Cordless phone backup circuit
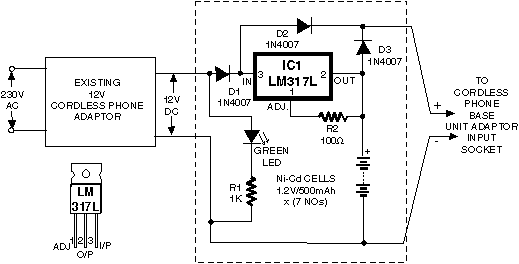
Normally the base of a cordless phone has an adaptor and the handset has Ni-Cd cells for its operation. The base unit becomes inoperative in case of power failure. In such conditions, it is better to provide a backup using Ni-Cd cells externally. Here is a simple circuit which can be used with cordless phone SANYO CLT-420 or similar sets. The working is simple. When AC mains is present, Ni-Cd cells are charged through IC LM317L, which is wired as a current source. Also, diode D3 is reverse-biased, which keeps Ni-Cd cells isolated from positive rail. When AC mains goes off, the Ni-Cd cells provide supply to the cordless phone base unit through diode D3. A green LED is used to indicate the presence of AC mains. Each Ni-Cd cell costs around Rs 34, and the cost of the backup unit, including the box and cells, would not exceed Rs 300. Hence the circuit is well worth the investment.
The described circuit provides a reliable backup power solution for cordless phone systems like the SANYO CLT-420. The circuit's primary components include the LM317L voltage regulator, which is configured as a constant current source to charge the Ni-Cd cells when the AC mains power is available. This configuration ensures that the cells are charged efficiently and safely, preventing overcharging, which can lead to reduced battery life or failure.
Diode D3 plays a crucial role in the circuit by acting as a blocking diode. When the AC mains is present, D3 is reverse-biased, which isolates the Ni-Cd cells from the power supply, ensuring that the charging current flows only into the cells without affecting the rest of the circuit. In the event of a power failure, D3 becomes forward-biased, allowing the stored energy in the Ni-Cd cells to supply power to the cordless phone base unit. This seamless transition between power sources ensures that the phone remains operational even during outages.
The inclusion of a green LED serves as an indicator of the AC mains presence, providing a visual cue to the user that the charging circuit is active. This feature enhances the usability of the circuit by allowing users to quickly ascertain the operational status of their backup power system.
The cost-effective nature of the circuit, with individual Ni-Cd cells priced at approximately Rs 34 and the total backup unit cost capped at around Rs 300, makes it an attractive investment for users seeking to enhance the reliability of their cordless phone systems. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an efficient solution for maintaining phone functionality during power interruptions.Normally the base of a cordless phone has an adaptor and the handset has Ni-Cd cells for its operation. The base unit becomes inoperative in case of power failure. In such conditions, it is better to provide a backup using Ni-Cd cells externally. Here is a simple circuit which can be used with cordless phone SANYO CLT-420 or similar sets. The working is simple. When AC mains is present, Ni-Cd cells are charged through IC LM317L, which is wired as a current source.
Also, diode D3 is reverse-biased, which keeps Ni-Cd cells isolated from positive rail. When AC mains goes off, the Ni-Cd cells provide supply to the cordless phone base unit through diode D3. A green LED is used to indicate the presence of AC mains. Each Ni-Cd cell costs around Rs 34, and the cost of the backup unit, including the box and cells, would not exceed Rs 300.
Hence the circuit is well worth the investment. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit provides a reliable backup power solution for cordless phone systems like the SANYO CLT-420. The circuit's primary components include the LM317L voltage regulator, which is configured as a constant current source to charge the Ni-Cd cells when the AC mains power is available. This configuration ensures that the cells are charged efficiently and safely, preventing overcharging, which can lead to reduced battery life or failure.
Diode D3 plays a crucial role in the circuit by acting as a blocking diode. When the AC mains is present, D3 is reverse-biased, which isolates the Ni-Cd cells from the power supply, ensuring that the charging current flows only into the cells without affecting the rest of the circuit. In the event of a power failure, D3 becomes forward-biased, allowing the stored energy in the Ni-Cd cells to supply power to the cordless phone base unit. This seamless transition between power sources ensures that the phone remains operational even during outages.
The inclusion of a green LED serves as an indicator of the AC mains presence, providing a visual cue to the user that the charging circuit is active. This feature enhances the usability of the circuit by allowing users to quickly ascertain the operational status of their backup power system.
The cost-effective nature of the circuit, with individual Ni-Cd cells priced at approximately Rs 34 and the total backup unit cost capped at around Rs 300, makes it an attractive investment for users seeking to enhance the reliability of their cordless phone systems. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an efficient solution for maintaining phone functionality during power interruptions.Normally the base of a cordless phone has an adaptor and the handset has Ni-Cd cells for its operation. The base unit becomes inoperative in case of power failure. In such conditions, it is better to provide a backup using Ni-Cd cells externally. Here is a simple circuit which can be used with cordless phone SANYO CLT-420 or similar sets. The working is simple. When AC mains is present, Ni-Cd cells are charged through IC LM317L, which is wired as a current source.
Also, diode D3 is reverse-biased, which keeps Ni-Cd cells isolated from positive rail. When AC mains goes off, the Ni-Cd cells provide supply to the cordless phone base unit through diode D3. A green LED is used to indicate the presence of AC mains. Each Ni-Cd cell costs around Rs 34, and the cost of the backup unit, including the box and cells, would not exceed Rs 300.
Hence the circuit is well worth the investment. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713