DCF77 Preamplifier
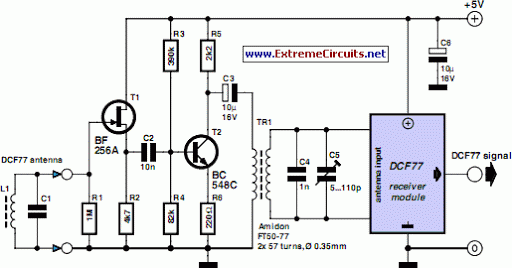
A popular project among microcontroller enthusiasts is to build a radio-controlled clock. Tiny receiver boards are available, featuring a pre-adjusted ferrite.
The radio-controlled clock project leverages a microcontroller to receive time signals transmitted from a time signal transmitter, typically operated by a national timekeeping authority. The core components of this project include a microcontroller unit (MCU), a radio receiver module, a display (such as an LCD or LED), and a power supply.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, interpreting the signals received from the radio receiver. The receiver module is designed to pick up specific frequencies, often in the range of 60 kHz, which are used for time synchronization. The pre-adjusted ferrite antenna enhances the sensitivity and selectivity of the receiver, allowing it to effectively capture weak signals.
The display component is responsible for presenting the time information to the user. It can be configured to show hours, minutes, and seconds, along with additional features such as date or temperature, depending on the complexity of the design.
Power supply can be provided through batteries or a direct connection to a power source, ensuring the clock remains operational without interruption. The circuit design typically incorporates a voltage regulator to maintain stable operation under varying load conditions.
Overall, this project exemplifies the integration of microcontroller technology with radio frequency communication, resulting in an accurate and reliable timekeeping device suitable for a variety of applications.A popular project among microcontroller aficionados is to build a radio-controlled clock. Tiny receiver boards are available, with a pre-adjusted ferrite.. 🔗 External reference
The radio-controlled clock project leverages a microcontroller to receive time signals transmitted from a time signal transmitter, typically operated by a national timekeeping authority. The core components of this project include a microcontroller unit (MCU), a radio receiver module, a display (such as an LCD or LED), and a power supply.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, interpreting the signals received from the radio receiver. The receiver module is designed to pick up specific frequencies, often in the range of 60 kHz, which are used for time synchronization. The pre-adjusted ferrite antenna enhances the sensitivity and selectivity of the receiver, allowing it to effectively capture weak signals.
The display component is responsible for presenting the time information to the user. It can be configured to show hours, minutes, and seconds, along with additional features such as date or temperature, depending on the complexity of the design.
Power supply can be provided through batteries or a direct connection to a power source, ensuring the clock remains operational without interruption. The circuit design typically incorporates a voltage regulator to maintain stable operation under varying load conditions.
Overall, this project exemplifies the integration of microcontroller technology with radio frequency communication, resulting in an accurate and reliable timekeeping device suitable for a variety of applications.A popular project among microcontroller aficionados is to build a radio-controlled clock. Tiny receiver boards are available, with a pre-adjusted ferrite.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713