Digital Entry Lock
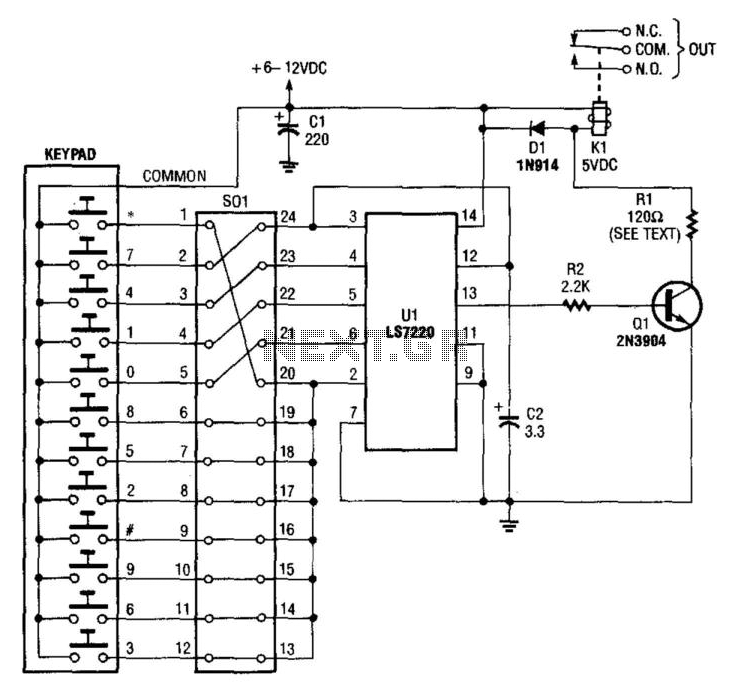
A keypad is used to input a four-digit access code, which is configured using jumpers on a 24-pin plug-in header and socket. The component Ul is an LST220, which detects a sequential four-digit data input. Upon successful entry of the correct code into the keypad, pin 13 of Ul goes high, activating Ql and Kl. K1 controls an external electric lock solenoid.
The circuit design incorporates a keypad interfaced with an LST220 integrated circuit (IC), which serves as the primary input detection mechanism. The keypad consists of a matrix arrangement that allows users to enter a four-digit code. This code is configured through the use of jumpers on a 24-pin header, enabling flexibility in code programming.
Upon entering the correct sequence, the LST220 IC processes the input and, upon validation, generates a high signal at pin 13. This output signal is crucial as it triggers the subsequent components in the circuit. Ql, typically a transistor or relay, is activated by this high signal, allowing it to switch on Kl.
Kl is responsible for driving an external electric lock solenoid, which engages or disengages the locking mechanism based on the input received from the keypad. The solenoid operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical movement, thereby securing or releasing the lock as required.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, resistors to limit current, and capacitors for noise filtering, ensuring stable operation. The design should also account for potential security measures, such as tamper detection or feedback mechanisms, to enhance the overall security of the access control system. A keypad enters a four-digit access code, which is programmed via jumpers on a 24-pin plug-in header and socket. Ul is a n LST220, which detects a four-digit sequential data input. When the correct data is entered into the keyboard, pin 13 of Ul goes high, which activates Ql and Kl. K1 drives an external electric lock solenoid, etc. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates a keypad interfaced with an LST220 integrated circuit (IC), which serves as the primary input detection mechanism. The keypad consists of a matrix arrangement that allows users to enter a four-digit code. This code is configured through the use of jumpers on a 24-pin header, enabling flexibility in code programming.
Upon entering the correct sequence, the LST220 IC processes the input and, upon validation, generates a high signal at pin 13. This output signal is crucial as it triggers the subsequent components in the circuit. Ql, typically a transistor or relay, is activated by this high signal, allowing it to switch on Kl.
Kl is responsible for driving an external electric lock solenoid, which engages or disengages the locking mechanism based on the input received from the keypad. The solenoid operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical movement, thereby securing or releasing the lock as required.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, resistors to limit current, and capacitors for noise filtering, ensuring stable operation. The design should also account for potential security measures, such as tamper detection or feedback mechanisms, to enhance the overall security of the access control system. A keypad enters a four-digit access code, which is programmed via jumpers on a 24-pin plug-in header and socket. Ul is a n LST220, which detects a four-digit sequential data input. When the correct data is entered into the keyboard, pin 13 of Ul goes high, which activates Ql and Kl. K1 drives an external electric lock solenoid, etc. 🔗 External reference