computer off switch schematics
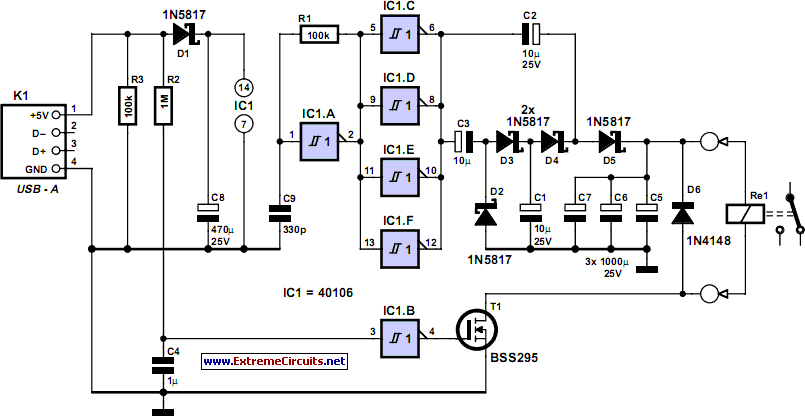
The circuit automatically powers down a computer after Windows has been shut down, preventing users from forgetting to turn off their machines. Upon shutting down Windows, a click occurs after one second, disconnecting the PC from the mains supply. This switch can fit into some older computer cases; if not, it requires a separate enclosure. A supply voltage of 5 V is chosen, which can be sourced from a USB port if the circuit is external to the PC case. It is advisable to solder the mains wires directly onto the switch and insulate them with heat shrink tubing. Capacitor C8 is charged through diode D1 to provide the power supply voltage for integrated circuit IC1. A square wave oscillator is formed around IC1a, resistor R1, and capacitor C9, which drives inverters IC1c to IC1f, generating a frequency of approximately 50 kHz. The four parallel inverters power a voltage multiplier constructed from capacitors C1 to C3 and diodes D2 to D5, achieving a multiplication factor of 3 to charge capacitors C5 to C7 to around 9 V. The actual voltage is lower than the theoretical 14.4 V due to voltage drops across the diode junctions. Capacitors C5 to C7 serve as a buffer to power the switch coil during shutdown. These capacitors charge within about two seconds after activation. When Windows is closed, the 5 V power supply is interrupted, causing capacitor C4 to discharge through resistor R2, resulting in a low signal at the input of inverter IC1b. The output then switches to high, activating transistor T1, which energizes the coil of the mains switch, cutting off power to the PC. Transistor T1, a BSS295 type, is used due to the coil's resistance of only 24 ohms. The circuit initially draws a peak current of approximately 200 mA when the PC is turned on, then drops to around 300 µA. The current during startup may vary based on the characteristics of the 5 V power supply and the PC's supply rails. Care must be taken during construction, particularly regarding the mains wires connected to the switch. It is essential to ensure that mains voltage does not reach the connections to the coil, requiring a minimum separation of 6 mm between the mains conductors and those connected to the low-voltage section of the circuit.
This circuit is an efficient solution for automating the shutdown process of a computer, ensuring that the device is completely powered off after use. The design incorporates safety features to prevent accidental exposure to mains voltage, which is critical in any circuit interfacing with high voltage. The use of a voltage multiplier allows the circuit to function effectively with minimal components, while the square wave oscillator provides the necessary frequency for the inverters to operate. The selection of components, such as the BSS295 transistor and the specific values of resistors and capacitors, is crucial for maintaining the desired operational parameters and ensuring reliable performance. Furthermore, the implementation of heat shrink insulation on mains connections enhances safety by preventing short circuits and accidental contact. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical approach to enhancing user convenience and safety in computer operation.How often does it happen that you close down Windows and then forget to turn off the computer This circuit does that automatically. After Windows is shut down there is a click` a second later and the PC is disconnected from the mains.
Surprisingly enough, this switch fits in some older computer cases. If the circuit doesn`t fit then it will have to be housed in a separate enclosure. That is why a supply voltage of 5 V was selected. This voltage can be obtained from a USB port when the circuit has to be on the outside of the PC case. It is best to solder the mains wires straight onto the switch and to insulate them with heat shrink sleeving.
C8 is charged via D1. This is how the power supply voltage for IC1 is obtained. A square wave oscillator is built around IC1a, R1 and C9, which drives inverters IC1c to f. The frequency is about 50 kHz. The four inverters in parallel power the voltage multiplier, which has a multiplication of 3, and is built from C1 to C3 and D2 to D5. This is used to charge C5 to C7 to a voltage of about 9 V. The generated voltage is clearly lower than the theoretical 3x4. 8=14. 4 V, because some voltage is lost across the PN-junctions of the diodes. C5 to C7 form the buffer that powers the coil of the switch when switching off. The capacitors charge up in about two seconds after switching on. The circuit is now ready for use. When Windows is closed down, the 5-V power supply voltage disappears. C4 is discharged via R2 and this results in a 0` at the input of inverter IC1b. The output then becomes a 1`, which causes T1 to turn on. A voltage is now applied to the coil in the mains switch and the power supply of the PC is turned off.
T1 is a type BSS295 because the resistance of the coil is only 24R. When the PC is switched on, the circuit draws a peak current of about 200 mA, after which the current consumption drops to about 300 µA. The current when switching on could be higher because this is strongly dependent on the characteristics of the 5-V power supply and the supply rails in the PC.
There isn`t much to say about the construction of the circuit itself. The only things to take care with are the mains wires to the switch. The mains voltage may not appear at the connections to the coil. That is why there has to be a distance of at least 6 mm between the conductors that are connected to the mains and the conductors that are connected to the low-voltage part of the circuit. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is an efficient solution for automating the shutdown process of a computer, ensuring that the device is completely powered off after use. The design incorporates safety features to prevent accidental exposure to mains voltage, which is critical in any circuit interfacing with high voltage. The use of a voltage multiplier allows the circuit to function effectively with minimal components, while the square wave oscillator provides the necessary frequency for the inverters to operate. The selection of components, such as the BSS295 transistor and the specific values of resistors and capacitors, is crucial for maintaining the desired operational parameters and ensuring reliable performance. Furthermore, the implementation of heat shrink insulation on mains connections enhances safety by preventing short circuits and accidental contact. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical approach to enhancing user convenience and safety in computer operation.How often does it happen that you close down Windows and then forget to turn off the computer This circuit does that automatically. After Windows is shut down there is a click` a second later and the PC is disconnected from the mains.
Surprisingly enough, this switch fits in some older computer cases. If the circuit doesn`t fit then it will have to be housed in a separate enclosure. That is why a supply voltage of 5 V was selected. This voltage can be obtained from a USB port when the circuit has to be on the outside of the PC case. It is best to solder the mains wires straight onto the switch and to insulate them with heat shrink sleeving.
C8 is charged via D1. This is how the power supply voltage for IC1 is obtained. A square wave oscillator is built around IC1a, R1 and C9, which drives inverters IC1c to f. The frequency is about 50 kHz. The four inverters in parallel power the voltage multiplier, which has a multiplication of 3, and is built from C1 to C3 and D2 to D5. This is used to charge C5 to C7 to a voltage of about 9 V. The generated voltage is clearly lower than the theoretical 3x4. 8=14. 4 V, because some voltage is lost across the PN-junctions of the diodes. C5 to C7 form the buffer that powers the coil of the switch when switching off. The capacitors charge up in about two seconds after switching on. The circuit is now ready for use. When Windows is closed down, the 5-V power supply voltage disappears. C4 is discharged via R2 and this results in a 0` at the input of inverter IC1b. The output then becomes a 1`, which causes T1 to turn on. A voltage is now applied to the coil in the mains switch and the power supply of the PC is turned off.
T1 is a type BSS295 because the resistance of the coil is only 24R. When the PC is switched on, the circuit draws a peak current of about 200 mA, after which the current consumption drops to about 300 µA. The current when switching on could be higher because this is strongly dependent on the characteristics of the 5-V power supply and the supply rails in the PC.
There isn`t much to say about the construction of the circuit itself. The only things to take care with are the mains wires to the switch. The mains voltage may not appear at the connections to the coil. That is why there has to be a distance of at least 6 mm between the conductors that are connected to the mains and the conductors that are connected to the low-voltage part of the circuit. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713