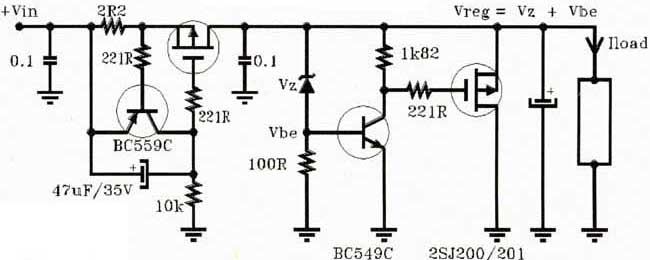
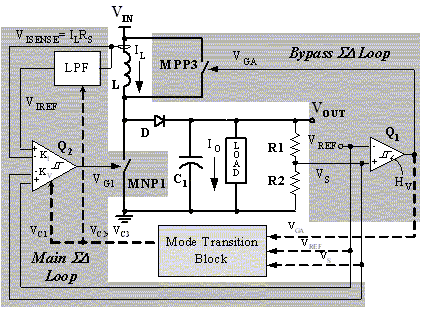
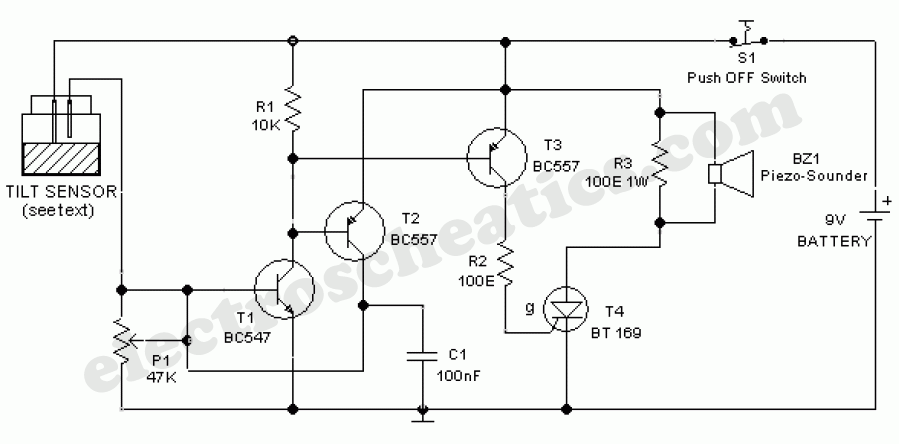
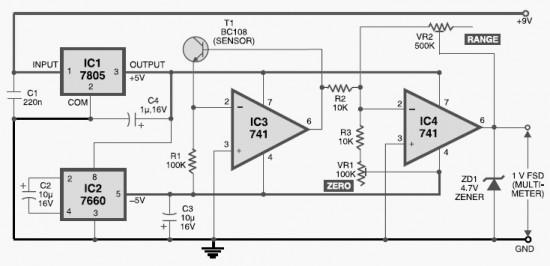
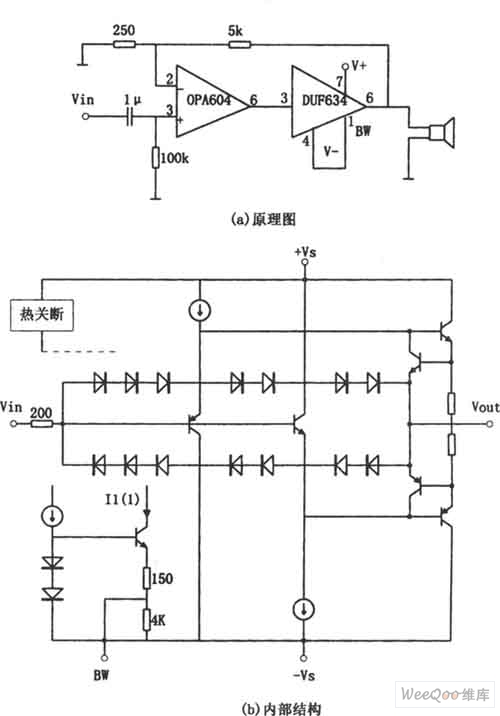
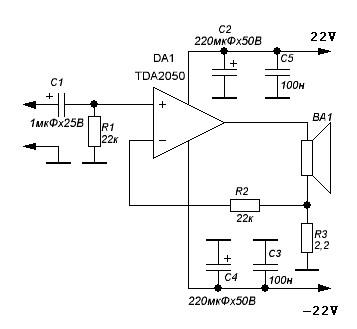
Photoreceiving circuit diagram LM307 amplifier configuration
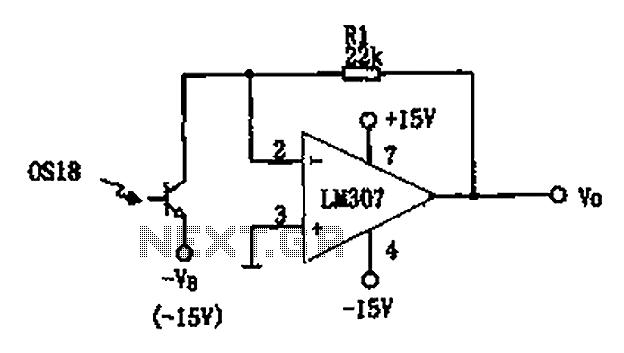
The circuit described is a photoelectric receiver amplifier designed to amplify the electrical signals generated by photodiodes or phototransistors in optoelectronic devices. When the intensity of incident light varies, the photosensitive device generates a corresponding voltage or current. The photoreceptor amplifier amplifies the changes in photocurrent using an operational amplifier (op-amp) model LM307. This configuration is particularly effective for achieving the desired amplification. In the case of the phototransistor OS18, a specific bias voltage (VB) is applied (for example, VB = -15V). The output current of the phototransistor is amplified by the operational amplifier to produce an output voltage (Vo) that is proportional to the photocurrent (Ip) multiplied by the resistor value (R1). The minimum photocurrent (Ip) is determined by the input bias current (IB) of the LM307 op-amp, while the maximum photocurrent (Ip) is constrained by the maximum allowable output voltage (Vomax) of the op-amp.
The photoelectric receiver amplifier circuit operates as a vital component in various optoelectronic applications, where accurate light intensity measurements are essential. The configuration typically consists of a photodiode or phototransistor connected to the non-inverting input of the LM307 op-amp. The output voltage (Vo) is monitored across a load resistor (R1), which converts the amplified photocurrent into a usable voltage signal.
The circuit's performance is influenced by several parameters, including the bias voltage (VB), which sets the operating point for the phototransistor. A negative bias, such as -15V, is commonly used to enhance the sensitivity and response time of the phototransistor. The LM307 op-amp is selected for its low input bias current and high gain characteristics, making it suitable for amplifying small signals generated by the photodetector.
In practice, the circuit can be fine-tuned by adjusting the value of R1 to achieve the desired sensitivity and output range. Additionally, the stability of the amplifier can be enhanced by incorporating feedback components that mitigate noise and improve linearity. The overall design ensures that the circuit can effectively respond to varying light conditions, making it applicable in fields such as optical communication, sensor technology, and automated lighting systems. As shown for the photoelectric receiver amplifier. Photo receiver amplifier for amplifying circuit amplifies the electrical signal photodiode or phototransistor optoelectronic device output and design. When the illuminance of the incident light changes, the photosensitive device will produce a corresponding voltage or current, and the photoreceptor amplifier is used to amplify the photocurrent change circuit constituted by the operational amplifier LM307 current amplifier it is ideally suited to achieve the above effect. In phototransistor OS18 with a certain bias voltage VB (FIG. (A) in VB -l5V), in the light of its output current operational amplifiers amplified output voltage Vo IpR1 to represent.
Minimum photocurrent Ip is determined by the LM307 op amp input bias current IB, the maximum value Ip by op amp maximum allowable output voltage Vomax decision.
The photoelectric receiver amplifier circuit operates as a vital component in various optoelectronic applications, where accurate light intensity measurements are essential. The configuration typically consists of a photodiode or phototransistor connected to the non-inverting input of the LM307 op-amp. The output voltage (Vo) is monitored across a load resistor (R1), which converts the amplified photocurrent into a usable voltage signal.
The circuit's performance is influenced by several parameters, including the bias voltage (VB), which sets the operating point for the phototransistor. A negative bias, such as -15V, is commonly used to enhance the sensitivity and response time of the phototransistor. The LM307 op-amp is selected for its low input bias current and high gain characteristics, making it suitable for amplifying small signals generated by the photodetector.
In practice, the circuit can be fine-tuned by adjusting the value of R1 to achieve the desired sensitivity and output range. Additionally, the stability of the amplifier can be enhanced by incorporating feedback components that mitigate noise and improve linearity. The overall design ensures that the circuit can effectively respond to varying light conditions, making it applicable in fields such as optical communication, sensor technology, and automated lighting systems. As shown for the photoelectric receiver amplifier. Photo receiver amplifier for amplifying circuit amplifies the electrical signal photodiode or phototransistor optoelectronic device output and design. When the illuminance of the incident light changes, the photosensitive device will produce a corresponding voltage or current, and the photoreceptor amplifier is used to amplify the photocurrent change circuit constituted by the operational amplifier LM307 current amplifier it is ideally suited to achieve the above effect. In phototransistor OS18 with a certain bias voltage VB (FIG. (A) in VB -l5V), in the light of its output current operational amplifiers amplified output voltage Vo IpR1 to represent.
Minimum photocurrent Ip is determined by the LM307 op amp input bias current IB, the maximum value Ip by op amp maximum allowable output voltage Vomax decision.