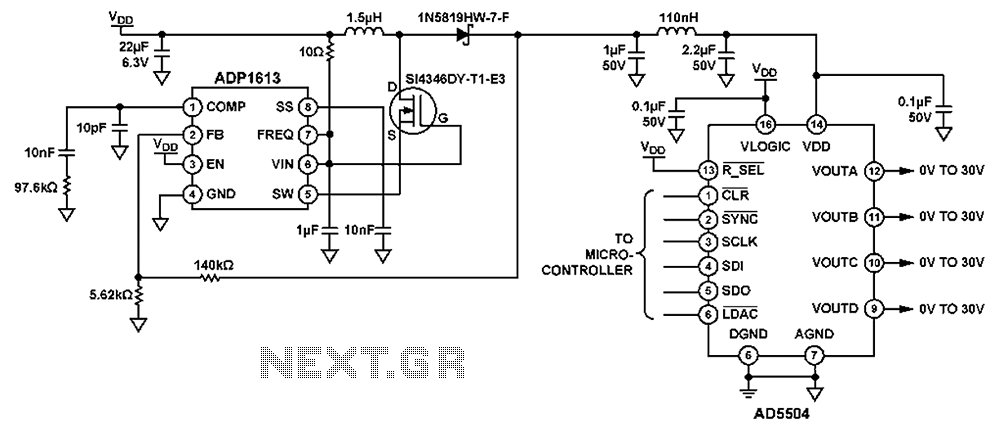
Direct Coupled Radio Circuit with Diagram
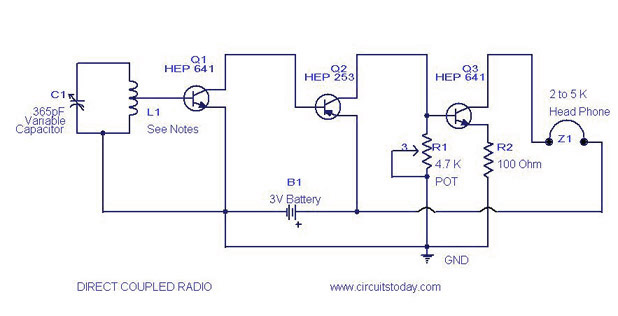
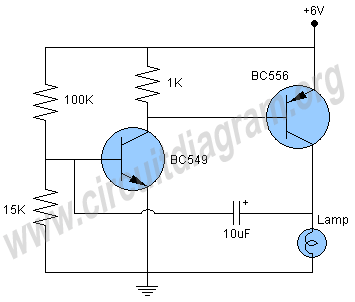
A simple direct-coupled radio circuit diagram and schematic, ideal for adjacent stations. This circuit uses Q1 as an audio amplifier, and the base-emitter capacitance provides radio filtering.
The described circuit is a direct-coupled radio receiver designed to effectively operate with nearby radio stations. It primarily utilizes a transistor, denoted as Q1, which functions as the audio amplifier in the circuit. The direct coupling method allows for improved signal fidelity by minimizing distortion and ensuring that the audio signal is amplified without unnecessary frequency shifts.
In this schematic, the base-emitter capacitance plays a crucial role in radio frequency filtering. This capacitance forms a low-pass filter that helps to eliminate high-frequency noise, allowing only the desired audio frequencies to pass through to the output. The choice of components, including the transistor type and the values of resistors and capacitors, is essential for optimizing the performance of the circuit.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors for biasing the transistor, capacitors for coupling and decoupling signals, and possibly inductors for tuning purposes. The layout should ensure minimal interference between components, particularly in the case of adjacent station reception, where selectivity is paramount.
Overall, this simple yet effective radio circuit design is suitable for hobbyists and engineers looking to explore the fundamentals of radio frequency amplification and filtering. Proper assembly and tuning of the components will result in an efficient radio receiver capable of picking up signals from nearby stations with clarity and minimal distortion.A simple direct coupled radio circuit diagram and schematic, ideal for adjacent stations.This circuit uses Q1 as audio amplifier and base emitter capacitance provides radio filtering.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a direct-coupled radio receiver designed to effectively operate with nearby radio stations. It primarily utilizes a transistor, denoted as Q1, which functions as the audio amplifier in the circuit. The direct coupling method allows for improved signal fidelity by minimizing distortion and ensuring that the audio signal is amplified without unnecessary frequency shifts.
In this schematic, the base-emitter capacitance plays a crucial role in radio frequency filtering. This capacitance forms a low-pass filter that helps to eliminate high-frequency noise, allowing only the desired audio frequencies to pass through to the output. The choice of components, including the transistor type and the values of resistors and capacitors, is essential for optimizing the performance of the circuit.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors for biasing the transistor, capacitors for coupling and decoupling signals, and possibly inductors for tuning purposes. The layout should ensure minimal interference between components, particularly in the case of adjacent station reception, where selectivity is paramount.
Overall, this simple yet effective radio circuit design is suitable for hobbyists and engineers looking to explore the fundamentals of radio frequency amplification and filtering. Proper assembly and tuning of the components will result in an efficient radio receiver capable of picking up signals from nearby stations with clarity and minimal distortion.A simple direct coupled radio circuit diagram and schematic, ideal for adjacent stations.This circuit uses Q1 as audio amplifier and base emitter capacitance provides radio filtering.. 🔗 External reference