Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit waveform sawtooth oscillator use blocking oscillator
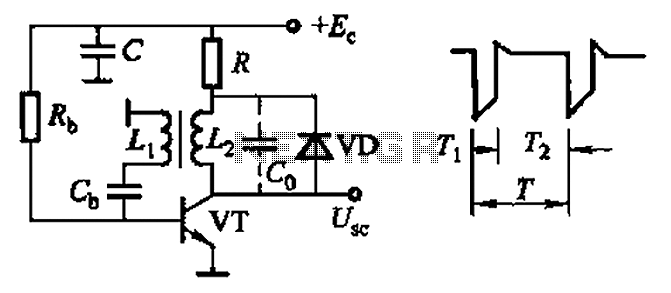
Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - sawtooth oscillator - use blocking oscillator
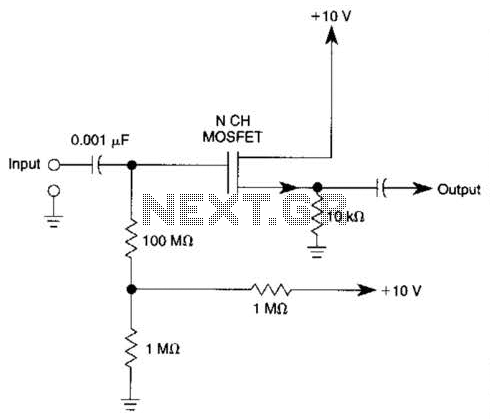
The sawtooth oscillator is a type of non-sinusoidal oscillator that generates a waveform characterized by a linear rise in voltage followed by a rapid drop. This waveform is commonly used in various applications, including signal generation, timing circuits, and audio synthesis. The sawtooth waveform is defined by its frequency and amplitude, which can be calculated using specific formulas.
In a typical sawtooth oscillator circuit, a blocking oscillator is employed to create the desired waveform. The blocking oscillator consists of a transistor or a similar active device, a feedback network, and timing components such as resistors and capacitors. The feedback network determines the charging and discharging time constants, which directly affect the frequency of the output waveform.
The frequency (f) of the sawtooth waveform can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (T1 + T2)
where T1 is the time it takes for the voltage to rise, and T2 is the time for the voltage to drop. The amplitude of the waveform is primarily determined by the supply voltage and the configuration of the circuit.
In practical implementations, additional components such as diodes may be included to improve the performance and stability of the oscillator. The output of the sawtooth oscillator can be used to drive other circuits or devices, making it a versatile component in electronic design. Overall, the sawtooth oscillator is a fundamental circuit that serves as a building block for more complex electronic systems. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - sawtooth oscillator - use blocking oscillator
The sawtooth oscillator is a type of non-sinusoidal oscillator that generates a waveform characterized by a linear rise in voltage followed by a rapid drop. This waveform is commonly used in various applications, including signal generation, timing circuits, and audio synthesis. The sawtooth waveform is defined by its frequency and amplitude, which can be calculated using specific formulas.
In a typical sawtooth oscillator circuit, a blocking oscillator is employed to create the desired waveform. The blocking oscillator consists of a transistor or a similar active device, a feedback network, and timing components such as resistors and capacitors. The feedback network determines the charging and discharging time constants, which directly affect the frequency of the output waveform.
The frequency (f) of the sawtooth waveform can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (T1 + T2)
where T1 is the time it takes for the voltage to rise, and T2 is the time for the voltage to drop. The amplitude of the waveform is primarily determined by the supply voltage and the configuration of the circuit.
In practical implementations, additional components such as diodes may be included to improve the performance and stability of the oscillator. The output of the sawtooth oscillator can be used to drive other circuits or devices, making it a versatile component in electronic design. Overall, the sawtooth oscillator is a fundamental circuit that serves as a building block for more complex electronic systems. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - sawtooth oscillator - use blocking oscillator
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713