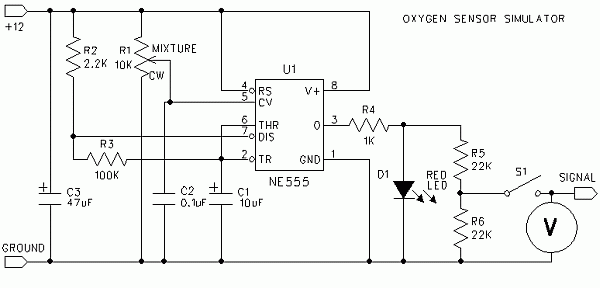
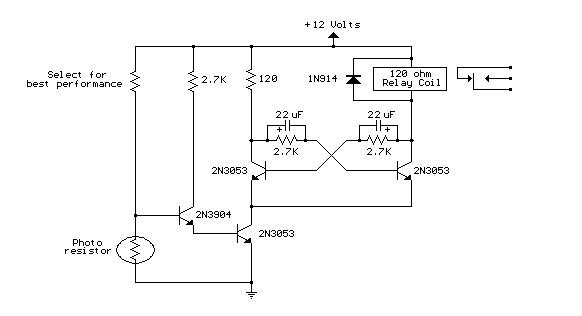
DIY parking sensor
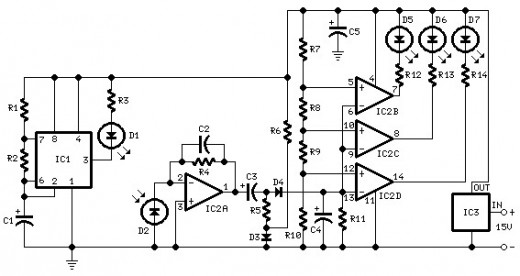
Read the article and learn how to create a parking sensor for only $4.99.
To design a cost-effective parking sensor, a basic understanding of ultrasonic sensor technology is essential. The parking sensor system typically consists of an ultrasonic sensor, a microcontroller, a power supply, and an output indicator, such as a buzzer or LED.
The ultrasonic sensor emits sound waves at a frequency beyond human hearing. When these sound waves encounter an object, they reflect back to the sensor. The time taken for the sound waves to return is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance to the object. This data is then processed by the microcontroller, which interprets the distance and triggers the output indicator based on predefined thresholds.
The microcontroller can be programmed to activate the buzzer or LED at specific distances, providing audio or visual feedback to the driver. For instance, the buzzer may sound continuously when the vehicle is within one meter of an obstacle, while an LED may flash to indicate proximity.
Power can be supplied using a battery or a DC adapter, ensuring the system is portable or can be integrated into the vehicle's electrical system. The entire assembly can be mounted discreetly on the vehicle, allowing for unobtrusive operation while enhancing safety during parking maneuvers.
In summary, a parking sensor can be constructed with minimal components and at a low cost, making it an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts.Read the article and learn how you can make your own parking sensor for just $4.99. 🔗 External reference
To design a cost-effective parking sensor, a basic understanding of ultrasonic sensor technology is essential. The parking sensor system typically consists of an ultrasonic sensor, a microcontroller, a power supply, and an output indicator, such as a buzzer or LED.
The ultrasonic sensor emits sound waves at a frequency beyond human hearing. When these sound waves encounter an object, they reflect back to the sensor. The time taken for the sound waves to return is measured, allowing the system to calculate the distance to the object. This data is then processed by the microcontroller, which interprets the distance and triggers the output indicator based on predefined thresholds.
The microcontroller can be programmed to activate the buzzer or LED at specific distances, providing audio or visual feedback to the driver. For instance, the buzzer may sound continuously when the vehicle is within one meter of an obstacle, while an LED may flash to indicate proximity.
Power can be supplied using a battery or a DC adapter, ensuring the system is portable or can be integrated into the vehicle's electrical system. The entire assembly can be mounted discreetly on the vehicle, allowing for unobtrusive operation while enhancing safety during parking maneuvers.
In summary, a parking sensor can be constructed with minimal components and at a low cost, making it an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts.Read the article and learn how you can make your own parking sensor for just $4.99. 🔗 External reference