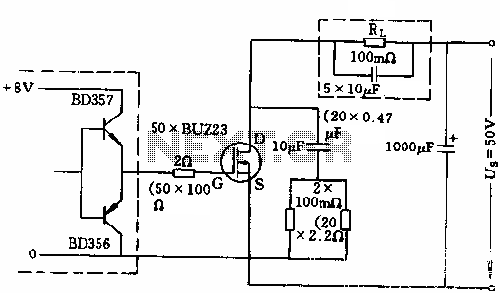
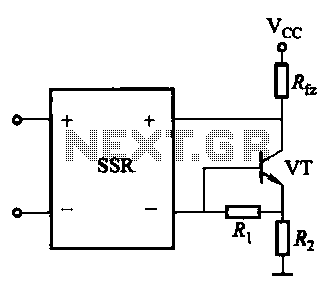
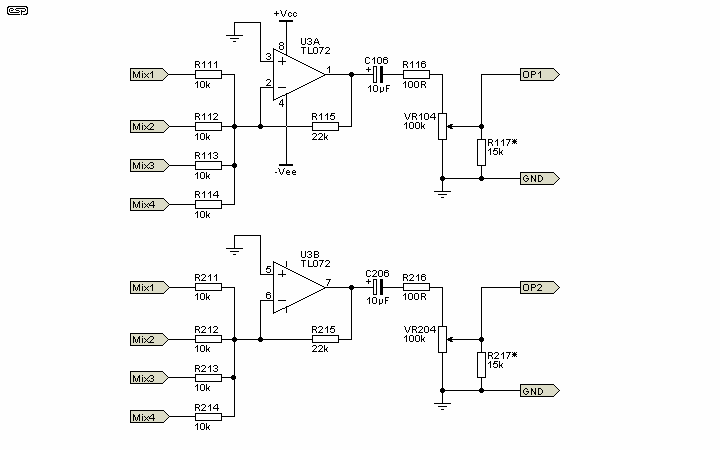
Controlled pulse signal generating circuit
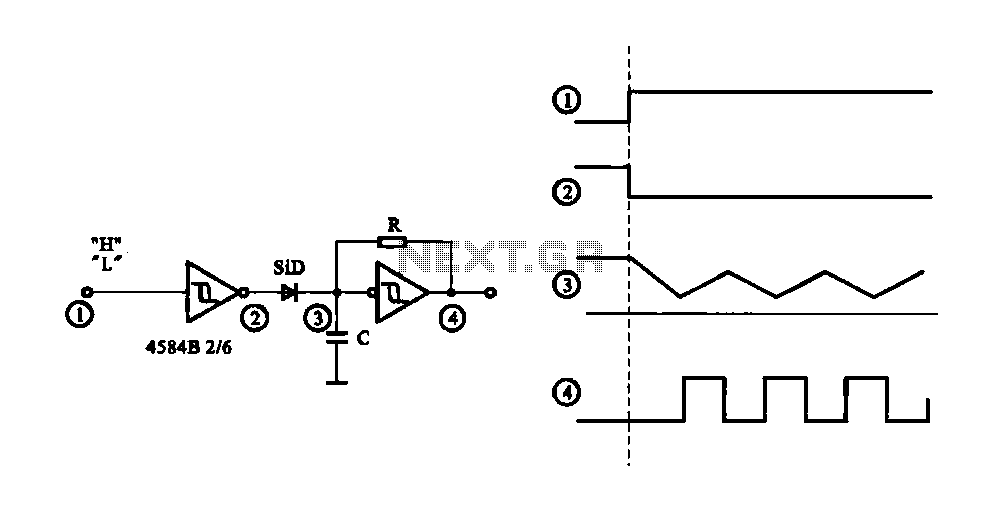
The circuit generates a controlled pulse signal. When a high pulse signal is applied to the input terminal O (start), the output pulse signal is activated. Conversely, when a low signal is received at the input terminal O (stop), the circuit ceases operation, resulting in no pulse signal output.
This pulse signal generating circuit operates based on a simple yet effective design that utilizes a combination of digital logic components, such as flip-flops, resistors, and capacitors. The circuit's primary function is to produce a square wave output signal that can be controlled through an input signal.
When the input terminal O receives a high signal, it triggers a flip-flop, which changes its state and allows current to flow through the output stage. This transition generates a pulse output, which can be used for various applications, such as timing circuits, frequency modulation, or as a clock signal for other digital circuits. The duration and frequency of the output pulse can be adjusted by modifying the values of the resistors and capacitors in the timing circuit.
Upon receiving a low signal at the input terminal O, the flip-flop resets to its initial state, cutting off the current flow and halting the output pulse. This feature allows for precise control over the timing of the output signal, making it suitable for applications that require on-demand pulse generation.
The design can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as diodes for signal conditioning or transistors for driving higher loads, depending on the requirements of the specific application. Additionally, integrating a microcontroller can provide programmable control over the pulse width and frequency, expanding the circuit's functionality and adaptability in various electronic systems.Controlled pulse signal generating circuit FIG controllable pulse signal generating circuit, when the input terminal O start (start) pulse signal (input high), electric road be gan work output pulse signal; when O stop signal input terminal (low level), the circuit stop working, no pulse signal output.
This pulse signal generating circuit operates based on a simple yet effective design that utilizes a combination of digital logic components, such as flip-flops, resistors, and capacitors. The circuit's primary function is to produce a square wave output signal that can be controlled through an input signal.
When the input terminal O receives a high signal, it triggers a flip-flop, which changes its state and allows current to flow through the output stage. This transition generates a pulse output, which can be used for various applications, such as timing circuits, frequency modulation, or as a clock signal for other digital circuits. The duration and frequency of the output pulse can be adjusted by modifying the values of the resistors and capacitors in the timing circuit.
Upon receiving a low signal at the input terminal O, the flip-flop resets to its initial state, cutting off the current flow and halting the output pulse. This feature allows for precise control over the timing of the output signal, making it suitable for applications that require on-demand pulse generation.
The design can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as diodes for signal conditioning or transistors for driving higher loads, depending on the requirements of the specific application. Additionally, integrating a microcontroller can provide programmable control over the pulse width and frequency, expanding the circuit's functionality and adaptability in various electronic systems.Controlled pulse signal generating circuit FIG controllable pulse signal generating circuit, when the input terminal O start (start) pulse signal (input high), electric road be gan work output pulse signal; when O stop signal input terminal (low level), the circuit stop working, no pulse signal output.