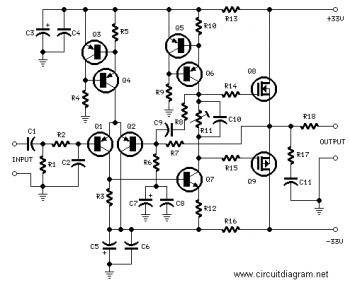
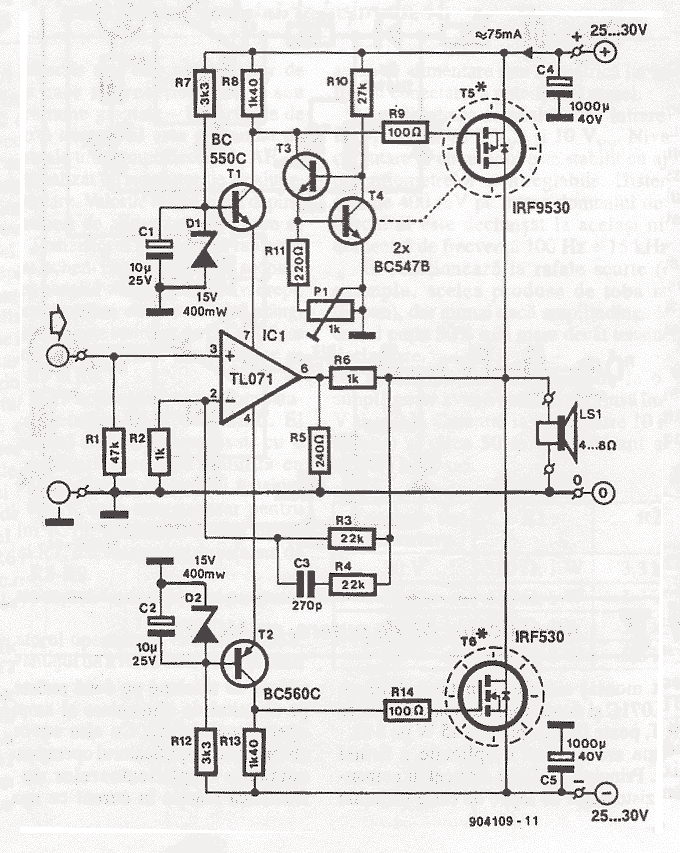
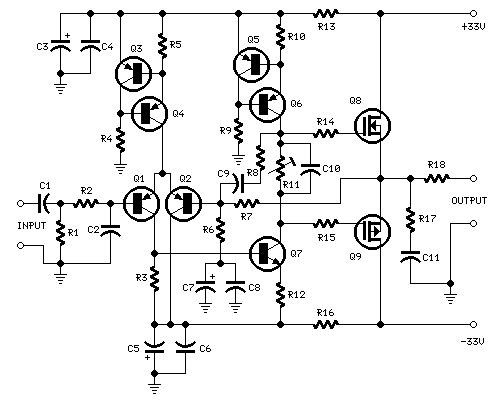
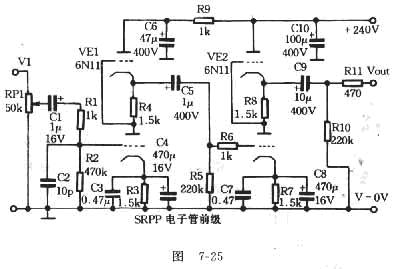
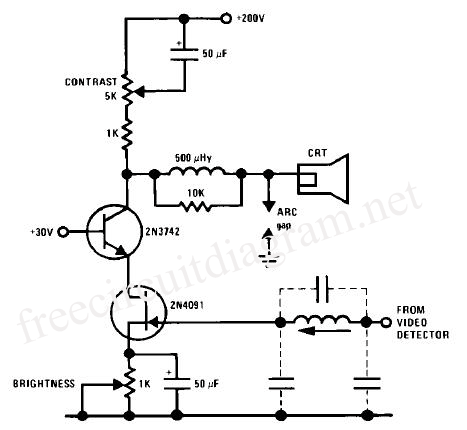
Complementary symmetry FET operating principle
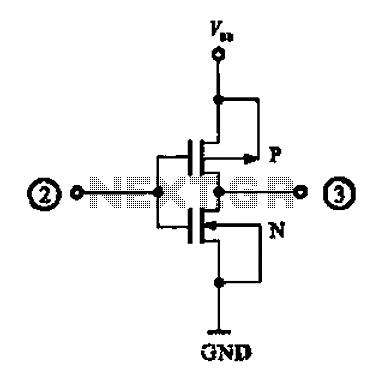
An N-channel MOSFET and P-channel MOSFET form a complementary symmetry circuit, which includes a CMOS complementary output short circuit, as illustrated in the schematic. When the input terminal is high (logical 1), the N-channel field-effect transistor is activated, resulting in a low output level (logical 0). Conversely, when the input pin is low (logical 0), the P-channel field-effect transistor is activated, producing a high output level (logical 1).
The described circuit utilizes complementary MOSFETs to create a basic inverter configuration, leveraging the properties of both N-channel and P-channel devices for efficient signal inversion. In this setup, the N-channel MOSFET is typically connected to ground, while the P-channel MOSFET is connected to the positive supply voltage. The input signal is applied to the gates of both MOSFETs.
When the input signal transitions to a high state (logical 1), the N-channel MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source, effectively pulling the output to a low state (logical 0). This is due to the fact that the N-channel device conducts when a sufficient positive voltage is applied to its gate relative to its source. At the same time, the P-channel MOSFET turns off since its gate-source voltage becomes negative, preventing current flow from the source to the drain.
Conversely, when the input signal is low (logical 0), the N-channel MOSFET turns off, and the P-channel MOSFET turns on. This configuration allows current to flow from the positive supply through the P-channel MOSFET to the output, raising the output voltage to a high state (logical 1). The complementary nature of this circuit ensures that only one of the MOSFETs is conducting at any given time, which minimizes power consumption and heat generation.
This complementary symmetry circuit is widely used in digital logic applications and can be found in various integrated circuits, including microcontrollers and digital signal processors. The CMOS technology provides high noise immunity and low static power consumption, making it the preferred choice for modern electronic devices. Proper biasing and sizing of the MOSFETs are essential for achieving optimal performance and ensuring that the switching characteristics meet the required specifications for speed and power efficiency.An N-channel MOSFET and P-channel points, with two complementary symmetry circuit composed of CMOS complementary output short circuit, as shown in the schematic for it. When th e input terminal is high (the number when lt) input, N-channel field effect transistor is turned on, pin output low level (digital o ) {When pin input low (digital o ), P-channel field effect transistor is turned on the output high (the number 1 ).
The described circuit utilizes complementary MOSFETs to create a basic inverter configuration, leveraging the properties of both N-channel and P-channel devices for efficient signal inversion. In this setup, the N-channel MOSFET is typically connected to ground, while the P-channel MOSFET is connected to the positive supply voltage. The input signal is applied to the gates of both MOSFETs.
When the input signal transitions to a high state (logical 1), the N-channel MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source, effectively pulling the output to a low state (logical 0). This is due to the fact that the N-channel device conducts when a sufficient positive voltage is applied to its gate relative to its source. At the same time, the P-channel MOSFET turns off since its gate-source voltage becomes negative, preventing current flow from the source to the drain.
Conversely, when the input signal is low (logical 0), the N-channel MOSFET turns off, and the P-channel MOSFET turns on. This configuration allows current to flow from the positive supply through the P-channel MOSFET to the output, raising the output voltage to a high state (logical 1). The complementary nature of this circuit ensures that only one of the MOSFETs is conducting at any given time, which minimizes power consumption and heat generation.
This complementary symmetry circuit is widely used in digital logic applications and can be found in various integrated circuits, including microcontrollers and digital signal processors. The CMOS technology provides high noise immunity and low static power consumption, making it the preferred choice for modern electronic devices. Proper biasing and sizing of the MOSFETs are essential for achieving optimal performance and ensuring that the switching characteristics meet the required specifications for speed and power efficiency.An N-channel MOSFET and P-channel points, with two complementary symmetry circuit composed of CMOS complementary output short circuit, as shown in the schematic for it. When th e input terminal is high (the number when lt) input, N-channel field effect transistor is turned on, pin output low level (digital o ) {When pin input low (digital o ), P-channel field effect transistor is turned on the output high (the number 1 ).