Compact and easy joule ringer circuit
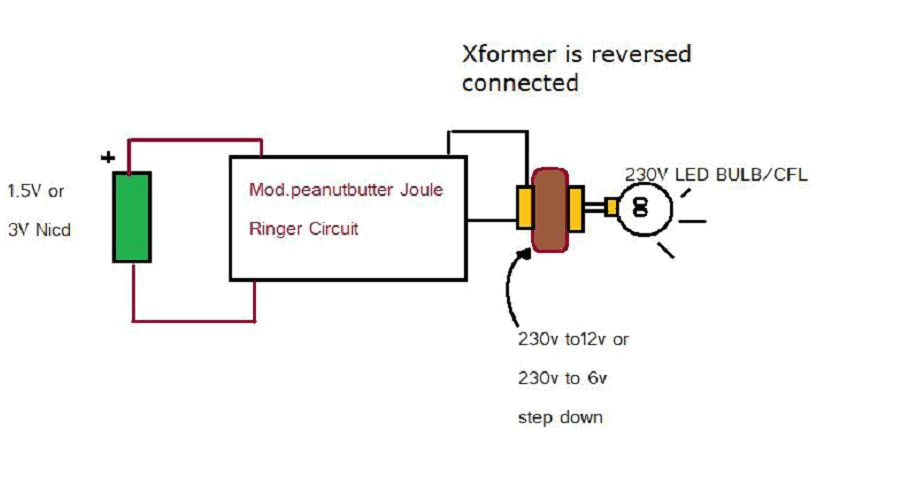
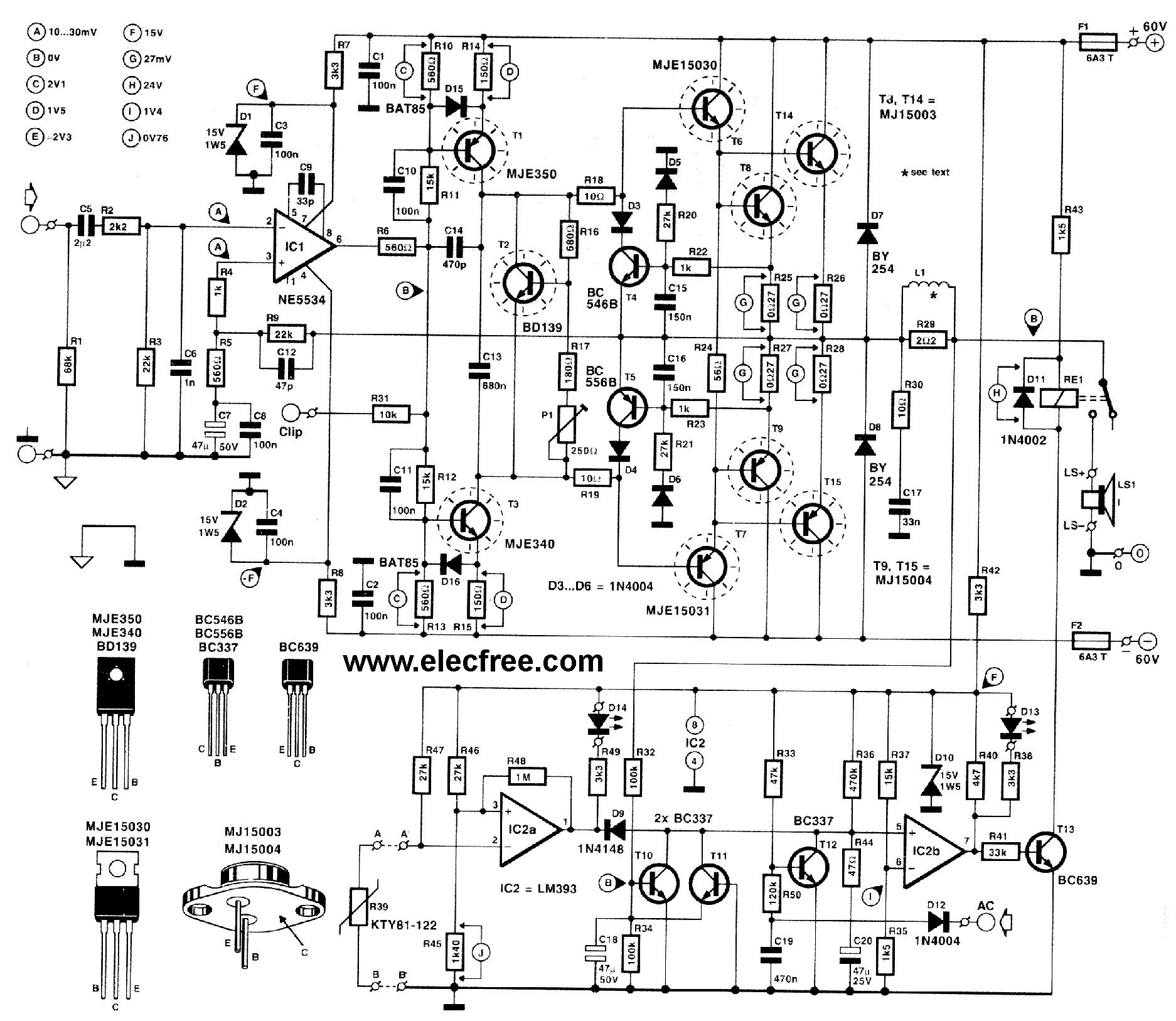
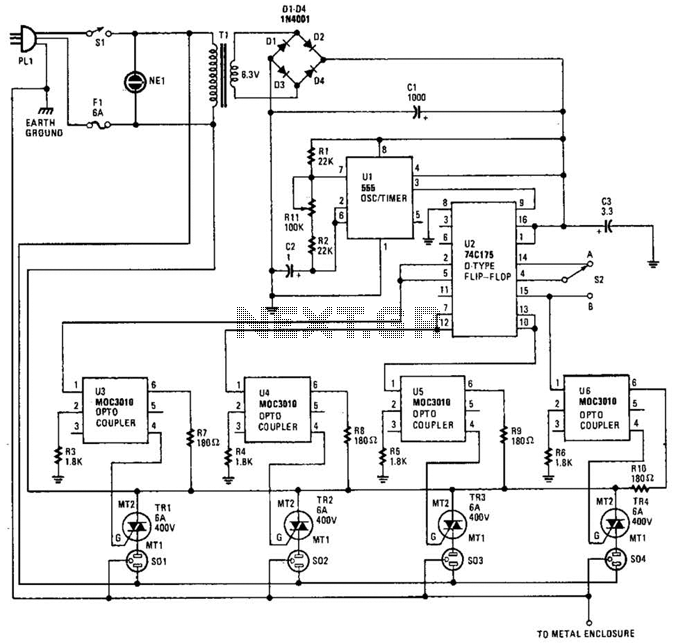
Various threads on ringer circuits have been observed, showcasing multiple variants, particularly concerning the types of transformers utilized, such as air core and step-down transformers. One notable circuit is the 12V-to-120V configuration, which employs a joule ringer that utilizes a 12V EI transformer, often referred to as the peanut butter model. The objective is to operate this circuit using a power supply of 1.5V or 3V, while limiting the power source to two nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries.
To implement a circuit that converts 12V to 120V using a joule ringer, a careful selection of components is essential. The core of this design involves an EI transformer, which is characterized by its laminated iron core that minimizes energy losses. The air core variant can also be employed for specific applications where weight and size are critical factors, though it may have lower efficiency compared to its iron core counterparts.
The circuit typically operates by utilizing a joule ringer topology, which is a type of resonant converter. This configuration allows for the efficient transfer of energy from the input voltage to a higher output voltage. The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the input voltage, while the secondary winding is designed to output a significantly higher voltage, in this case, 120V.
To achieve the desired voltage conversion with a low input voltage of 1.5V or 3V from two NiCd batteries, the circuit may include a switching mechanism, such as a transistor, to rapidly turn the current on and off. This switching action generates a high-frequency oscillation, which is crucial for the transformer to step up the voltage effectively. The use of capacitors in the circuit can further enhance the energy transfer and stabilize the output voltage.
It is important to incorporate protective components, such as diodes and fuses, to safeguard the circuit against overvoltage and current surges. Additionally, proper heat dissipation measures should be implemented, as transformers can generate heat during operation, especially at higher output levels.
This configuration allows for the practical application of low-voltage power sources to achieve high-voltage outputs, making it suitable for various applications where compact and efficient power conversion is required.I have followed some threads on ringer and have seen many variants, specially the transformer used like aircore and stepdown transformer types. Some similar circuits : 1)12V-to-120V joule ringer,uses 12v EI transformer: exists(peanut butter model) we want to power with 1.5 or 3V,limiting to 2 nicd 🔗 External reference
To implement a circuit that converts 12V to 120V using a joule ringer, a careful selection of components is essential. The core of this design involves an EI transformer, which is characterized by its laminated iron core that minimizes energy losses. The air core variant can also be employed for specific applications where weight and size are critical factors, though it may have lower efficiency compared to its iron core counterparts.
The circuit typically operates by utilizing a joule ringer topology, which is a type of resonant converter. This configuration allows for the efficient transfer of energy from the input voltage to a higher output voltage. The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the input voltage, while the secondary winding is designed to output a significantly higher voltage, in this case, 120V.
To achieve the desired voltage conversion with a low input voltage of 1.5V or 3V from two NiCd batteries, the circuit may include a switching mechanism, such as a transistor, to rapidly turn the current on and off. This switching action generates a high-frequency oscillation, which is crucial for the transformer to step up the voltage effectively. The use of capacitors in the circuit can further enhance the energy transfer and stabilize the output voltage.
It is important to incorporate protective components, such as diodes and fuses, to safeguard the circuit against overvoltage and current surges. Additionally, proper heat dissipation measures should be implemented, as transformers can generate heat during operation, especially at higher output levels.
This configuration allows for the practical application of low-voltage power sources to achieve high-voltage outputs, making it suitable for various applications where compact and efficient power conversion is required.I have followed some threads on ringer and have seen many variants, specially the transformer used like aircore and stepdown transformer types. Some similar circuits : 1)12V-to-120V joule ringer,uses 12v EI transformer: exists(peanut butter model) we want to power with 1.5 or 3V,limiting to 2 nicd 🔗 External reference