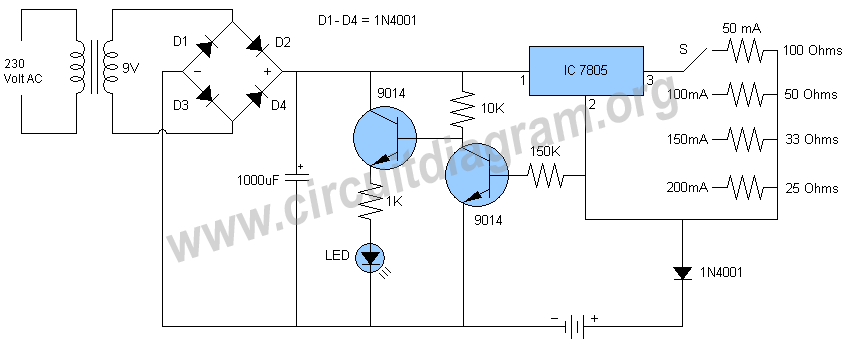
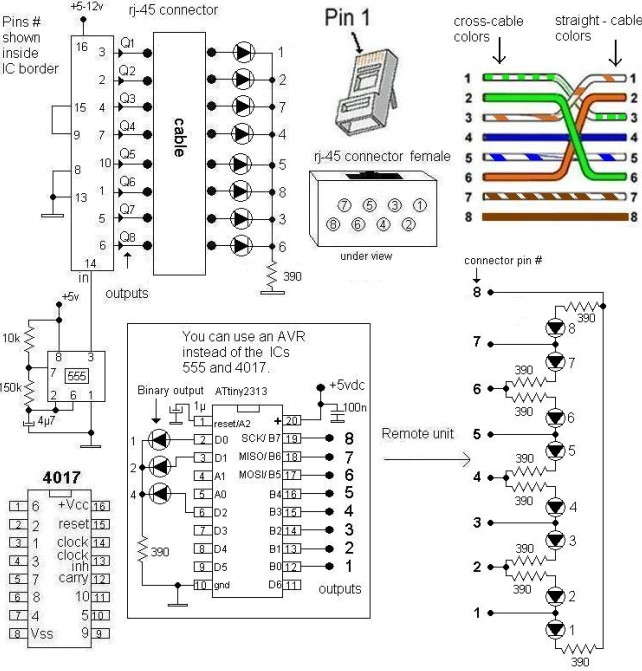
quick on board junction tester circuit diagram
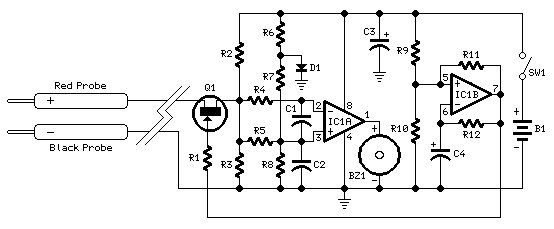
Short circuits or broken PCB tracks can be easily identified using a multimeter. However, this tool may yield inaccurate results when assessing the efficiency of a transistor or diode unless the device is unsoldered and removed from the PCB. An additional limitation of this testing method is the requirement to maintain a firm grip on the probes connected to the pins of the device while simultaneously turning the head to read the multimeter display.
In electronic circuit diagnostics, the identification of short circuits and broken tracks on printed circuit boards (PCBs) is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. A multimeter serves as a fundamental tool in this process, allowing for the detection of continuity and resistance in the circuitry. When measuring the integrity of components such as transistors and diodes, the multimeter can provide misleading readings if these components remain soldered to the PCB. This is due to the influence of surrounding circuitry, which can alter the expected values.
To obtain accurate measurements, it is recommended that transistors and diodes be desoldered from the PCB prior to testing. This ensures that the multimeter readings reflect the true characteristics of the device without interference from other components. Additionally, the physical constraints of using a multimeter can complicate the testing process. The user must maintain a stable connection with the probes while also positioning the multimeter for visibility, which can lead to potential errors in reading.
For enhanced testing efficiency, alternative methods such as using a dedicated transistor tester or diode tester can be employed. These specialized devices are designed to measure the performance of semiconductors with greater accuracy and ease of use. They typically feature built-in displays that eliminate the need for awkward positioning of the multimeter, thereby streamlining the testing process.
Furthermore, incorporating automated testing systems can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in diagnosing PCB issues. These systems can perform multiple tests in succession and provide detailed reports on the condition of various components, thus facilitating quicker and more accurate troubleshooting. By leveraging advanced testing methodologies, the reliability of electronic circuits can be assured, leading to improved overall performance and longevity of the devices.Short circuits or broken pcb tracks can be easily recognized by means of a Multimeter, but this tool can give wrong results when testing the efficiency of a transistor or diode, unless the device under test is unsoldered and removed from the pcb. A further shortcoming affecting such way of testing is the necessity to keep firmly the probes on the pins of the device under test and at the same time to turn the head continually to read the Multimeter display..
🔗 External reference
In electronic circuit diagnostics, the identification of short circuits and broken tracks on printed circuit boards (PCBs) is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. A multimeter serves as a fundamental tool in this process, allowing for the detection of continuity and resistance in the circuitry. When measuring the integrity of components such as transistors and diodes, the multimeter can provide misleading readings if these components remain soldered to the PCB. This is due to the influence of surrounding circuitry, which can alter the expected values.
To obtain accurate measurements, it is recommended that transistors and diodes be desoldered from the PCB prior to testing. This ensures that the multimeter readings reflect the true characteristics of the device without interference from other components. Additionally, the physical constraints of using a multimeter can complicate the testing process. The user must maintain a stable connection with the probes while also positioning the multimeter for visibility, which can lead to potential errors in reading.
For enhanced testing efficiency, alternative methods such as using a dedicated transistor tester or diode tester can be employed. These specialized devices are designed to measure the performance of semiconductors with greater accuracy and ease of use. They typically feature built-in displays that eliminate the need for awkward positioning of the multimeter, thereby streamlining the testing process.
Furthermore, incorporating automated testing systems can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in diagnosing PCB issues. These systems can perform multiple tests in succession and provide detailed reports on the condition of various components, thus facilitating quicker and more accurate troubleshooting. By leveraging advanced testing methodologies, the reliability of electronic circuits can be assured, leading to improved overall performance and longevity of the devices.Short circuits or broken pcb tracks can be easily recognized by means of a Multimeter, but this tool can give wrong results when testing the efficiency of a transistor or diode, unless the device under test is unsoldered and removed from the pcb. A further shortcoming affecting such way of testing is the necessity to keep firmly the probes on the pins of the device under test and at the same time to turn the head continually to read the Multimeter display..
🔗 External reference