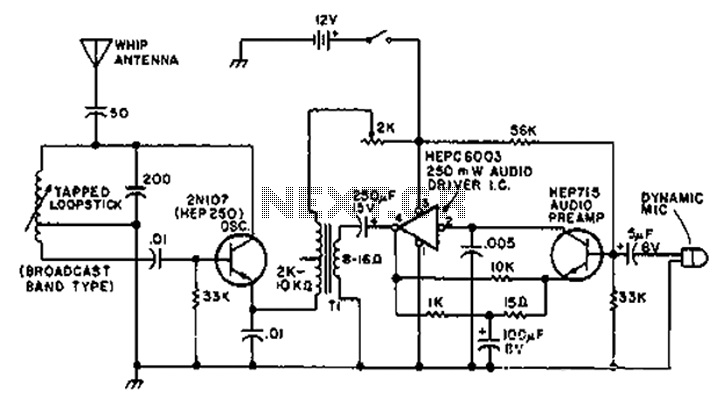
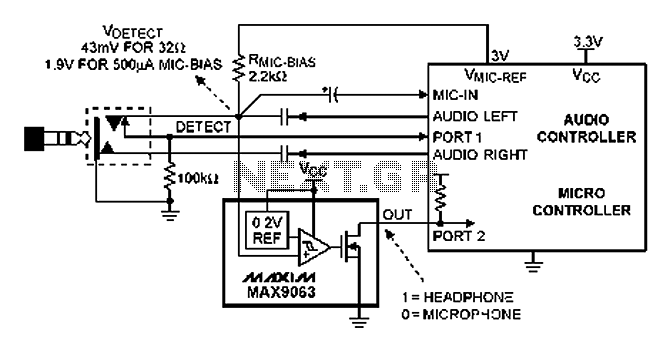
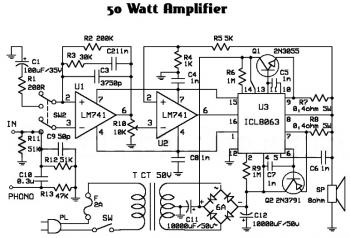
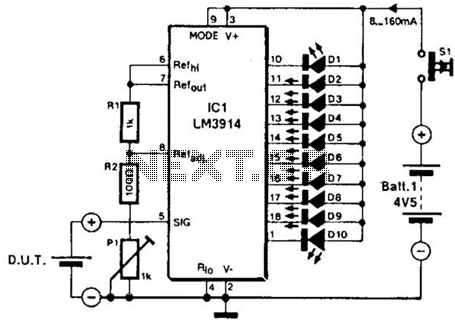
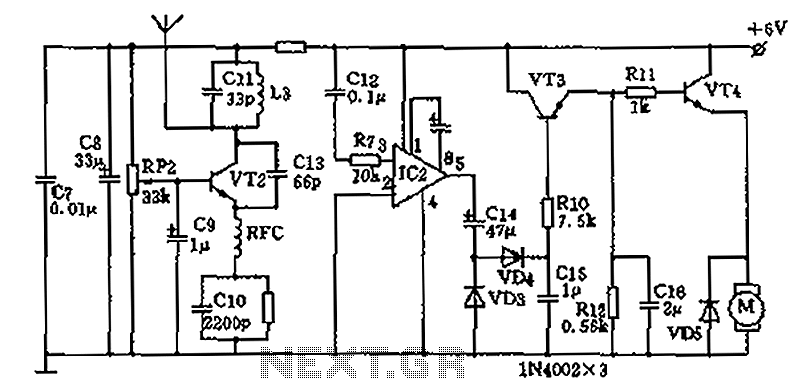
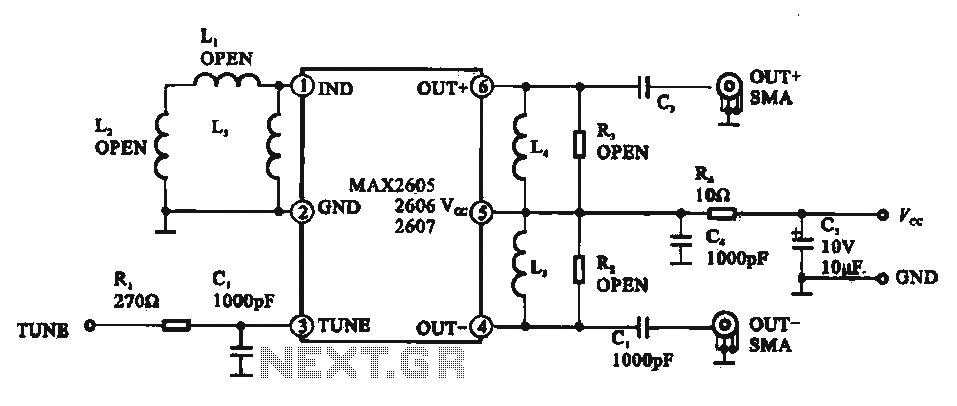
define active and passive circuit elements
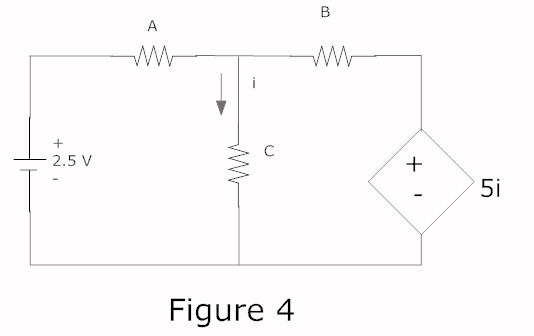
In a complete circuit, there are two types of elements: active and passive elements. Active elements generate energy, while passive elements dissipate energy. Examples of passive elements include resistors and capacitors.
In electronic circuits, active and passive components serve distinct yet complementary roles. Active elements, such as transistors and operational amplifiers, are capable of supplying power to the circuit and can control the flow of electricity. They are essential for amplifying signals, switching applications, and generating oscillations.
On the other hand, passive elements, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not generate energy but rather manage and modify the energy within the circuit. Resistors limit current flow and divide voltages, while capacitors store and release electrical energy, smoothing out voltage fluctuations and filtering signals. Inductors, another type of passive component, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them and are often used in applications involving alternating current (AC).
The interplay between active and passive components is fundamental in designing circuits for various applications, from simple electronic devices to complex systems. Understanding the characteristics and functions of each component type is crucial for engineers to create efficient and reliable electronic designs.In a complete circuit two types of elements found active and passive elements.Active elements generate energy.Passive elements drop energy.Resistor,capacitor . 🔗 External reference
In electronic circuits, active and passive components serve distinct yet complementary roles. Active elements, such as transistors and operational amplifiers, are capable of supplying power to the circuit and can control the flow of electricity. They are essential for amplifying signals, switching applications, and generating oscillations.
On the other hand, passive elements, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not generate energy but rather manage and modify the energy within the circuit. Resistors limit current flow and divide voltages, while capacitors store and release electrical energy, smoothing out voltage fluctuations and filtering signals. Inductors, another type of passive component, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them and are often used in applications involving alternating current (AC).
The interplay between active and passive components is fundamental in designing circuits for various applications, from simple electronic devices to complex systems. Understanding the characteristics and functions of each component type is crucial for engineers to create efficient and reliable electronic designs.In a complete circuit two types of elements found active and passive elements.Active elements generate energy.Passive elements drop energy.Resistor,capacitor . 🔗 External reference