digital clock
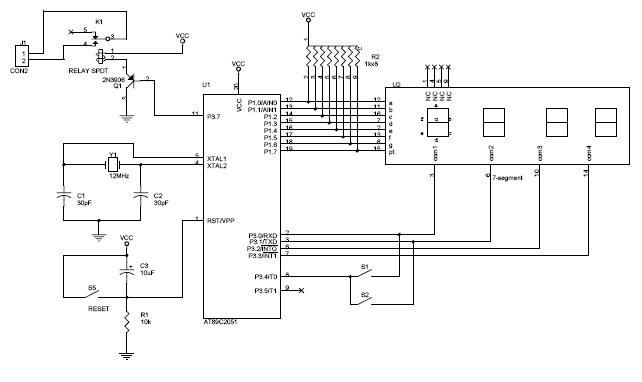
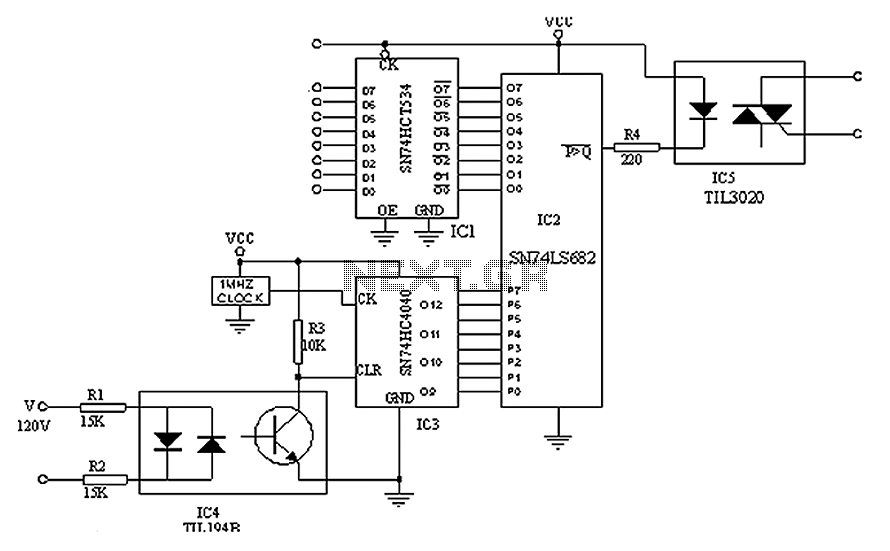
This is a digital clock schematic diagram. The circuit is relatively complex and may pose challenges for beginners due to the intricate connections involving integrated circuits (ICs). The circuit operates with two voltage supply lines. The voltage +5VA powers all ICs except for IC9 through IC13, which are supplied with voltage in case of a network voltage interruption. Conversely, the voltage line +5VB exclusively supplies IC9 through IC13 and the display, and it is also interrupted in the event of a network voltage failure to conserve battery life. The process of creating a printed circuit board (PCB) can be accomplished in simple steps. To design the PCB, utilize PCB design software such as Eagle, print the design on photo or glossy paper with a laser printer, adhere the printed design to the copper side of the PCB, and then apply heat using a hot iron plate. This will transfer the ink onto the PCB, preparing it for the etching process. If a laser printer is unavailable, the design can be printed on standard paper and copied at a local copy service using glossy paper.
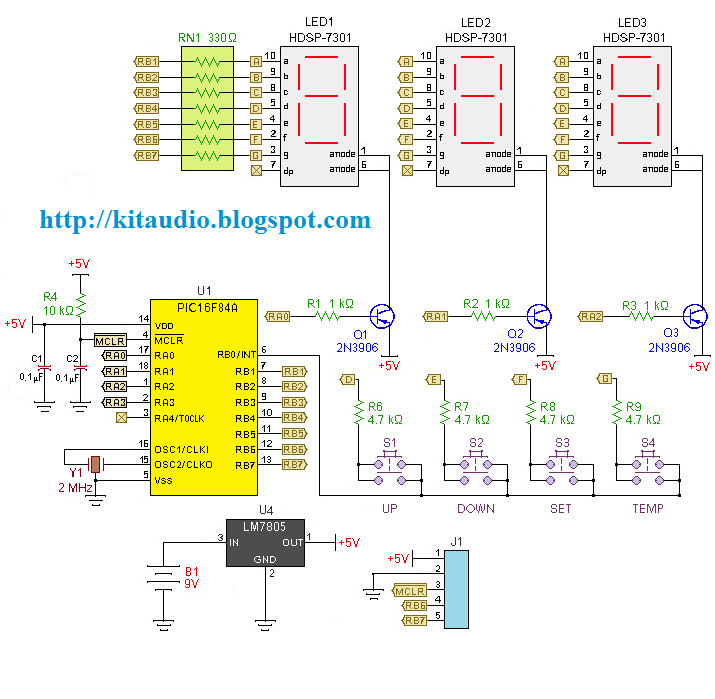
The digital clock circuit utilizes a combination of integrated circuits to manage timekeeping and display functions. The primary components include a microcontroller or timer IC, which serves as the core of the clock, along with additional ICs that handle the display and power management. The use of two distinct voltage lines, +5VA and +5VB, is crucial for the operation of this circuit. The +5VA line ensures that the majority of the circuit components are powered, while the +5VB line is specifically designated for the display and certain ICs, allowing for efficient power management.
In the event of a power failure, the circuit is designed to switch to battery operation, maintaining timekeeping functionality. This is achieved through a carefully designed power management system that disconnects the display from the main power supply while keeping the microcontroller operational. The incorporation of this feature is essential for ensuring that the clock remains functional even during power outages, thereby enhancing its reliability.
For PCB fabrication, the process begins with designing the layout in software such as Eagle, which provides tools for creating and modifying circuit schematics. Once the design is finalized, it can be printed onto photo or glossy paper using a laser printer, which is critical for achieving a high-quality transfer of the circuit pattern to the PCB. The printed design must then be adhered to the copper side of the PCB, followed by the application of heat using a hot iron. This step is crucial as it allows the ink to bond with the copper, creating a resist for the etching process.
After the design has been transferred, the PCB can be etched using a suitable etching solution, which removes the unprotected copper and leaves behind the desired circuit pattern. Once the etching is complete, the board can be drilled for component placement, and the components can be soldered in place to complete the assembly of the digital clock circuit. This methodical approach ensures that the final product is both functional and reliable, suitable for practical applications in timekeeping.This is digital clock schematic diagram. This circuit is quite complex and quite difficult for a newbie because this circuit uses IC with some a complicated connections. The voltages that supplied to the circuit are divided in two lines. The voltage +5VA supplies all IC except the IC9 until IC13 and is supplied with voltage in case of break of ne
twork voltage. On the other side, the voltage linr of +5VB only supplies the IC9 until IC13 and display and is interrupted in case of interruption of network voltage, it is to ensure the economy of battery. Make a PCB in very easy steps. ! Create your PCB design using PCB designer software like Eagle, print out your design on photo paper or glossy paper with laserjet printer.
Stick the printed design on the PCB (copper side) and then heat it using hot iron plate. The ink will stick on the PCB and it will be ready for etching process. Note: If you don`t have laserjet printer, then you can print the design on standard paper. Copy the printed design at Copy Service around your location (with glossy paper). 🔗 External reference
The digital clock circuit utilizes a combination of integrated circuits to manage timekeeping and display functions. The primary components include a microcontroller or timer IC, which serves as the core of the clock, along with additional ICs that handle the display and power management. The use of two distinct voltage lines, +5VA and +5VB, is crucial for the operation of this circuit. The +5VA line ensures that the majority of the circuit components are powered, while the +5VB line is specifically designated for the display and certain ICs, allowing for efficient power management.
In the event of a power failure, the circuit is designed to switch to battery operation, maintaining timekeeping functionality. This is achieved through a carefully designed power management system that disconnects the display from the main power supply while keeping the microcontroller operational. The incorporation of this feature is essential for ensuring that the clock remains functional even during power outages, thereby enhancing its reliability.
For PCB fabrication, the process begins with designing the layout in software such as Eagle, which provides tools for creating and modifying circuit schematics. Once the design is finalized, it can be printed onto photo or glossy paper using a laser printer, which is critical for achieving a high-quality transfer of the circuit pattern to the PCB. The printed design must then be adhered to the copper side of the PCB, followed by the application of heat using a hot iron. This step is crucial as it allows the ink to bond with the copper, creating a resist for the etching process.
After the design has been transferred, the PCB can be etched using a suitable etching solution, which removes the unprotected copper and leaves behind the desired circuit pattern. Once the etching is complete, the board can be drilled for component placement, and the components can be soldered in place to complete the assembly of the digital clock circuit. This methodical approach ensures that the final product is both functional and reliable, suitable for practical applications in timekeeping.This is digital clock schematic diagram. This circuit is quite complex and quite difficult for a newbie because this circuit uses IC with some a complicated connections. The voltages that supplied to the circuit are divided in two lines. The voltage +5VA supplies all IC except the IC9 until IC13 and is supplied with voltage in case of break of ne
twork voltage. On the other side, the voltage linr of +5VB only supplies the IC9 until IC13 and display and is interrupted in case of interruption of network voltage, it is to ensure the economy of battery. Make a PCB in very easy steps. ! Create your PCB design using PCB designer software like Eagle, print out your design on photo paper or glossy paper with laserjet printer.
Stick the printed design on the PCB (copper side) and then heat it using hot iron plate. The ink will stick on the PCB and it will be ready for etching process. Note: If you don`t have laserjet printer, then you can print the design on standard paper. Copy the printed design at Copy Service around your location (with glossy paper). 🔗 External reference