Diac-Triac Phase/Power Control without Hysteresis
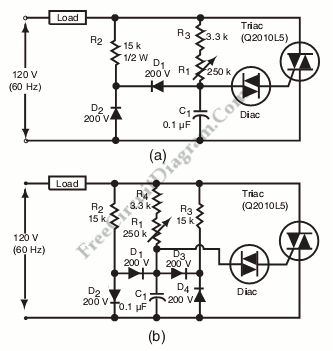
Hysteresis in a lamp dimmer or other electrical appliances may cause issues when fine-tuning, leading to a feeling of being out of control. This is a circuit of.
Hysteresis in dimmer circuits can lead to undesirable fluctuations in brightness levels, particularly in applications requiring precise control. The circuit typically employs a feedback mechanism that stabilizes the output against small variations in input voltage or load conditions.
In a standard lamp dimmer circuit, the hysteresis effect is often introduced by components such as operational amplifiers or comparators, which help to define a threshold level for switching the output state. This threshold creates a zone of operation where small changes in input do not affect the output state, thereby preventing rapid on-off cycling, which can be perceived as flickering.
To design a more reliable dimmer circuit with minimal hysteresis, a careful selection of resistor and capacitor values is essential. The feedback loop should be configured to ensure that the operational amplifier or comparator responds only to significant changes in input, thus avoiding unnecessary adjustments in output.
For example, in a typical dimmer circuit, a variable resistor (potentiometer) can be used to adjust the reference voltage at the inverting input of the comparator. The non-inverting input receives the feedback voltage from the output, which is influenced by the load current. The output of the comparator drives a power transistor or a TRIAC, controlling the AC voltage applied to the lamp.
To further enhance fine-tuning capabilities, additional circuitry such as a low-pass filter can be incorporated to smooth out rapid fluctuations in the input signal. This will help to maintain a stable dimming effect, allowing for more precise adjustments without the adverse effects of hysteresis.
In summary, addressing hysteresis in lamp dimmers involves a thoughtful approach to circuit design, focusing on feedback mechanisms and component selection to achieve stable and controllable brightness levels.Hysteresis in lamp dimmer or in other electric appliance might cause some trouble if you need a fine tuning, something like out of control. This is a circuit of. 🔗 External reference
Hysteresis in dimmer circuits can lead to undesirable fluctuations in brightness levels, particularly in applications requiring precise control. The circuit typically employs a feedback mechanism that stabilizes the output against small variations in input voltage or load conditions.
In a standard lamp dimmer circuit, the hysteresis effect is often introduced by components such as operational amplifiers or comparators, which help to define a threshold level for switching the output state. This threshold creates a zone of operation where small changes in input do not affect the output state, thereby preventing rapid on-off cycling, which can be perceived as flickering.
To design a more reliable dimmer circuit with minimal hysteresis, a careful selection of resistor and capacitor values is essential. The feedback loop should be configured to ensure that the operational amplifier or comparator responds only to significant changes in input, thus avoiding unnecessary adjustments in output.
For example, in a typical dimmer circuit, a variable resistor (potentiometer) can be used to adjust the reference voltage at the inverting input of the comparator. The non-inverting input receives the feedback voltage from the output, which is influenced by the load current. The output of the comparator drives a power transistor or a TRIAC, controlling the AC voltage applied to the lamp.
To further enhance fine-tuning capabilities, additional circuitry such as a low-pass filter can be incorporated to smooth out rapid fluctuations in the input signal. This will help to maintain a stable dimming effect, allowing for more precise adjustments without the adverse effects of hysteresis.
In summary, addressing hysteresis in lamp dimmers involves a thoughtful approach to circuit design, focusing on feedback mechanisms and component selection to achieve stable and controllable brightness levels.Hysteresis in lamp dimmer or in other electric appliance might cause some trouble if you need a fine tuning, something like out of control. This is a circuit of. 🔗 External reference