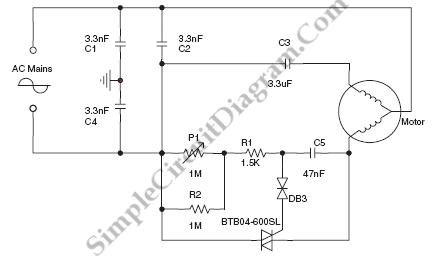
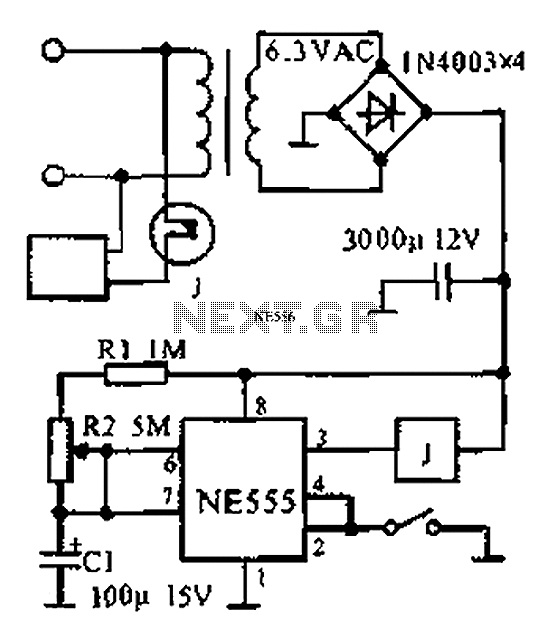
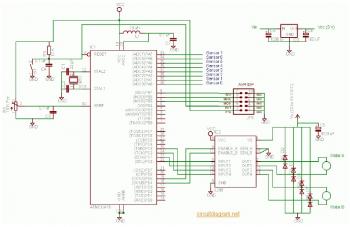
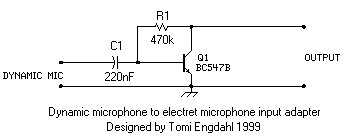
Conducting pipe control rechargeable delay circuit
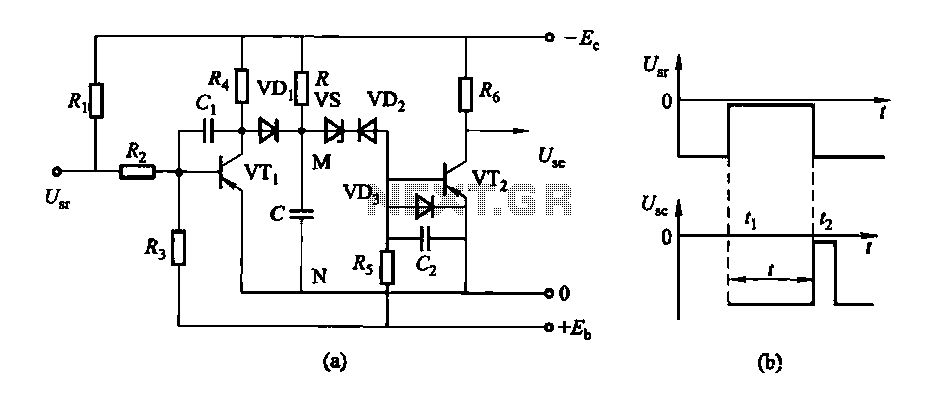
The circuit features a delay action with an instantaneous reset control mechanism. It is categorized into three types: a conducting pipe rechargeable delay circuit, a tube cut-off control rechargeable delay circuit, and a discharge-type delay circuit. In the conducting pipe control rechargeable delay circuit, under normal conditions, the input voltage (U) is negative, causing transistor VT1 to conduct while transistor VT2 remains off, resulting in an output voltage (U) that is also negative. When the input voltage reaches zero, transistor VT1 turns off, and transistor VT2 conducts, bringing the output voltage to zero. A potentiometer is utilized to adjust the voltage from U to zero, with the time interval (t) representing the delay time of the circuit.
The described delay action circuit operates by utilizing transistors as switches to control the flow of current based on the input voltage levels. The conducting pipe rechargeable delay circuit is designed to maintain a negative output when a negative input is applied, indicating that the circuit is in a stable state. When the input voltage transitions to zero, the circuit switches states, effectively resetting the output to zero.
The incorporation of a potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the delay time, providing flexibility in applications where precise timing is critical. The time interval (t) can be adjusted by changing the resistance in the circuit, which directly influences the charging and discharging characteristics of the associated capacitors. This configuration can be utilized in various electronic applications where a delay is required, such as in timing circuits, pulse generators, or in scenarios where sequential operation is necessary.
In the tube cut-off control rechargeable delay circuit, a similar principle applies, but with different operational characteristics that may involve additional components such as diodes or capacitors to enhance performance or adjust timing parameters. The discharge-type delay circuit, on the other hand, typically involves a capacitor discharging through a resistor, creating a delay before the output reaches a certain threshold.
Overall, the design of these delay circuits emphasizes the importance of transistor switching behavior and the role of passive components in defining timing characteristics, making them essential for a wide range of electronic control applications.Delay action, the instantaneous reset control circuit is divided into conducting pipe rechargeable delay circuit, tube cut-off control rechargeable delay circuit and a delay ci rcuit discharge type categories. Conducting pipe control rechargeable delay circuit Under normal circumstances, the input U., Negative potential, the transistor VTi conduction, VT2 off, the output U.. A negative potential. When [,. When zero potential, VTi off, VT2 conduction, the output goes to zero Use potentiometer. From U.. Zero potential to the U.. It becomes a zero potential time interval t is the delay time of the circuit.
The described delay action circuit operates by utilizing transistors as switches to control the flow of current based on the input voltage levels. The conducting pipe rechargeable delay circuit is designed to maintain a negative output when a negative input is applied, indicating that the circuit is in a stable state. When the input voltage transitions to zero, the circuit switches states, effectively resetting the output to zero.
The incorporation of a potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the delay time, providing flexibility in applications where precise timing is critical. The time interval (t) can be adjusted by changing the resistance in the circuit, which directly influences the charging and discharging characteristics of the associated capacitors. This configuration can be utilized in various electronic applications where a delay is required, such as in timing circuits, pulse generators, or in scenarios where sequential operation is necessary.
In the tube cut-off control rechargeable delay circuit, a similar principle applies, but with different operational characteristics that may involve additional components such as diodes or capacitors to enhance performance or adjust timing parameters. The discharge-type delay circuit, on the other hand, typically involves a capacitor discharging through a resistor, creating a delay before the output reaches a certain threshold.
Overall, the design of these delay circuits emphasizes the importance of transistor switching behavior and the role of passive components in defining timing characteristics, making them essential for a wide range of electronic control applications.Delay action, the instantaneous reset control circuit is divided into conducting pipe rechargeable delay circuit, tube cut-off control rechargeable delay circuit and a delay ci rcuit discharge type categories. Conducting pipe control rechargeable delay circuit Under normal circumstances, the input U., Negative potential, the transistor VTi conduction, VT2 off, the output U.. A negative potential. When [,. When zero potential, VTi off, VT2 conduction, the output goes to zero Use potentiometer. From U.. Zero potential to the U.. It becomes a zero potential time interval t is the delay time of the circuit.