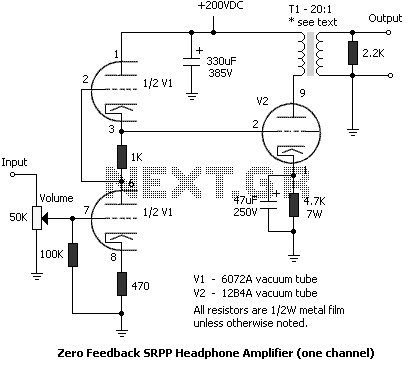
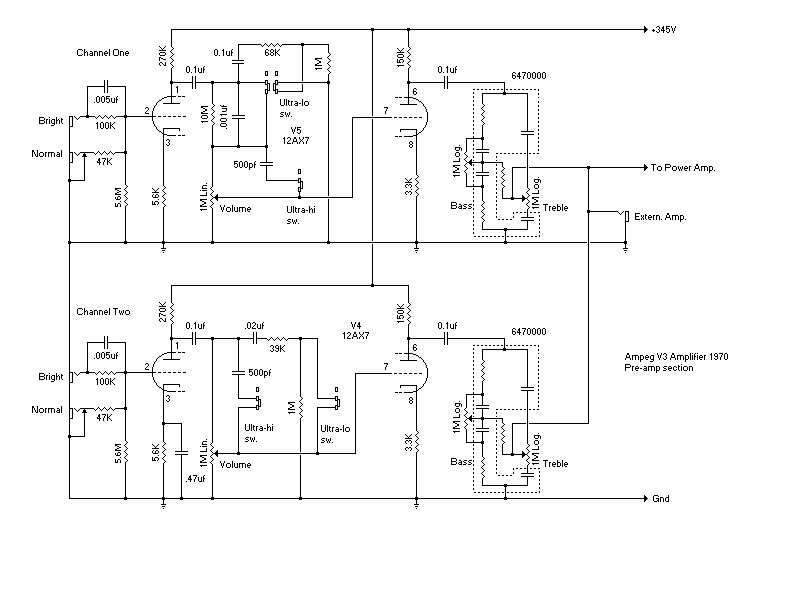
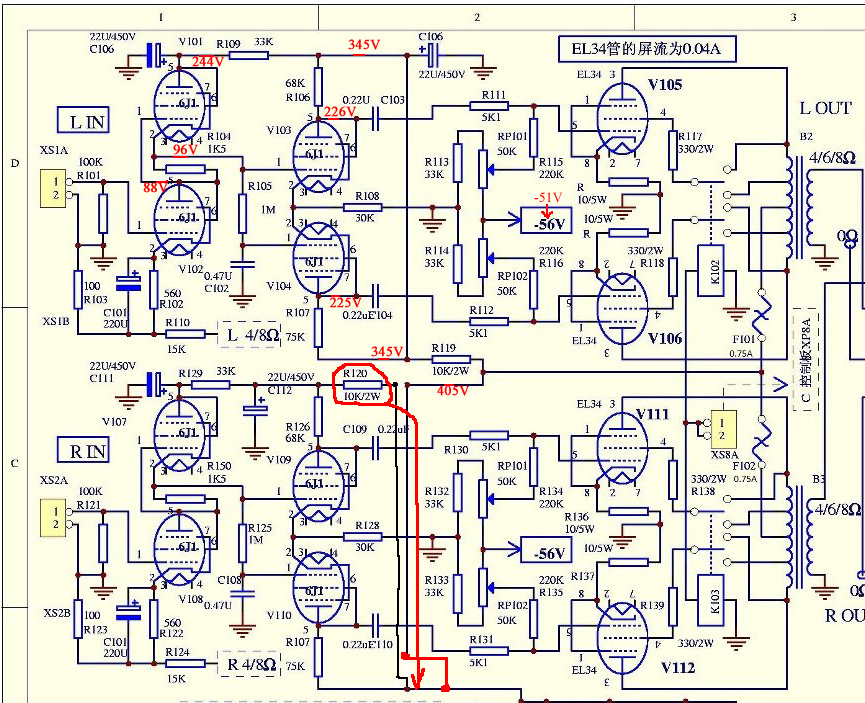
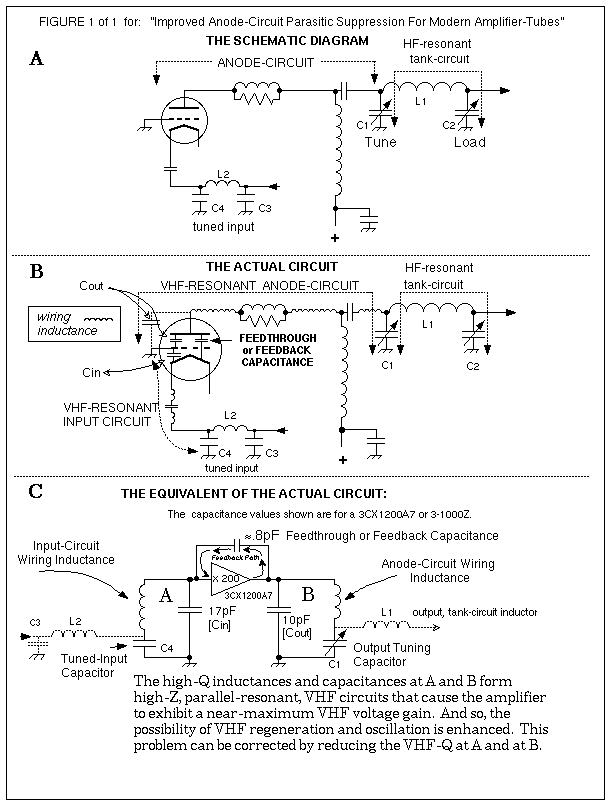
Diode Tube
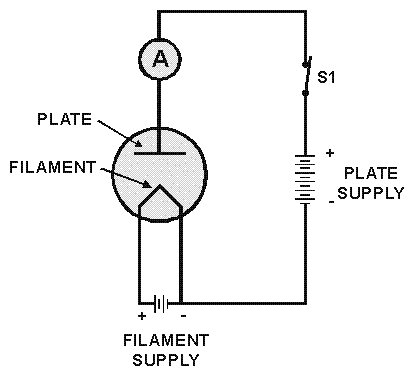
The diode tube under examination is essentially Edison’s early incandescent bulb containing a plate. The term "diode" refers to the two elements or electrodes within the glass container that constitute the tube. Shortly after the discovery of the Edison effect, significant advancements in understanding electricity occurred. By the early 1900s, J. J. Thomson in England had identified the electron, while Marconi demonstrated wireless technology, which later evolved into radio. The theoretical comprehension of electrical phenomena was rapidly expanding. J. A. Fleming, an English scientist, sought to enhance Marconi’s basic wireless receiver and reflected on Edison’s earlier contributions. Before discussing Fleming’s valve, the precursor to the modern diode, it is essential to review Edison’s original circuit. This will be illustrated as a schematic diagram, using the diode symbol rather than a simplistic depiction. The schematic comprises two series circuits: the filament circuit, which includes the filament battery and the filament itself, and the plate circuit, which connects one side of the filament to the plate, through an ammeter and battery, returning to the filament. A segment of the filament circuit overlaps with the plate circuit, allowing electrons emitted from the filament to return. Without this return path, electron flow would be impossible. The current measured by the ammeter is referred to as the plate current, while the voltage between the filament and plate is termed plate voltage.
The diode tube, as described, serves as a fundamental component in early electronic circuits, showcasing the principles of electron flow and voltage application. The filament circuit operates by heating the filament, which emits electrons through thermionic emission, a phenomenon first observed by Edison. The emitted electrons travel toward the positively charged plate, creating a flow of current. The schematic representation highlights the dual nature of the circuit, emphasizing the interdependence of both the filament and plate circuits.
In practical applications, the plate voltage is critical as it influences the rate of electron emission from the filament. A higher plate voltage increases the electric field strength, enhancing the attraction of electrons from the filament to the plate, thereby increasing the plate current. Conversely, if the plate voltage is insufficient, the emission of electrons is reduced, resulting in lower plate current.
The ammeter placed in the plate circuit is essential for measuring the plate current, providing insights into the operational characteristics of the diode. This measurement is crucial for understanding the efficiency and performance of the diode tube in various applications, such as amplification and rectification in early radio and audio equipment.
Overall, the evolution from Edison’s incandescent bulb to Fleming’s valve illustrates the progression of electronic technology, laying the groundwork for modern diodes and semiconductor devices that continue to shape the field of electronics today.The diode tube we are about to study is really Edison`s old incandescent bulb with the plate in it. Diode means two elements or two electrodes, and refers to the two parts within the glass container that make up the tube. Within a few years after the discovery of the Edison effect, scientists had learned a great deal more than Edison knew at the t
ime of his discovery. By the early 1900s, J. J. Thomson in England had discovered the electron. Marconi, in Italy and England, had demonstrated the wireless, which was to become the radio. The theoretical knowledge of the nature of electricity and things electrical was increasing at a rapid rate. J. A. Fleming, an English scientist, was trying to improve on Marconi`s relatively crude wireless receiver when his mind went back to Edison`s earlier work.
Before learning about Fleming`s valve, the forerunner of the modern diode, let`s look at Edison`s original circuit. This time, however, we`ll draw it as a schematic diagram, using the symbol for a diode instead of a cartoon-like picture.
(The schematic shown below). Note that this is really two series circuits. The filament battery and the filament itself form a series circuit. This circuit is known as the filament circuit. The path of the second series circuit is from one side of the filament, across the space to the plate, through the ammeter and battery, then back to the filament. This circuit is known as the plate circuit. You will note that a part of the filament circuit is also common to the plate circuit. This part enables the electrons boiled from the filament to return to the filament. No electron could flow anywhere if this return path were not completed. The electron flow measured by the ammeter is known as plate current. The voltage applied between the filament and plate is known as plate voltage. 🔗 External reference
The diode tube, as described, serves as a fundamental component in early electronic circuits, showcasing the principles of electron flow and voltage application. The filament circuit operates by heating the filament, which emits electrons through thermionic emission, a phenomenon first observed by Edison. The emitted electrons travel toward the positively charged plate, creating a flow of current. The schematic representation highlights the dual nature of the circuit, emphasizing the interdependence of both the filament and plate circuits.
In practical applications, the plate voltage is critical as it influences the rate of electron emission from the filament. A higher plate voltage increases the electric field strength, enhancing the attraction of electrons from the filament to the plate, thereby increasing the plate current. Conversely, if the plate voltage is insufficient, the emission of electrons is reduced, resulting in lower plate current.
The ammeter placed in the plate circuit is essential for measuring the plate current, providing insights into the operational characteristics of the diode. This measurement is crucial for understanding the efficiency and performance of the diode tube in various applications, such as amplification and rectification in early radio and audio equipment.
Overall, the evolution from Edison’s incandescent bulb to Fleming’s valve illustrates the progression of electronic technology, laying the groundwork for modern diodes and semiconductor devices that continue to shape the field of electronics today.The diode tube we are about to study is really Edison`s old incandescent bulb with the plate in it. Diode means two elements or two electrodes, and refers to the two parts within the glass container that make up the tube. Within a few years after the discovery of the Edison effect, scientists had learned a great deal more than Edison knew at the t
ime of his discovery. By the early 1900s, J. J. Thomson in England had discovered the electron. Marconi, in Italy and England, had demonstrated the wireless, which was to become the radio. The theoretical knowledge of the nature of electricity and things electrical was increasing at a rapid rate. J. A. Fleming, an English scientist, was trying to improve on Marconi`s relatively crude wireless receiver when his mind went back to Edison`s earlier work.
Before learning about Fleming`s valve, the forerunner of the modern diode, let`s look at Edison`s original circuit. This time, however, we`ll draw it as a schematic diagram, using the symbol for a diode instead of a cartoon-like picture.
(The schematic shown below). Note that this is really two series circuits. The filament battery and the filament itself form a series circuit. This circuit is known as the filament circuit. The path of the second series circuit is from one side of the filament, across the space to the plate, through the ammeter and battery, then back to the filament. This circuit is known as the plate circuit. You will note that a part of the filament circuit is also common to the plate circuit. This part enables the electrons boiled from the filament to return to the filament. No electron could flow anywhere if this return path were not completed. The electron flow measured by the ammeter is known as plate current. The voltage applied between the filament and plate is known as plate voltage. 🔗 External reference
.jpg)