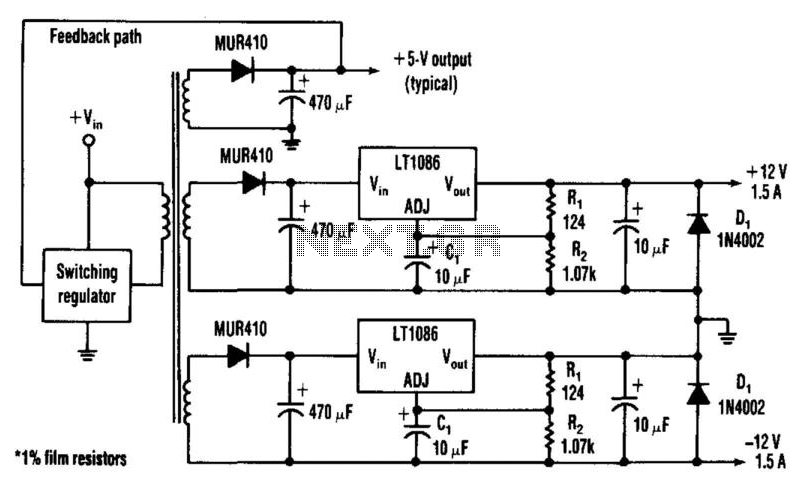
Common mode input voltage of the differential amplifier circuit diagram up l00V
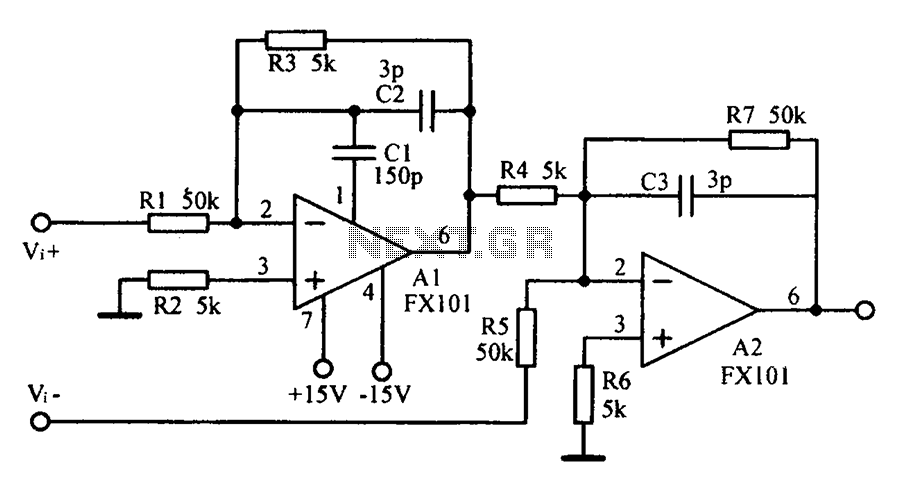
Common mode input voltage up to a difference of 100V enlarged circuit diagram.
The circuit diagram described features a design capable of handling a common mode input voltage with a differential range of up to 100V. Such a configuration is essential in applications where high voltage signals may be present, and it is crucial to maintain signal integrity while minimizing noise and interference.
In this circuit, the common mode voltage refers to the average voltage level present on both input lines, while the differential voltage is the voltage difference between these two lines. The ability to manage a common mode input voltage of 100V indicates that the circuit employs robust components designed to withstand high voltages without compromising performance.
Typically, this type of circuit may utilize instrumentation amplifiers or differential amplifiers that are specifically designed to reject common mode signals while amplifying the differential signal. Key components may include precision resistors, operational amplifiers, and possibly isolation techniques to ensure that the circuit operates safely and effectively under high voltage conditions.
In practical applications, such circuits are often found in industrial sensor systems, data acquisition systems, and communication devices where high-voltage signals need to be accurately measured or processed without distortion. Proper layout and shielding techniques are also critical in these designs to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure reliable operation. The enlarged circuit diagram would typically illustrate these components and their interconnections, providing a clear visual representation of the circuit's functionality. Common mode input voltage up to difference l00V enlarged circuit diagram:
The circuit diagram described features a design capable of handling a common mode input voltage with a differential range of up to 100V. Such a configuration is essential in applications where high voltage signals may be present, and it is crucial to maintain signal integrity while minimizing noise and interference.
In this circuit, the common mode voltage refers to the average voltage level present on both input lines, while the differential voltage is the voltage difference between these two lines. The ability to manage a common mode input voltage of 100V indicates that the circuit employs robust components designed to withstand high voltages without compromising performance.
Typically, this type of circuit may utilize instrumentation amplifiers or differential amplifiers that are specifically designed to reject common mode signals while amplifying the differential signal. Key components may include precision resistors, operational amplifiers, and possibly isolation techniques to ensure that the circuit operates safely and effectively under high voltage conditions.
In practical applications, such circuits are often found in industrial sensor systems, data acquisition systems, and communication devices where high-voltage signals need to be accurately measured or processed without distortion. Proper layout and shielding techniques are also critical in these designs to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure reliable operation. The enlarged circuit diagram would typically illustrate these components and their interconnections, providing a clear visual representation of the circuit's functionality. Common mode input voltage up to difference l00V enlarged circuit diagram: